Die Forging Titanium Services
Powerful forging facilities and die manufacturing capabilities determine the quality of forged titanium parts. Full-size quality inspection reports are supported.
- ASTM B381
- 2,000 to 6,000 Tons
- ISO 13485 & ISO 9001
- ROSH Certified Materials Available.
- Full-Size Quality Inspection Report.
WSTITANIUM FACTORY
Our Powerful Facilities

Die Forged Titanium Parts Manufacturer
As an efficient and precise forming technology, die forging can fully stimulate the performance potential of titanium materials and meet the strict requirements of various industries for the shape, dimensional accuracy and performance of titanium parts. Wstitanium is a leading forged titanium manufacturer in China with ISO 9001 & ISO 13485 certification, manufacturing complex geometric titanium products for you, not limited to titanium bars, titanium ingots, titanium plates, titanium flanges, titanium shafts and customized titanium parts.
What is die forged titanium?
Die forging refers to the application of pressure through equipment such as hydraulic presses to plastically deform the heated titanium billet in the die, thereby creating various titanium products with complex shapes and high precision requirements. For example, titanium alloy blades and engine parts in the aerospace field, and titanium alloy implants in the medical field.
The design and manufacture of the die is crucial for forging titanium. The shape of the die should be designed according to the final shape of the forging, and the fluidity of titanium during the forging process should also be considered. Because the fluidity of titanium is relatively poor, the structure of the die cavity should try to avoid sharp internal angles and complex channels to ensure that the titanium material can smoothly fill the die cavity.

Heating is a key step in die forging titanium. Since titanium is highly chemically active at high temperatures, the heating process needs to be carried out in a special protective atmosphere, such as in an inert gas environment such as argon, to prevent titanium from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, etc. in the air and affecting its performance.
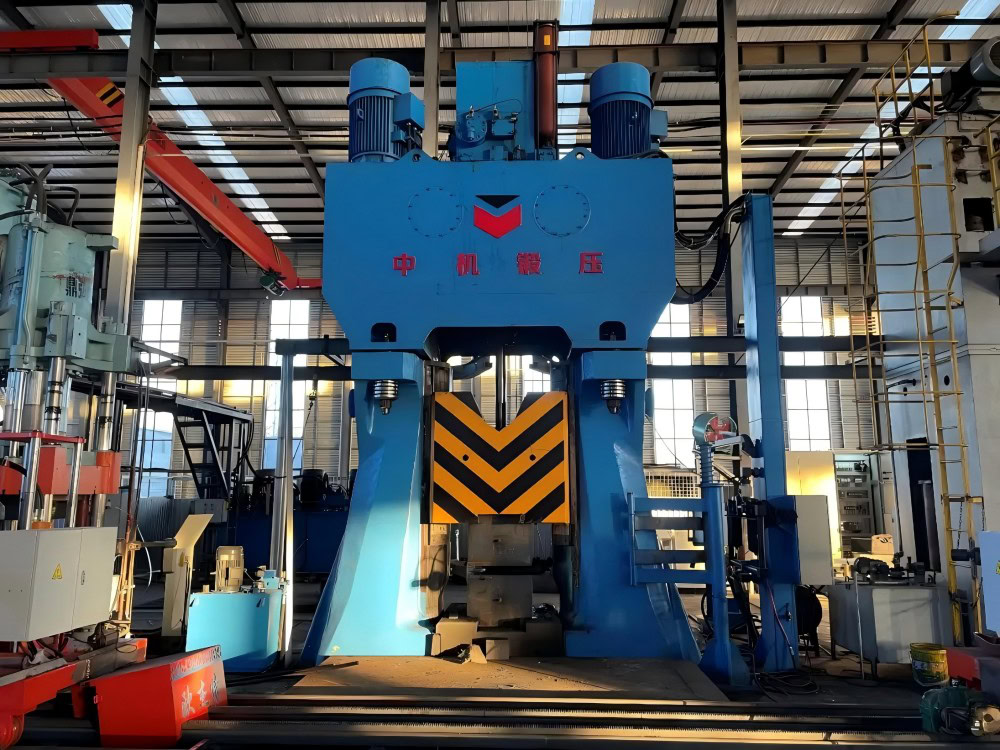
Wstitanium Capacity of die forging titanium
Invest in multiple advanced heating equipment, forging equipment and quality inspection equipment. Including 2 high-power vacuum consumable arc furnaces with a maximum heating power of 2000kW to meet the rapid heating needs of titanium billets of different specifications; 3 large hydraulic presses of 5,000 tons and above, which can forge titanium alloy forgings with a maximum weight of 10 tons; at the same time, equipped with heat treatment equipment, high-precision ultrasonic flaw detectors and metallographic microscopes to strictly control the quality of forgings.
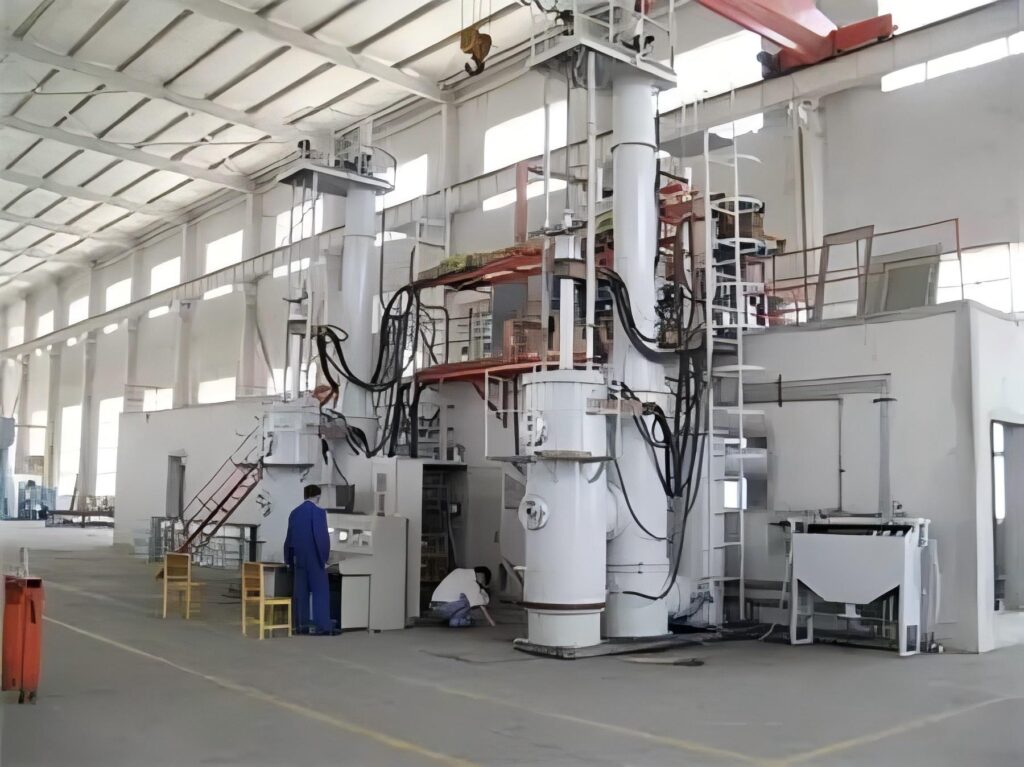
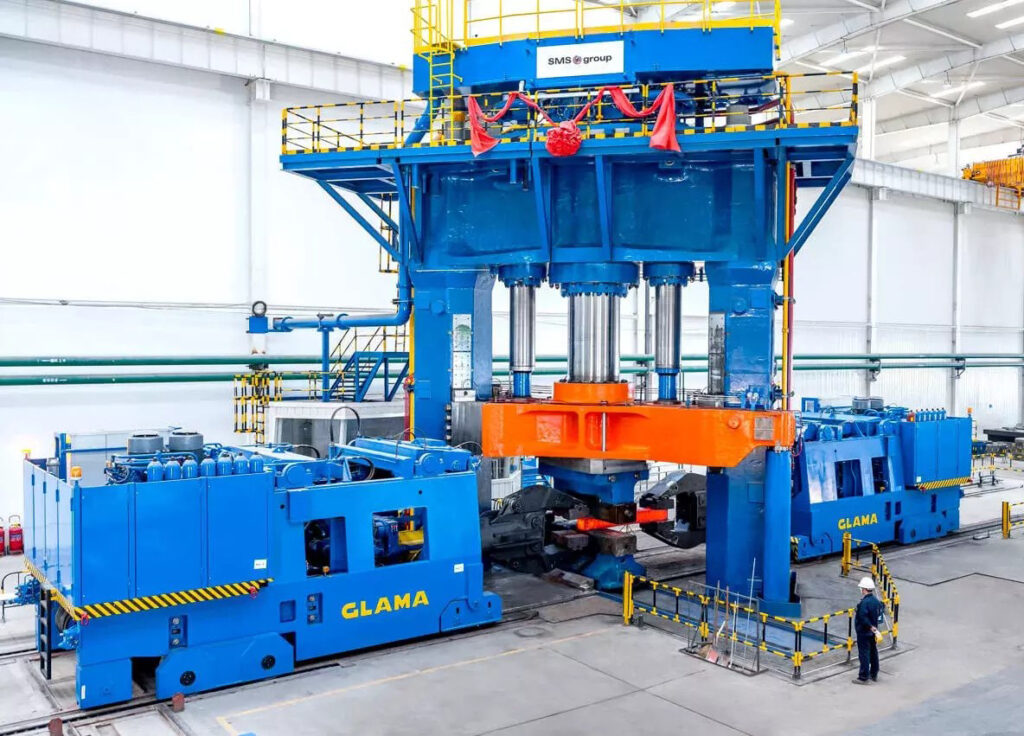
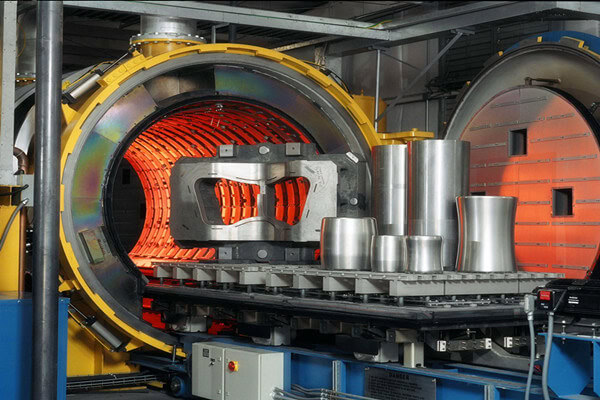



Throughout the process of forging titanium in the die, Wstitanium needs to consider many details. For example, titanium is highly chemically active at high temperatures and easily reacts with elements such as oxygen and nitrogen in the air, so the heating and forging process usually needs to be carried out under a protective atmosphere, such as using inert gases such as argon for protection. At the same time, the forged titanium alloy parts may also require subsequent heat treatment, CNC machining and other processes to further improve their performance and achieve the final dimensional accuracy requirements. This process is widely used in many fields that require extremely high material properties and shape accuracy, such as aerospace, medical equipment, and high-end sports equipment.
Advantages of die forged titanium
– Grain refinement: During the forging process, the titanium material is crushed and refined under pressure. For example, in the forging of titanium alloys for aerospace, the original coarse grains can be refined to a few microns or even smaller after forging. This refined grain structure can significantly improve the strength and toughness of the material, making it less likely to crack and break when subjected to complex stresses. Studies have shown that the yield strength of titanium alloys after grain refinement can be increased by 20%-30%, and the impact toughness can also be increased by 15%-20%.
– Eliminate defects: Titanium will inevitably produce internal defects such as pores and shrinkage during the smelting and ingot casting process. During forging, the strong pressure is like an invisible hand, compacting and bridging these defects. After forging large titanium alloy forgings, it was found that the original tiny pores and loose areas were completely eliminated, and the material density was increased from about 98% of the cast state to more than 99.5%, effectively reducing stress concentration points and improving the stability of the overall performance of the material.
– Optimize the organizational structure: Forging can change the organizational structure of titanium materials and make it more uniform. For titanium alloys, the distribution of different phases will be more reasonable, for example, making the distribution of α phase and β phase in the alloy more uniform, thereby improving the comprehensive performance of the material, such as fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance.
– Near-net forming: Titanium parts only need a small amount of subsequent processing after forging to meet the requirements of the final product, which greatly reduces material waste. For example, some aviation structural parts forged from titanium alloys can control the processing allowance within 1-2mm through precision forging technology, and the material utilization rate can be increased by 30%-50% compared with traditional CNC processing.
Treatment of titanium parts after forging
After cooling, titanium forgings may need a series of treatment processes, such as heat treatment, machining, surface treatment, etc. Heat treatment can further improve the structure and performance of forgings, such as through annealing, quenching, aging and other heat treatment processes, to improve the strength, hardness, toughness and other performance indicators of forgings. CNC machining is to achieve the final dimensional accuracy and surface roughness requirements of forgings. Common machining methods include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, etc. Surface treatment can improve the corrosion resistance, wear resistance and other surface properties of forgings. Common surface treatment methods include electroplating, anodizing, passivation, etc.
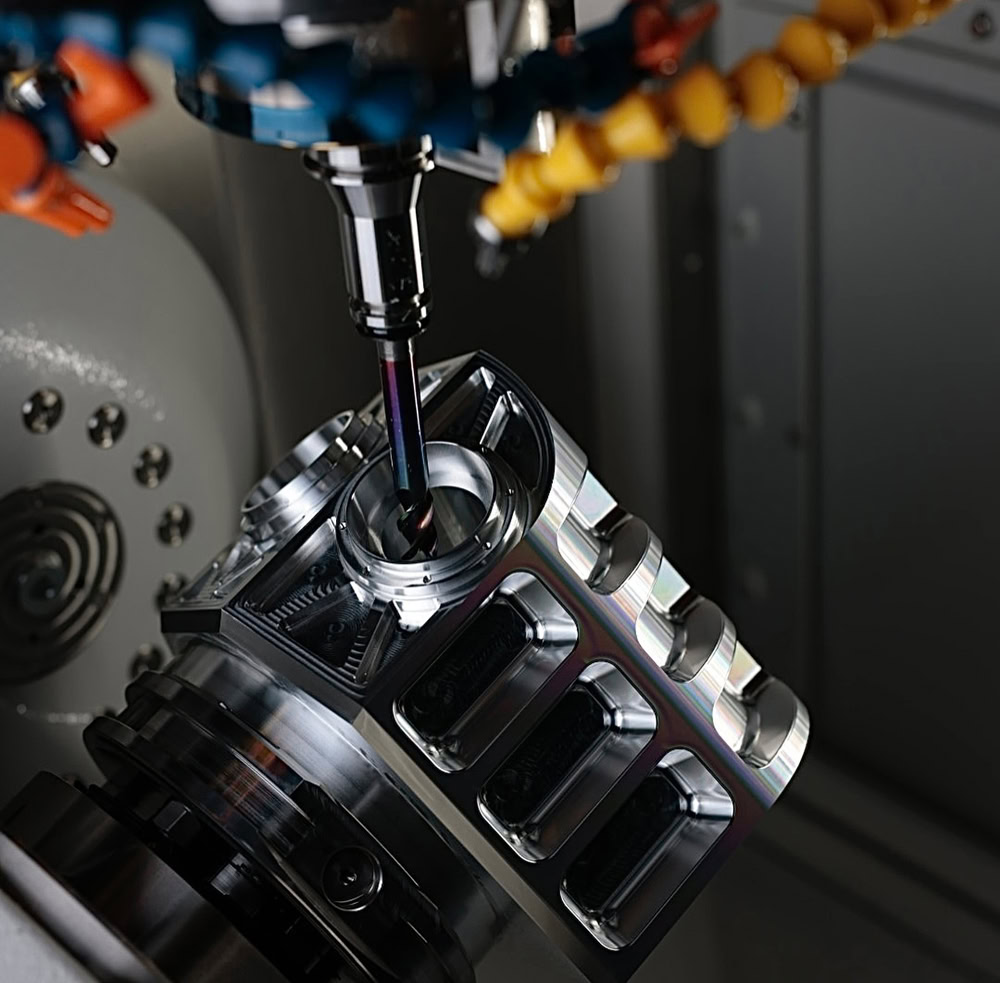
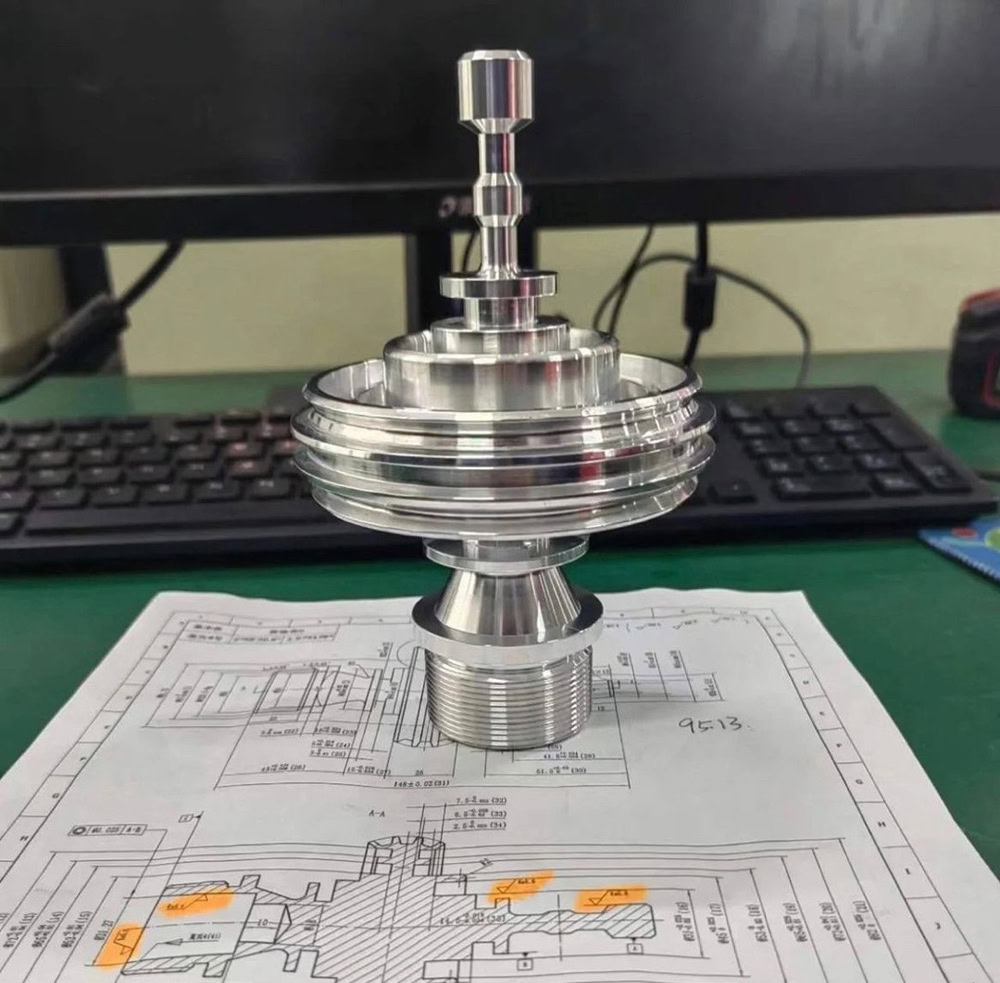
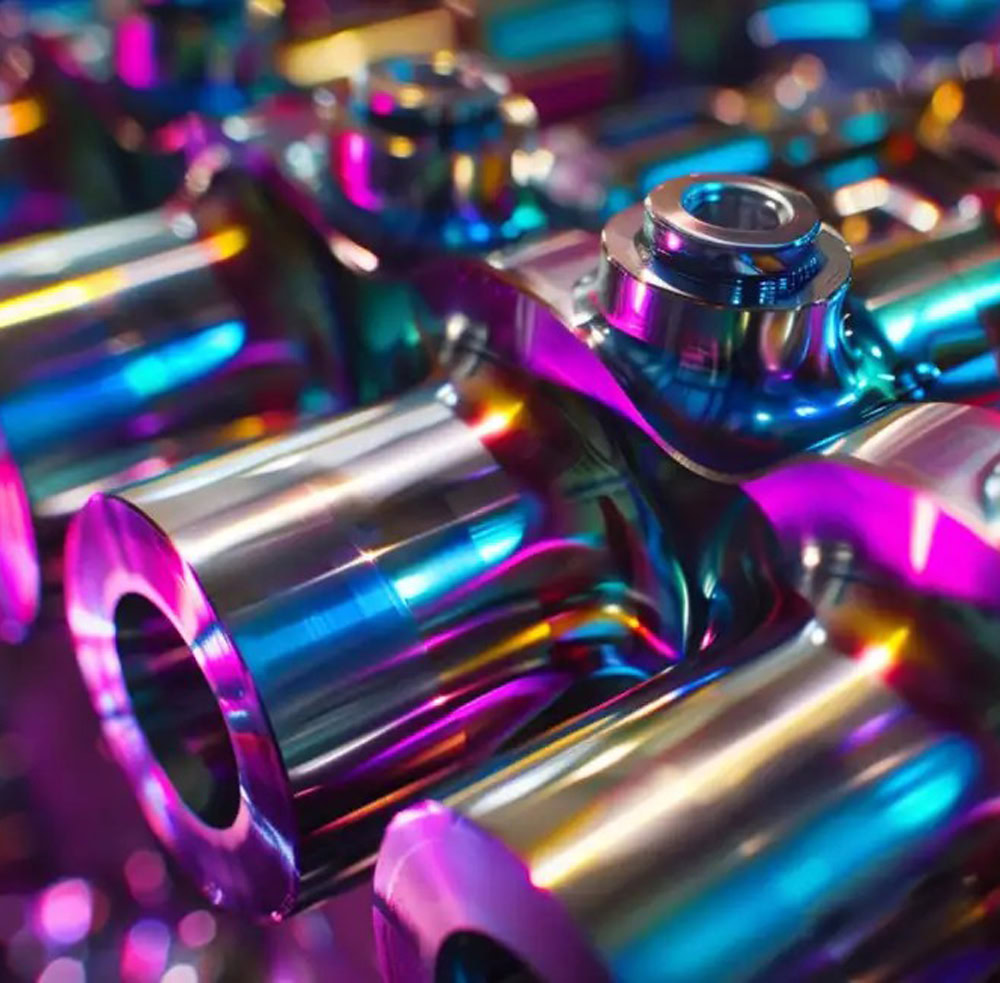



Forged Titanium Parts Application
Forged titanium parts have become the “pillar” of many fields with their incomparable characteristics, supporting the heavy task of technological leap and industrial innovation.
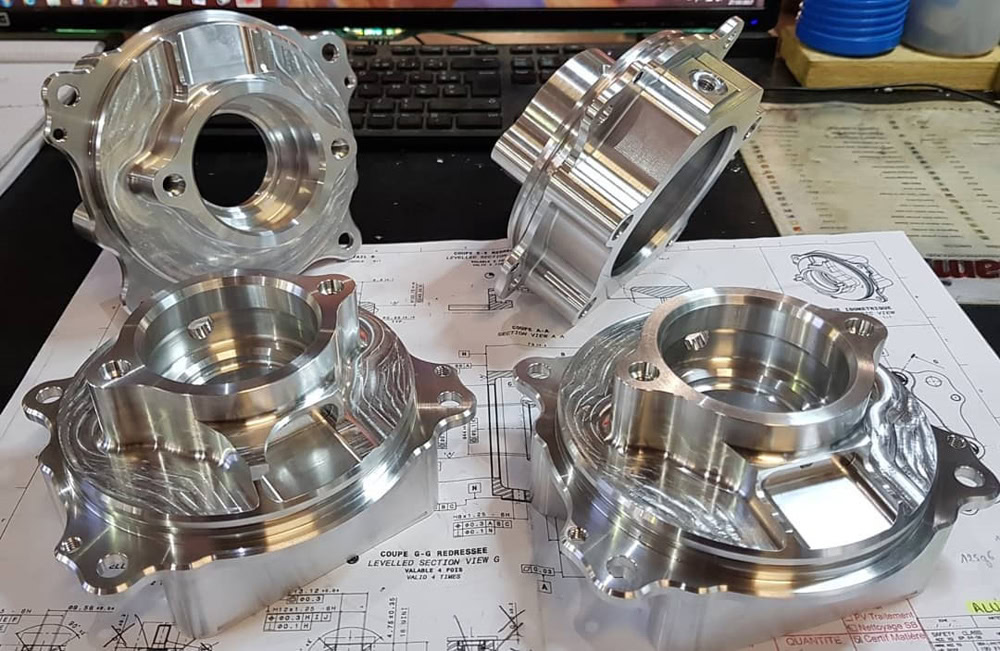

Forging titanium alloys with dies can produce complex-shaped structural parts, and reduce structural weight while ensuring sufficient strength, increasing the payload and range of aircraft.
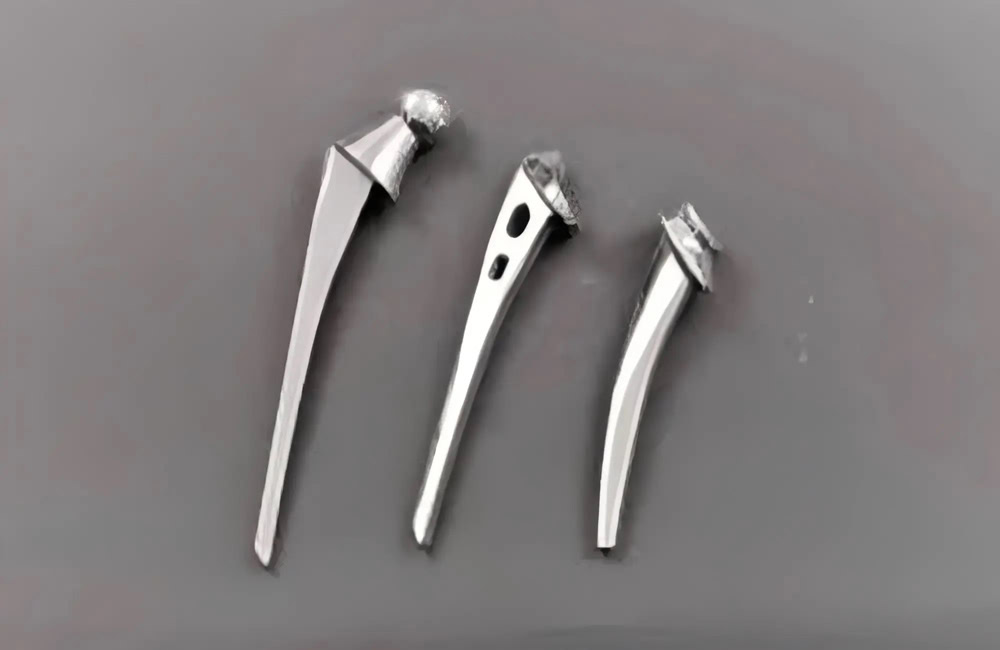

For example, artificial hip joints, knee joints, etc. Die-forged titanium alloys can make the shape of the implant more closely fit the human bone structure, improving the stability after implantation and the comfort of the patient.
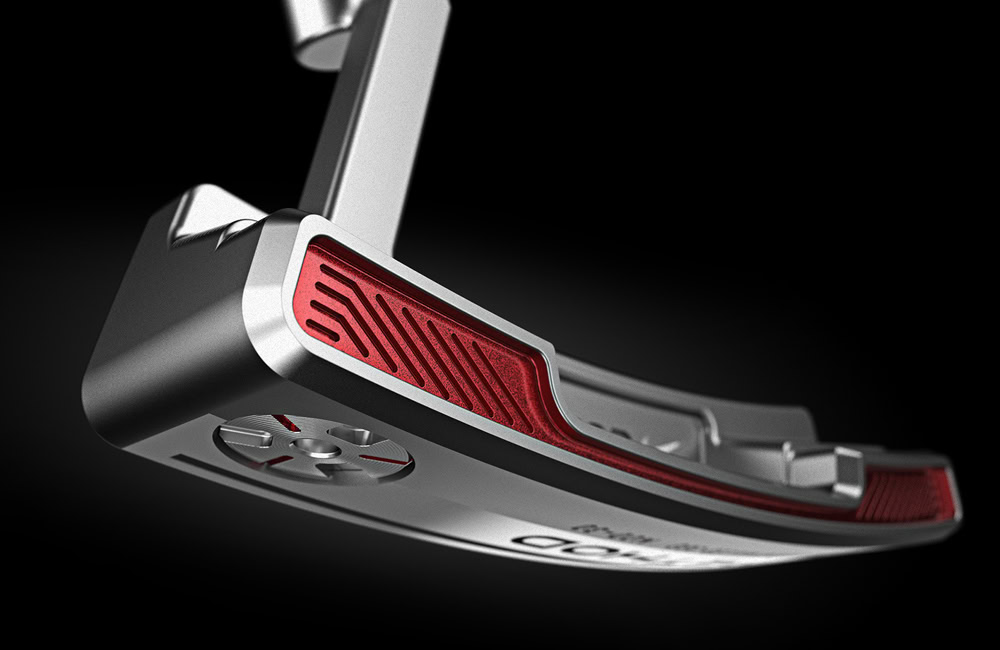

Sports
Golf club heads forged with titanium alloy dies can precisely control the shape and weight distribution, making the shots more accurate and farther. Titanium alloy frames are lightweight and high-strength, improving riding performance.
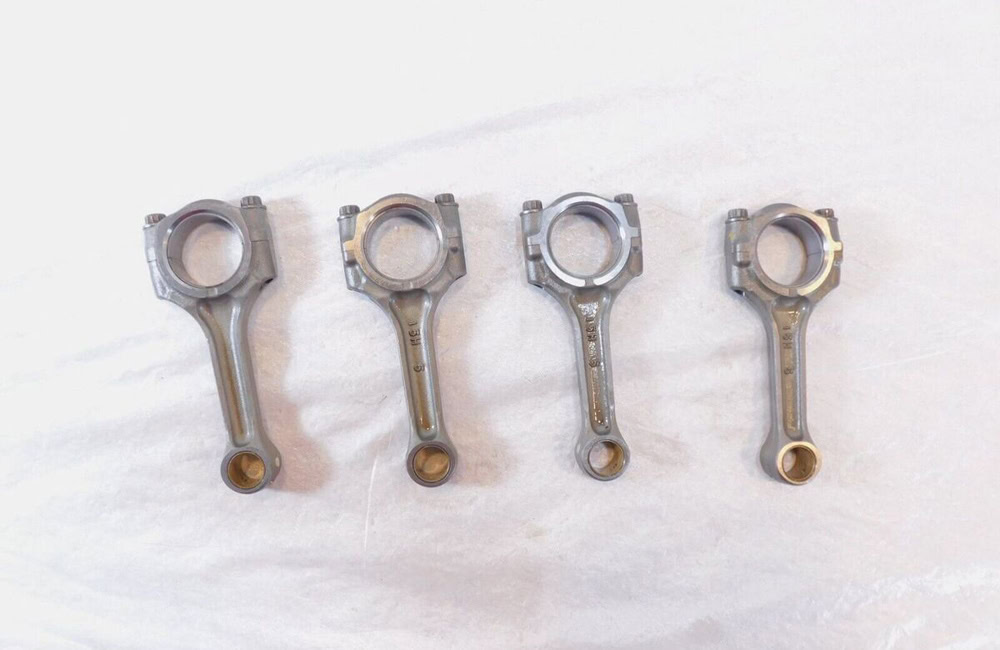

After die forging, titanium alloy impellers have good high-temperature resistance and high-speed rotation performance, which can improve the engine’s intake efficiency and thus enhance the engine’s power output.
Electronic
For example, the housings of laptops and mobile phones. Die-forged titanium alloy housings can provide solid protection, and their metallic texture also increases the product’s aesthetics and quality.
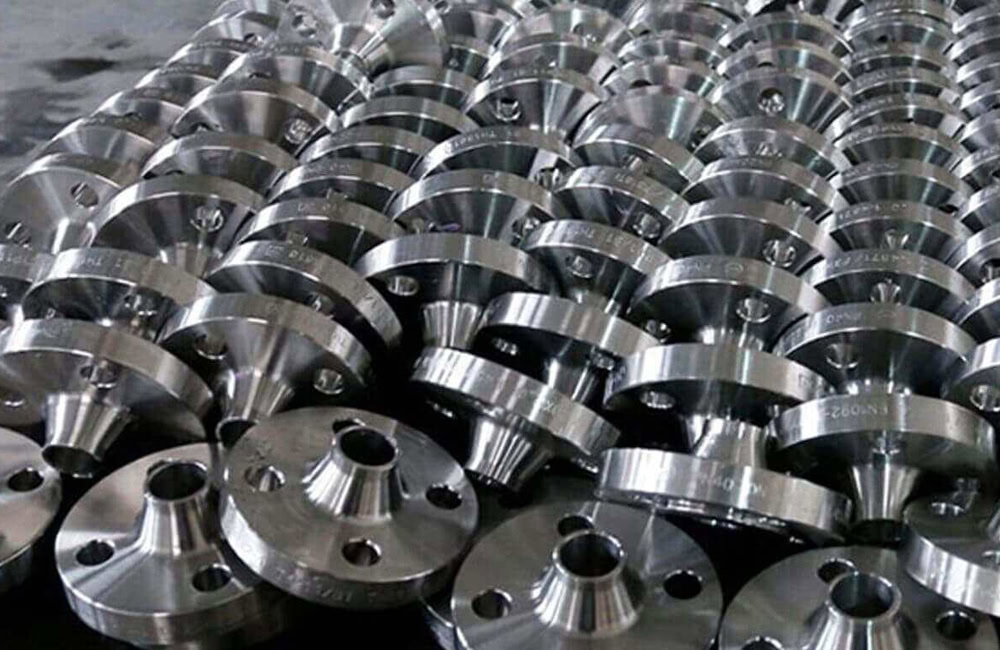

Industrial
Valve balls, valve stems and other parts made of titanium alloy through die forging can effectively resist the erosion of corrosive media and extend the service life of valves.