Titanium Parts For Automobiles
Wstitanium is committed to providing high-quality, customized titanium parts solutions to global automakers, such as engines, chassis, exhaust systems, etc.
- ISO 9001:2016 Certified
- ISO 13485:2015 Certified
- 24/7 Engineering Support
- Tight Tolerance: +/- 0.005mm
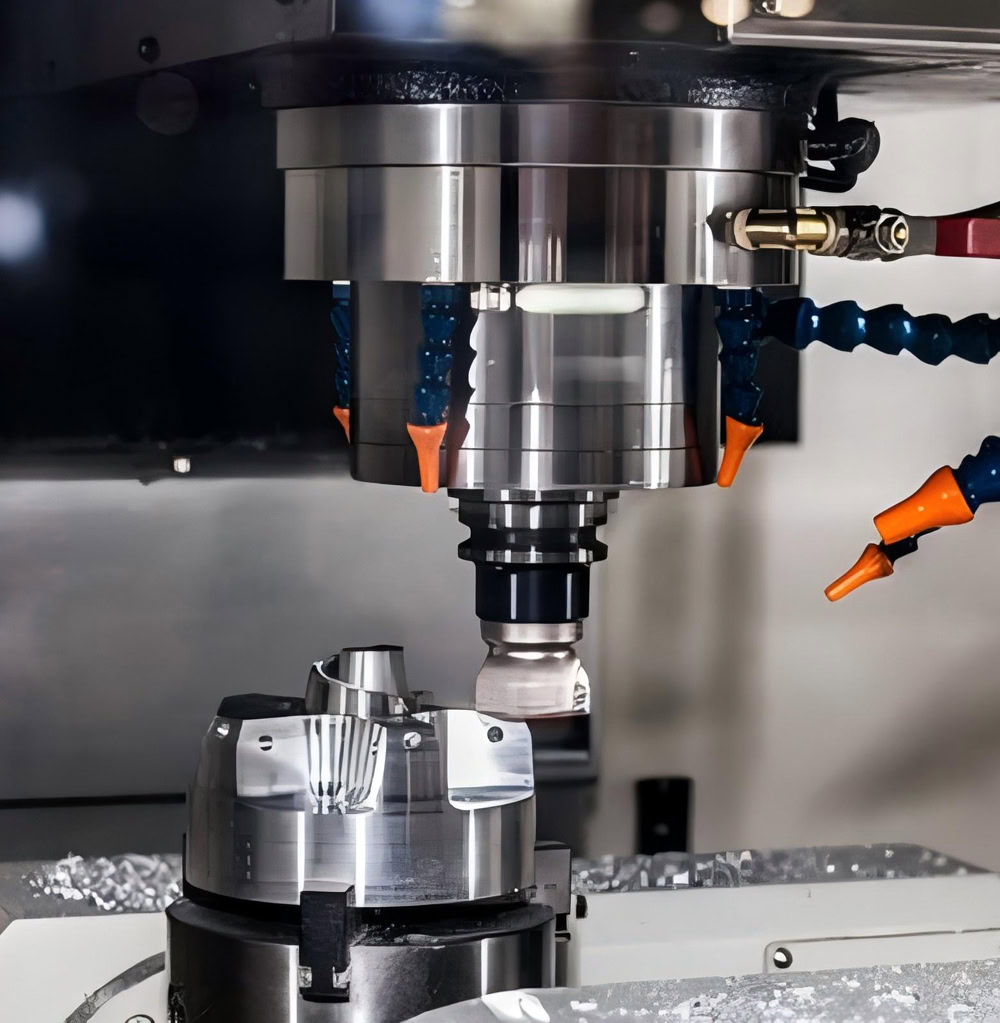

CNC Machining Titanium Parts For Automobiles
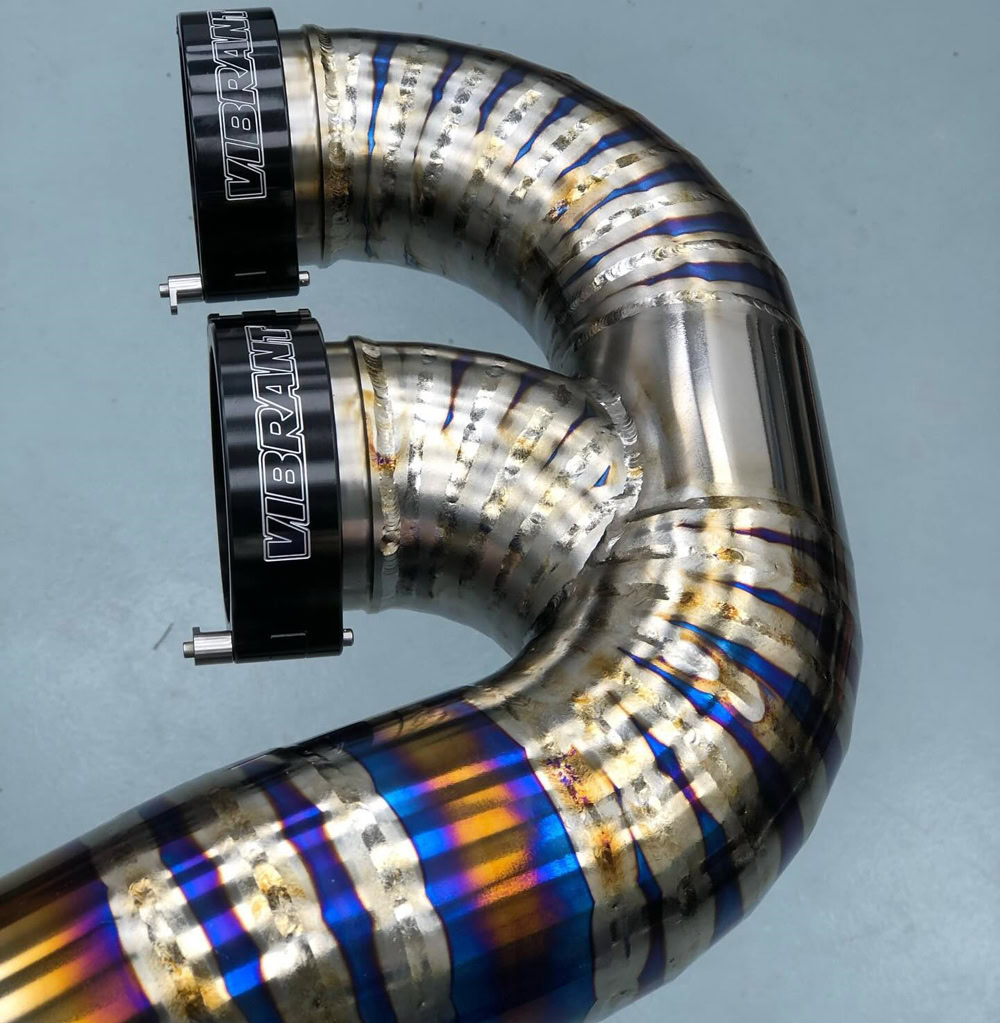
Welding Automotive Titanium Exhaust Pipe
Automotive Titanium Parts Manufacturer
Titanium and titanium alloys are becoming increasingly popular in the automotive industry due to their excellent comprehensive properties, from high-end racing cars to luxury cars. Wstitanium is committed to providing high-quality, customized titanium parts solutions to global automakers, such as engines, chassis, exhaust systems, etc.
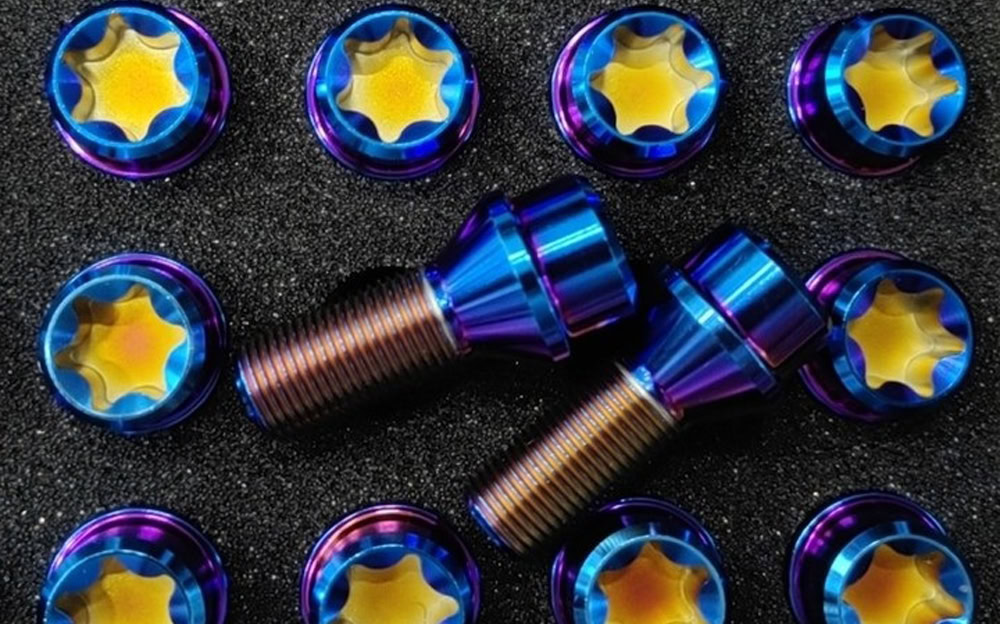
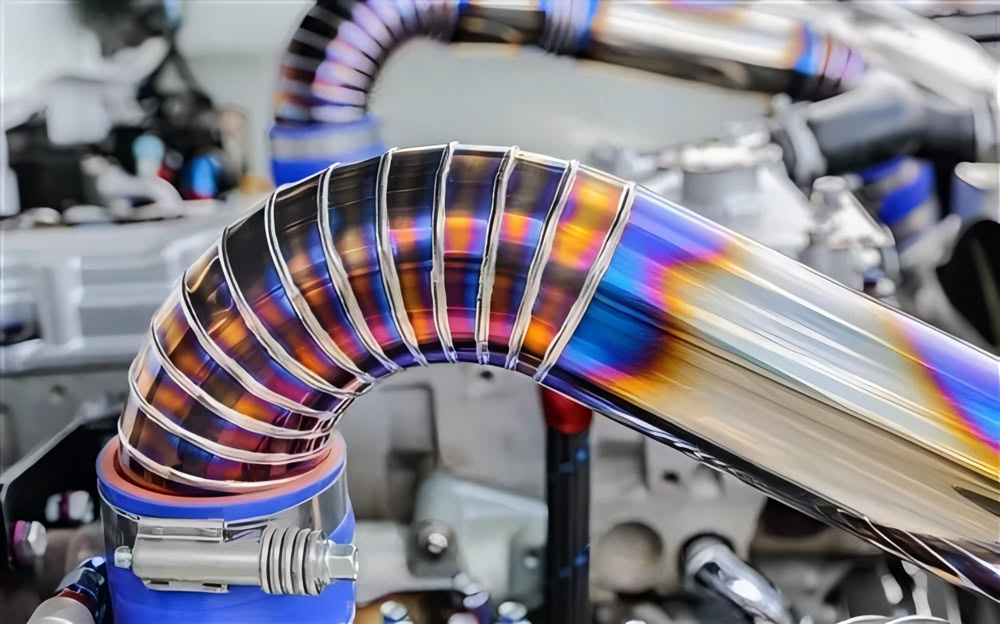


Advantages of Titanium Auto Parts
Titanium and titanium alloys have shown great application potential in automobiles due to their low density, high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, good high temperature performance and excellent fatigue performance. From the valves, valve springs, connecting rods, crankshafts of the engine system, to the suspension swing arms, control arms, and half shafts of the chassis system, to the exhaust manifolds and exhaust pipes of the exhaust system, and the bolts and nuts of the body system, body structural parts, etc., titanium has been used in various key parts of the car.

High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
The strength of titanium is comparable to that of steel, but its density is only 60%. Its tensile strength can reach 900-1100MPa. The use of titanium alloys in crankshafts, connecting rods and other parts of automobile engines can significantly reduce the weight of the parts.
Good Performance
Titanium alloy can still maintain good mechanical properties at high temperatures. Using titanium alloy in engine valves and turbocharger parts can effectively avoid performance degradation caused by high temperatures.
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
Titanium's excellent corrosion resistance can resist the erosion of various chemicals, including automobile exhaust. The use of titanium alloys in automobile exhaust systems, chassis components, etc. can greatly extend the service life of components.
Fatigue Resistance
Titanium has excellent fatigue performance and can withstand millions of alternating loads without breaking. It is used in titanium components such as suspension systems and transmission systems to effectively improve service life and safety.
Application Cases of Titanium Parts in Automobiles
Titanium was originally used in high-end racing cars and luxury sports cars. These vehicles have reached the extreme in their pursuit of performance and are willing to pay a high cost for titanium, a high-performance material. For example, in Formula One (F1), titanium alloys are widely used in key engine components. With the continuous advancement of material technology, the application of titanium and titanium alloys in ordinary passenger cars and commercial vehicles has gradually increased.
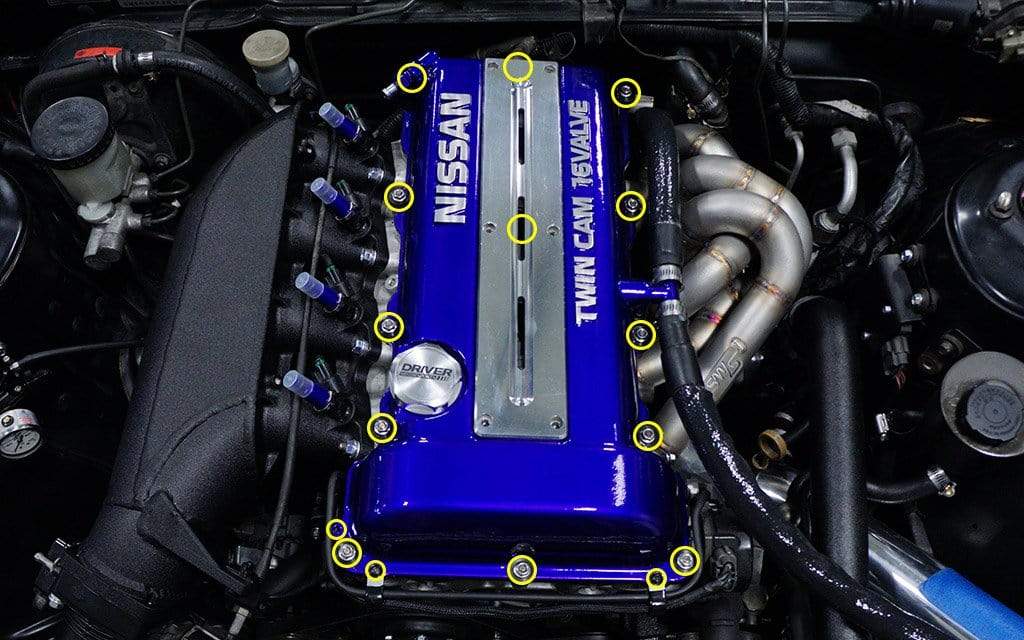

Valve
Valve is the control component of engine intake and exhaust, and needs to be opened and closed frequently. Titanium alloy valves can reduce the weight by 30% – 50%. Some models of brands such as Ferrari and Lamborghini widely use titanium alloy valves. Titanium alloy valves can help the engine easily reach a higher speed and release more powerful power.
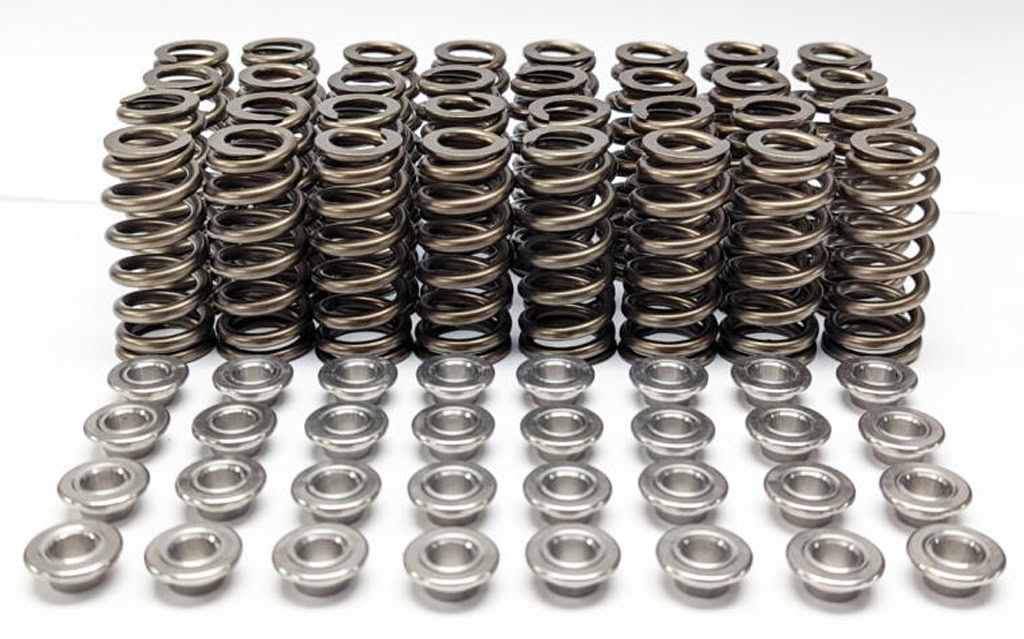

Valve Springs
The main function of the valve spring is to prevent air leakage and provide elastic force for the valve to return. Mercedes-Benz’s AMG series high-performance engines use titanium alloy valve springs. These engines run under high load and high speed conditions. Titanium alloy valve springs can work stably to ensure the normal opening and closing of the valve.
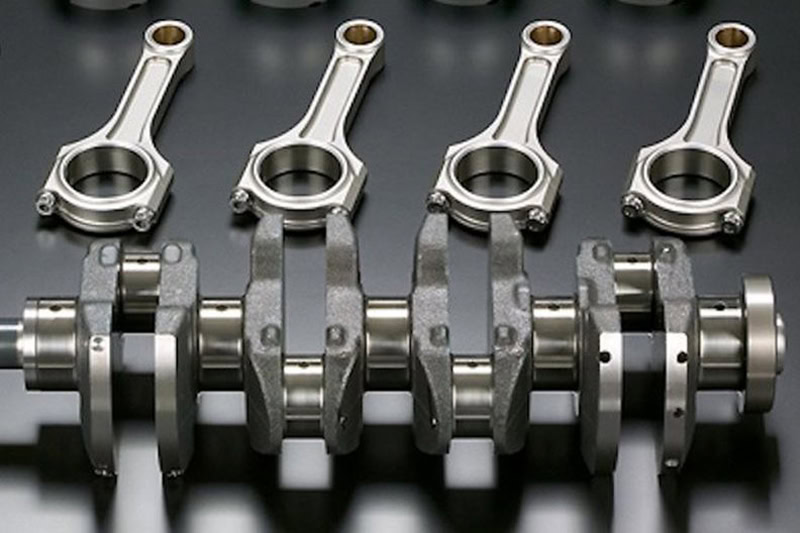

Connecting Rod
The connecting rod is a key component in the engine that converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotational motion of the crankshaft. Titanium alloy connecting rods can reduce fuel consumption by 5% – 10% and increase power output by 8% – 12%. For example, in F1 racing engines, titanium alloy connecting rods are standard.
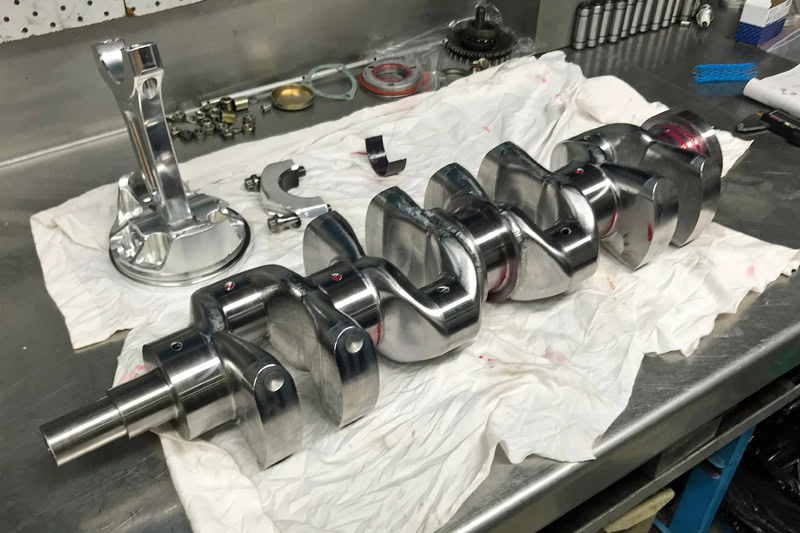

Crankshaft
The crankshaft is subjected to complex bending, torsion and impact loads during operation, and is also affected by high temperature and lubrication conditions. The high strength and good fatigue performance of titanium alloy can withstand greater loads and reduce the risk of fatigue fracture. For example, Rolls-Royce uses a titanium alloy crankshaft.
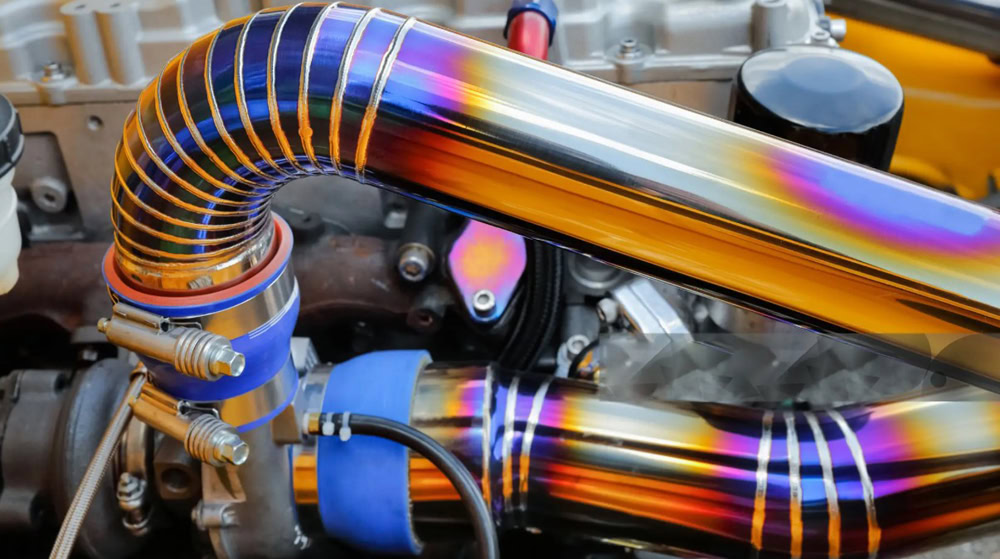

Exhaust Pipe
The titanium alloy exhaust pipe with high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance can maintain good performance in high temperature and corrosive gas for a long time and is not easy to rust and damage. For example, Ducati motorcycles widely use titanium alloy exhaust pipes.
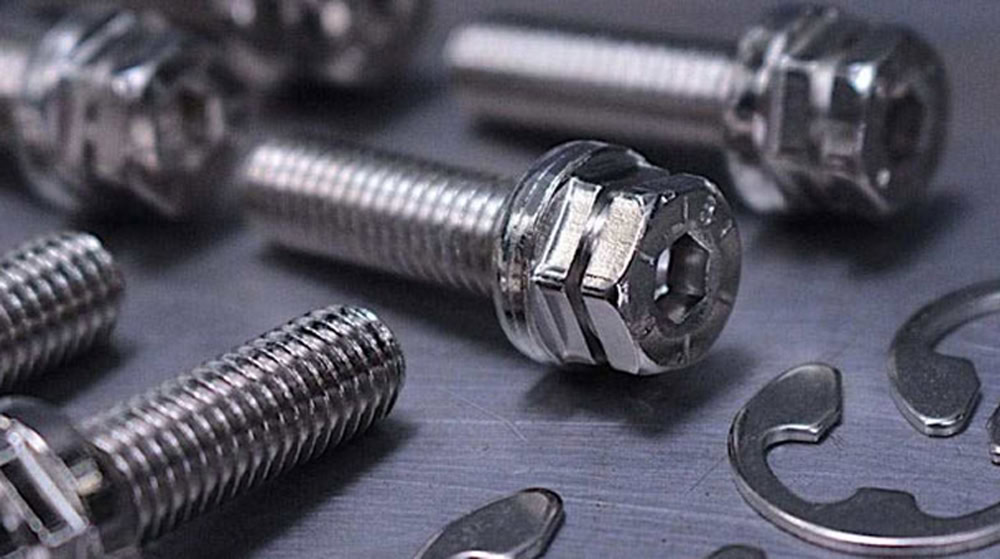

Bolts and nuts
Titanium alloy bolts and nuts significantly reduce weight while ensuring connection strength. They are not easy to rust or loosen in humid and corrosive environments. For example, some models of Tesla use titanium alloy bolts and nuts.
Manufacturing Technology of Automotive Titanium Parts
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Casting
Investment casting is one of the technologies for manufacturing complex-shaped parts with high dimensional accuracy (up to ±0.1 – ±0.2mm) and good surface quality (surface roughness Ra up to 3.2 – 6.3μm), such as engine blocks and cylinder heads. Sand casting is relatively low-cost and suitable for the production of large, relatively simple-shaped titanium parts. The dimensional tolerance is generally ±0.5 – ±1.5mm, and the surface roughness Ra is 12.5 – 50μm.
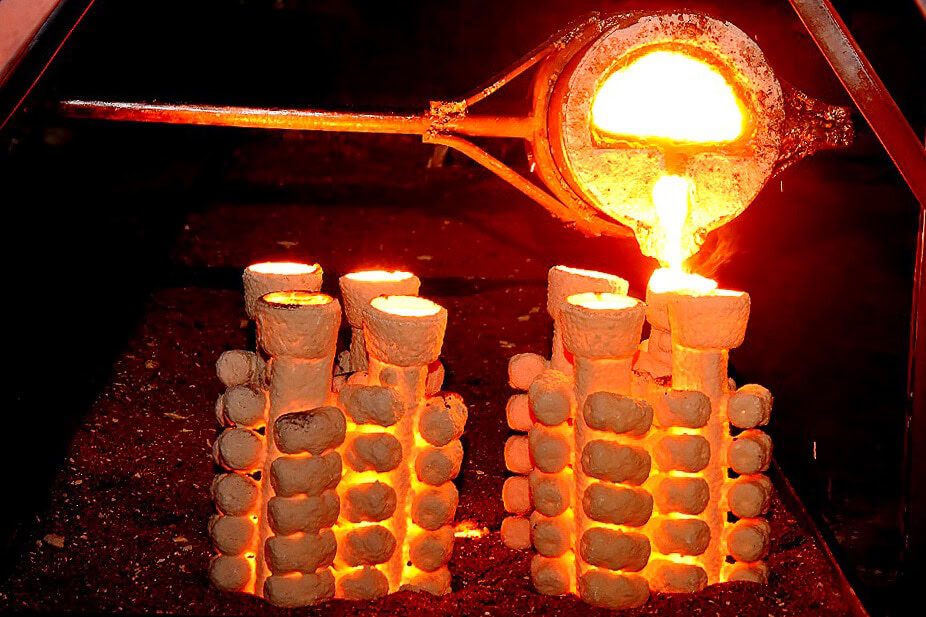

Forging
Hot forging is forging performed above the recrystallization temperature of the titanium alloy (generally 850 – 1050℃). Hot forging can be divided into free forging and die forging. Free forging is suitable for prototype and low-volume manufacturing of titanium parts. Die forging is to put the blank into a specific mold cavity, fill the cavity with the blank under pressure, and obtain a forging with the same shape as the mold.
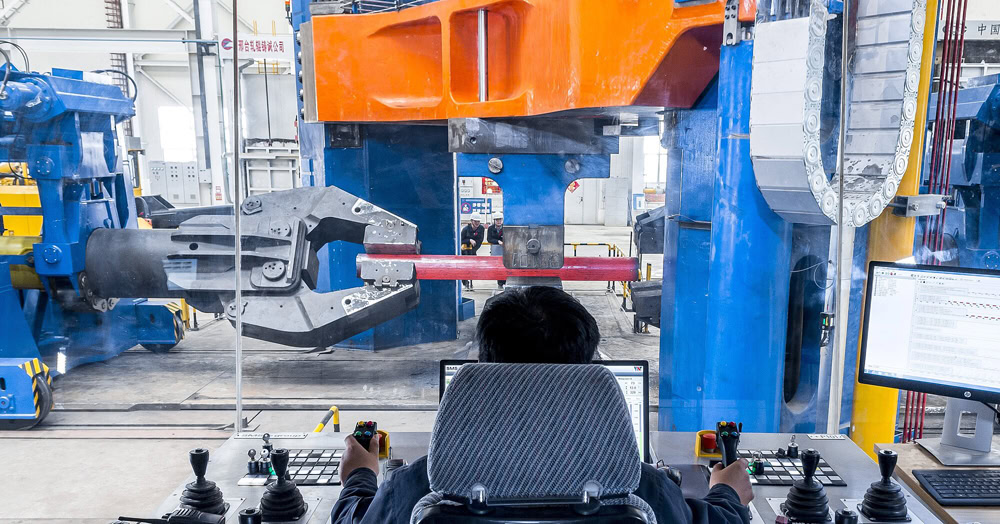

Warm forging is a forging process performed in a temperature range below the recrystallization temperature and above room temperature (generally 400 – 800℃). Warm forging has high requirements for molds, and special mold materials and lubrication measures are required to ensure the service life of the mold and the quality of the forgings. Warm forging is suitable for manufacturing some small and medium-sized titanium parts with high requirements for dimensional accuracy and surface quality, such as engine valves, connecting rods, etc.
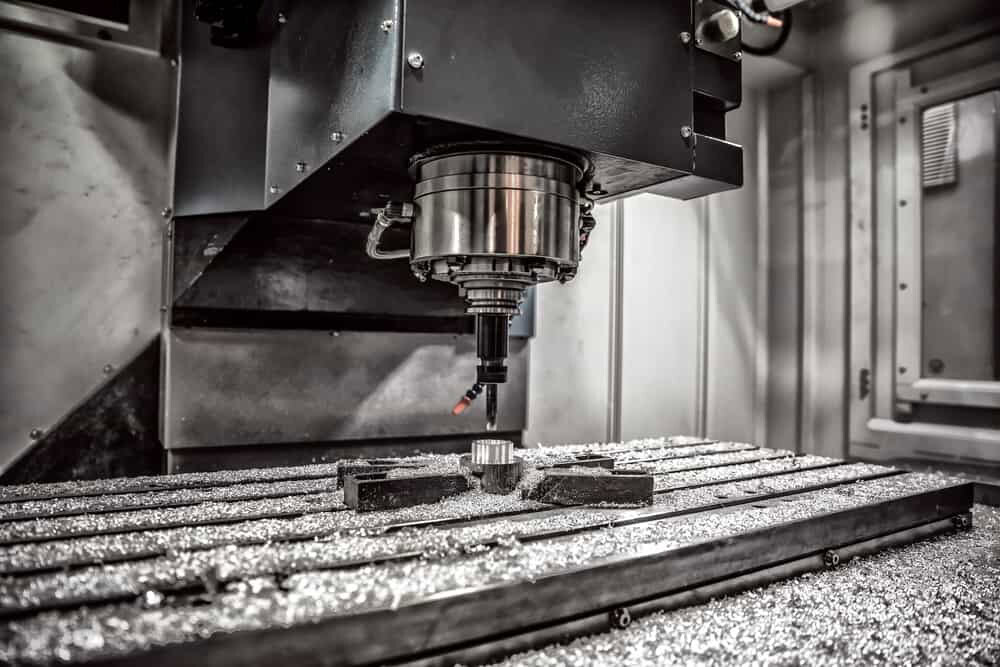
CNC Machining
CNC machining requires the selection of appropriate tools, geometric parameters and cutting parameters. Common tool materials are cemented carbide, ceramics and cubic boron nitride (CBN). Use a smaller rake angle (-5° – 5°) and a larger back angle (8° – 12°) to enhance the strength of the cutting edge and reduce tool wear; the blade inclination angle is generally – 5° – 0°. The principle of selecting cutting parameters is low cutting speed, large feed rate and small cutting depth. Generally speaking, the cutting speed is 30 – 80m/min, the feed rate is 0.1 – 0.3mm/r, and the cutting depth is 0.5 – 2mm. At the same time, make full use of cutting fluid to play a role in cooling and lubrication.

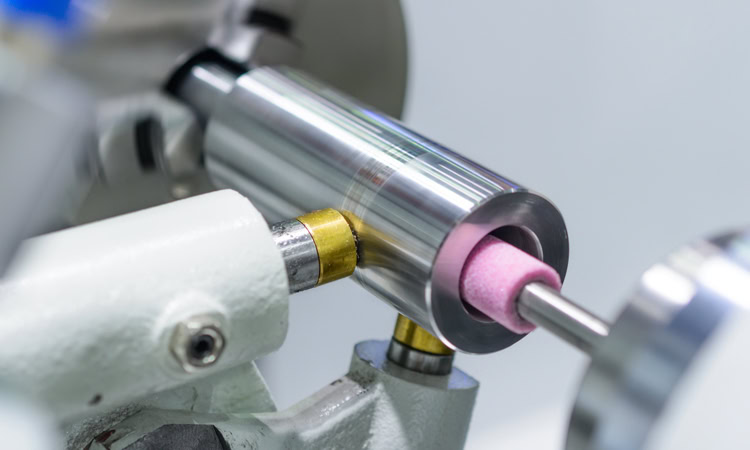
CNC Grinding
Grinding is used to improve the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of titanium parts. The abrasive of the grinding wheel is generally silicon carbide (SiC) or cubic boron nitride (CBN), and the binder can be ceramic, resin or metal. In terms of grinding parameters, a lower grinding speed (20 – 30m/s), a smaller grinding depth (0.01 – 0.05mm) and a larger feed rate (0.1 – 0.3mm/r) are used. At the same time, cooling and lubrication are strengthened, and a large flow of grinding fluid is used to remove grinding heat in time to prevent parts from burning.

Titanium parts play an important role in various systems of automobiles due to their excellent performance, and have made important contributions to the performance improvement and lightweight design of automobiles. At present, automotive titanium parts are facing challenges such as cost, but with the continuous advancement of material technology, their future development prospects are broad. It is believed that in the near future, automotive titanium parts will be more widely used, promoting the development of the automotive industry to a higher level.