Titanium Electrolyzer Manufacturers and Suppliers In China
As a leading company in the field of titanium electrolytic manufacturing, Wstitanium’s research and development achievements and technological breakthroughs have provided new ideas and directions for the development of the industry.
- Sodium Hypochlorite Electrolyzer
- Sodium Chloride Electrolyzer
- Concentric Tube Electrolytic
- Parallel Plate Electrolytic
- Customized Titanium Electrolyzers
- Ruthenium-Iridium Coated
- Iridium-Tantalum Coated
- Platinum Coated
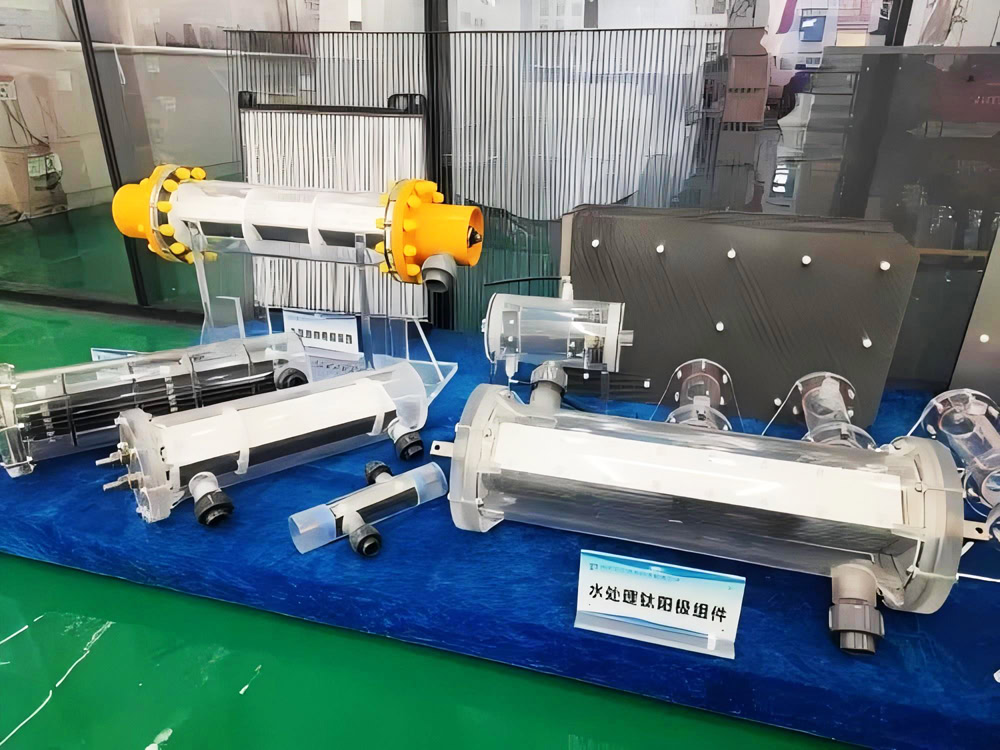

Respectable Titanium Electrolyzer Manufacturer-Wstitanium
Wstitanium has made remarkable achievements in the field of titanium electrolytic cell manufacturing. With its outstanding advantages, advanced production processes, superb technical and professional team and good customer reputation, it has established a good image in the market. Its electrolytic cells are widely used in many fields such as chlor-alkali, electroplating, metallurgy, water treatment, etc.

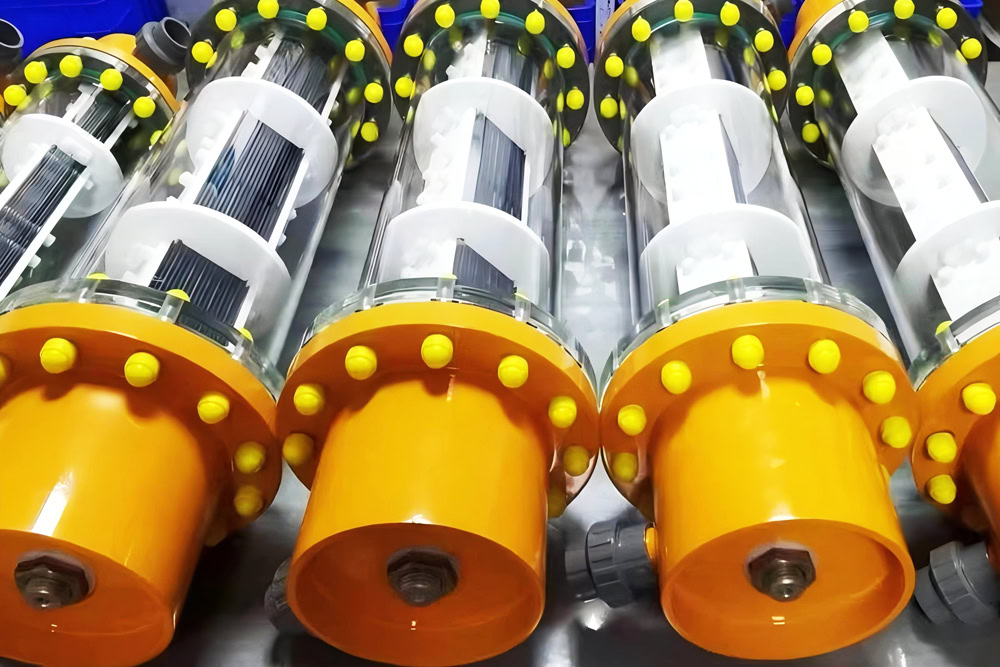
Sodium Hypochlorite Electrolyzer
Sodium hypochlorite is produced by electrolyzing salt water. The oxidation reaction at the anode causes chloride ions to generate chlorine gas, which reacts with water to generate sodium hypochlorite. It is commonly used in water treatment, disinfection, etc.

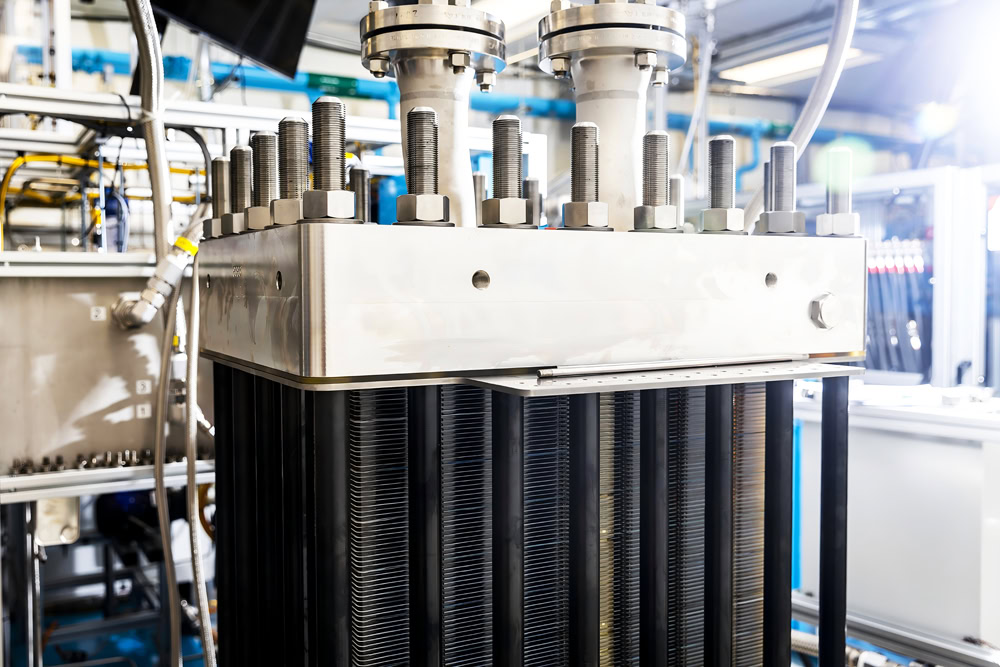
Sodium Chloride Electrolyzer
Caustic soda, chlorine gas, hydrogen, etc. can be obtained when electrolyzing aqueous solution. Electrolysis of molten sodium chloride is mainly used to produce metallic sodium. It is widely used in the chlor-alkali industry.

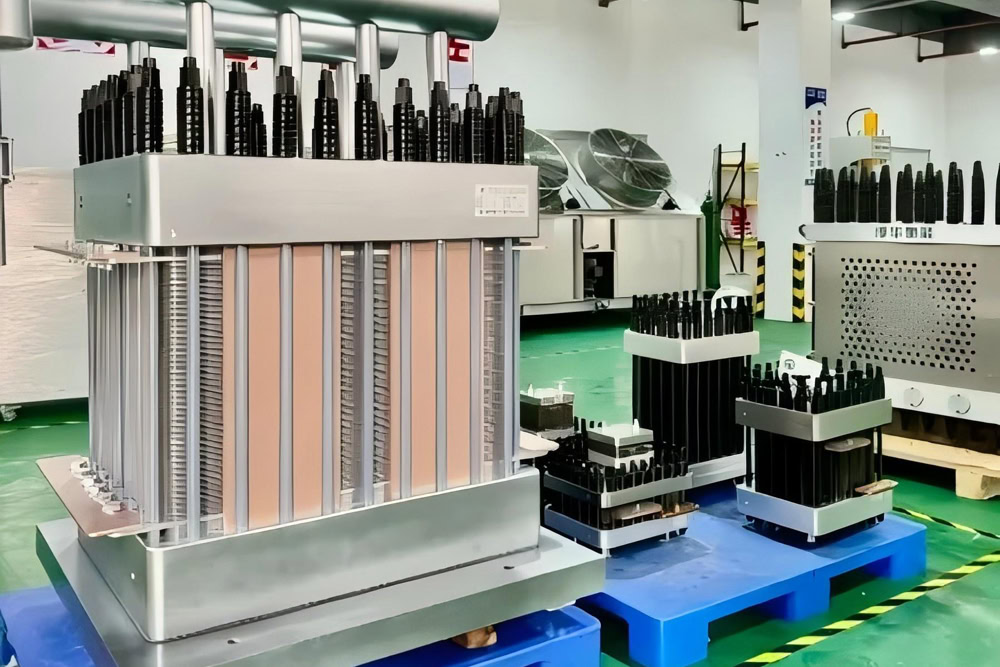
For Chemical Industry
It is used in the electrolysis process in various chemical production, such as organic synthesis, electroplating, electrolytic refining, etc. It plays an indispensable role in the chemical industry and can meet the production requirements of different chemical products.
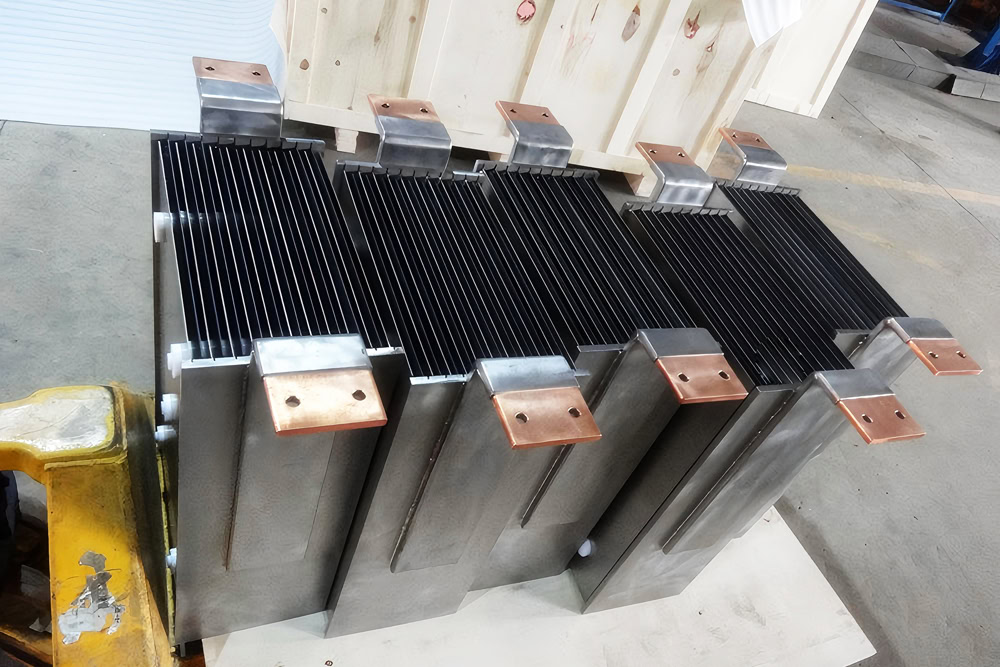

Parallel Plate Electrolytic
The electrodes are placed in parallel so that the electrolyte flows evenly between them and the electric field is evenly distributed, which is conducive to the stability of the electrolytic reaction. It is used in wastewater treatment, metal electrodeposition, etc.
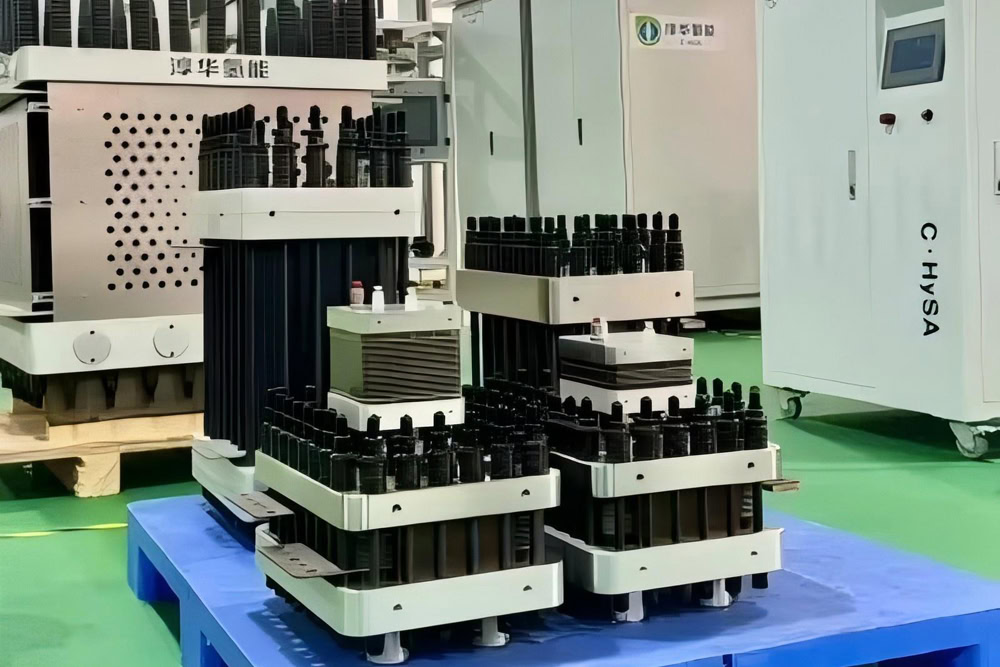

Customized Titanium Electrolyzers
An electrolytic cell designed and manufactured according to your specific needs, including size, shape, material, electrode structure, working conditions, etc. Provide tailor-made solutions for special electrolysis processes.
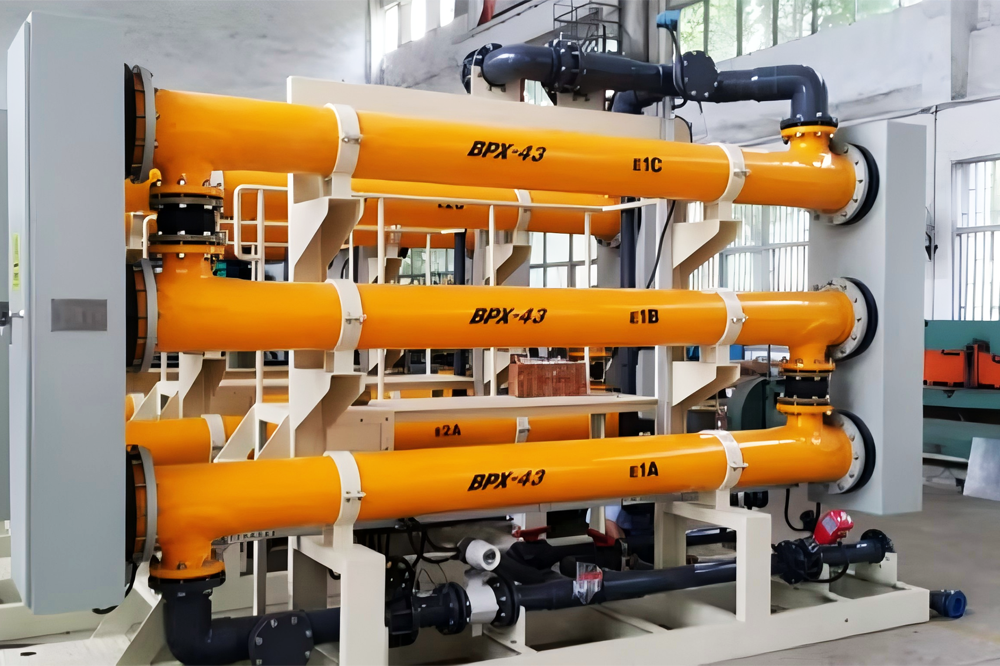

Concentric Tube Electrolytic
It consists of concentrically arranged inner and outer tubes, and the electrolyte flows in the annular space. It is used for electrolysis reactions with special requirements for material contact mode and flow field, such as battery materials, etc.
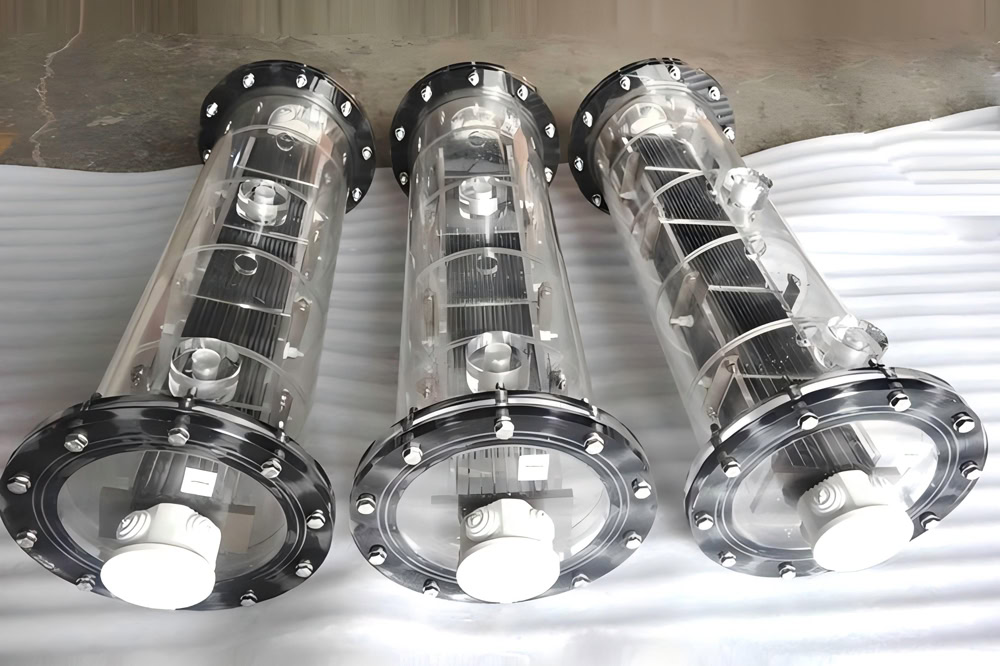

Iridium-Tantalum Coated
The surface of the titanium electrode is coated with iridium-tantalum oxide coating, which improves the corrosion resistance and catalytic activity of the electrode. It is commonly used in seawater desalination, sewage treatment, chlor-alkali, etc.
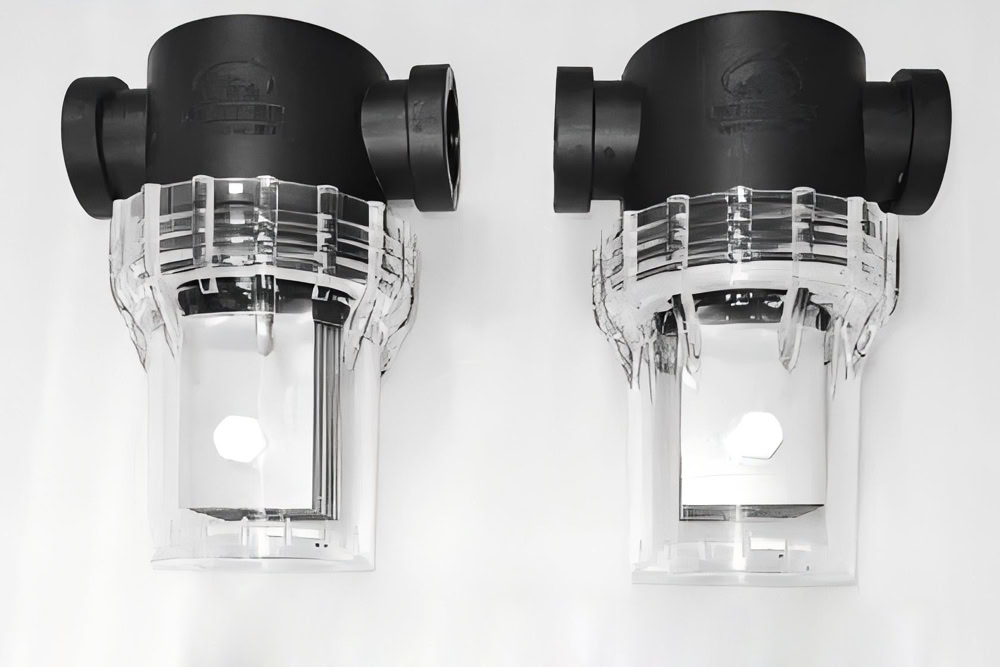

Platinum Coated
Coating the platinum coating on the surface of the titanium electrode can significantly improve the electrolysis efficiency and electrode stability by utilizing the high catalytic activity and good corrosion resistance of platinum.

Ruthenium-Iridium Coated
It has excellent electrocatalytic performance and corrosion resistance, effectively reduces the overpotential of the electrolysis process, and improves the oxygen evolution and chlorine evolution reaction activity of the electrode.
How Does Titanium Electrolyzer Work?
The titanium electrode participates in the electrolysis reaction either as an anode or as a cathode. When the titanium electrode is used as an anode, the active coating on the surface of the titanium electrode will play a catalytic role and promote the anodic oxidation reaction according to the composition of the electrolyte and the requirements of the electrolysis reaction. For example, in the process of electrolysis of salt water, salt (NaCl) is ionized into sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻) in water. In addition, water will also ionize a small amount of hydrogen ions (H⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻). At the anode, the chloride ions lose electrons and undergo an oxidation reaction to produce chlorine gas (Cl₂): 2Cl⁻ – 2e⁻ = Cl₂↑. At the cathode, the hydrogen ions gain electrons and undergo a reduction reaction to produce hydrogen gas (H₂): 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ = H₂↑. At the same time, the remaining hydroxide ions in the solution combine with sodium ions to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Titanium Electrolyzer Design Guide
Different industries have different requirements for the performance, structure and size of titanium electrolytic cells. Wstitanium will first communicate with you in depth to understand the production process, electrolytic products, output requirements, existing equipment and site conditions. Determine the basic parameters of the electrolytic cell, such as cell size, electrode material and structure, electrolyte circulation method, current and voltage requirements, etc. According to the results of the demand assessment, the design team uses advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation analysis software to simulate and calculate the electric field distribution, flow field distribution, temperature field distribution, etc. of the electrolytic cell to ensure the scientificity and reliability of the design scheme.
Electrolytic Size
The size of the electrolytic cell is one of the important parameters for the customization of titanium electrolytic cells. Its size mainly depends on factors such as production scale, electrolyte volume and electrode arrangement. The length, width and height of the cell can be customized according to your actual needs, and the volume ranges from a few liters to thousands of liters.
Electrode Material
The electrodes of titanium electrolytic cells are usually titanium composite materials, that is, a coating with specific electrocatalytic properties is coated on the surface of the titanium substrate. The coating depends on the type and requirements of the electrolytic reaction. Common ones include ruthenium, iridium, platinum and other precious metal oxides.
Electrode Shape
The electrode shape can be customized according to the structure of the electrolytic cell and the requirements of the electrolytic process. Common electrode shapes include flat, mesh, tubular, columnar, etc. The size of the electrode can also be adjusted according to the size of the electrolytic cell and the requirements of the current density, including parameters such as the length, width, thickness, mesh size of the electrode.
Electrolyte flow rate
In order to avoid concentration polarization, the electrolyte needs to maintain a certain flow rate. Generally speaking, the electrolyte flow rate needs to be ≥0.3m/s. The electrolyte flow rate can ensure that the ions in the electrolyte can be replenished to the electrode surface in time to maintain the continuous electrolysis reaction, and also help to remove the heat generated during the electrolysis process.
Effective volume
In order to avoid concentration polarization, the electrolyte needs to maintain a certain flow rate. Generally speaking, the electrolyte flow rate needs to be ≥0.3m/s. The electrolyte flow rate can ensure that the ions in the electrolyte can be replenished to the electrode surface in time to maintain the continuous electrolysis reaction, and also help to remove the heat generated during the electrolysis process.
Current density
Current density refers to the current passing through a unit electrode area, and the conventional range is between 100-1000A/m². The choice of current density has an important impact on the rate of electrolytic reaction, the purity of the product, and energy consumption. Higher current density can increase the rate of electrolytic reaction, but it may also lead to increased electrode polarization, increased energy consumption, and higher requirements for electrode materials.
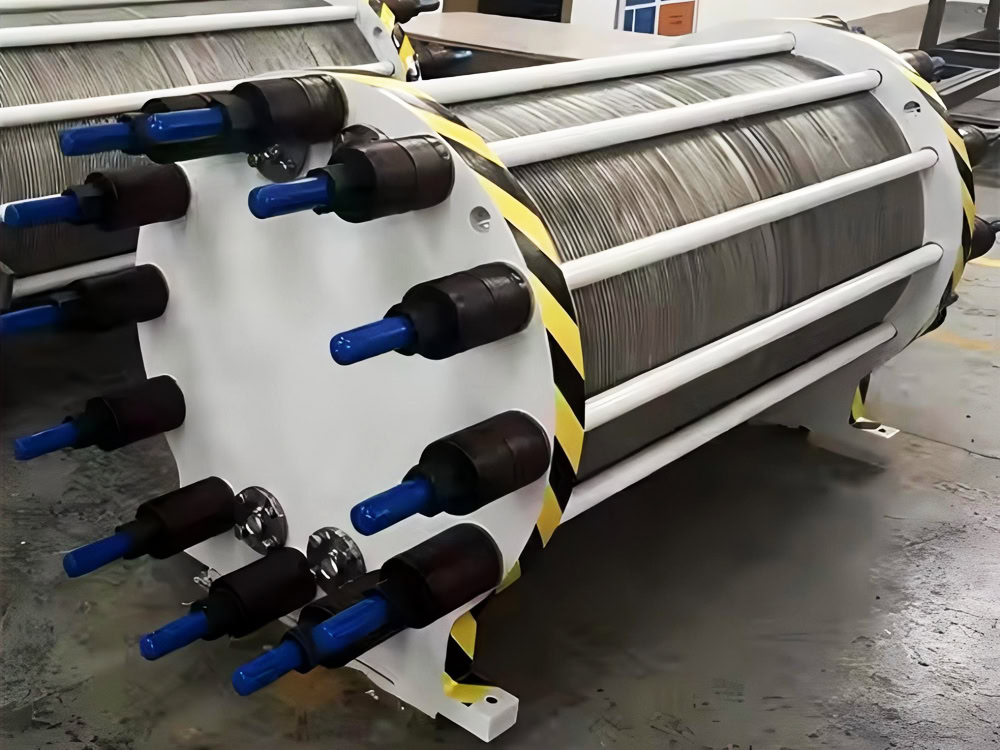
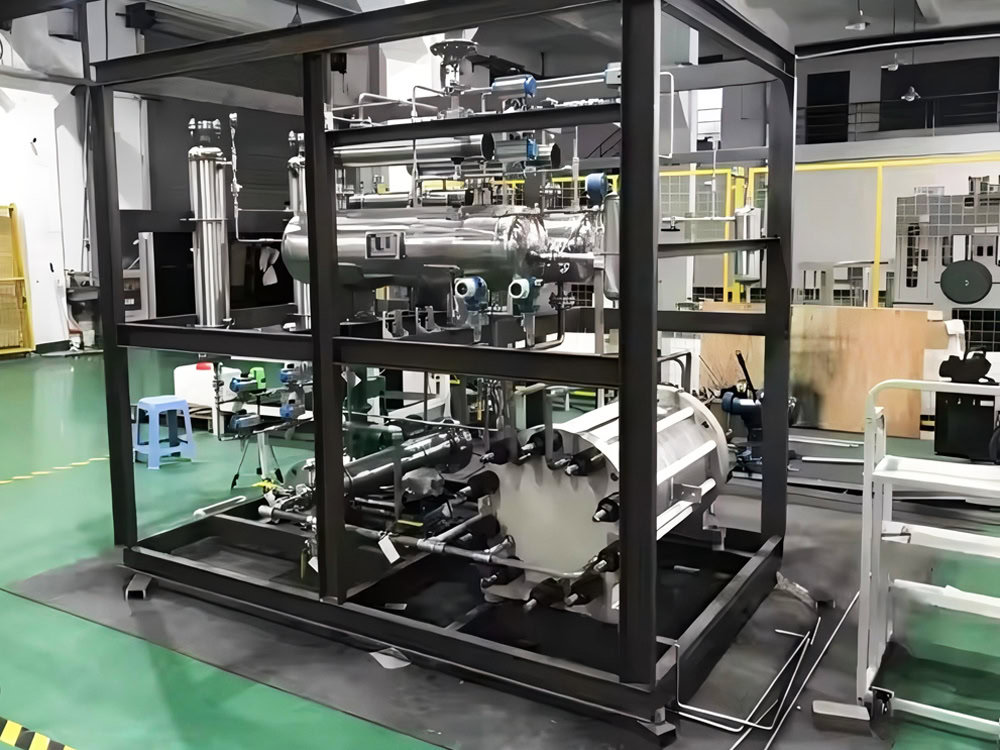


Electrode Spacing
The electrode spacing is one of the important parameters that affect the performance of the electrolytic cell. It directly determines the size of the cell voltage, which is calculated as follows: V cell = V theory + IR drop + η, where V theory is the theoretical decomposition voltage, IR drop is the voltage drop caused by the electrolyte resistance, and η is the overpotential. The smaller the electrode spacing, the smaller the resistance, the lower the cell voltage, and the lower the energy consumption. However, too small an electrode spacing may increase the risk of short circuits between the electrodes, and also increase the resistance to the flow of the electrolyte. Therefore, it is necessary to consider various factors comprehensively during the design and select a suitable electrode spacing.
Titanium Electrolytic Manufacturing Process
Before manufacturing the titanium electrolytic cell, the raw materials must first be strictly inspected. Including whether the specifications, chemical composition, mechanical properties, etc. meet the design requirements. For example, the purity of titanium materials should meet certain standards (>99.5%) to ensure its corrosion resistance and other properties. Titanium materials need to be surface treated to remove impurities such as oil stains and scale on the surface. Surface treatment includes grinding, sandblasting, etc.) or chemical treatment (such as pickling, alkali washing, etc.) to achieve a smooth surface without defects.
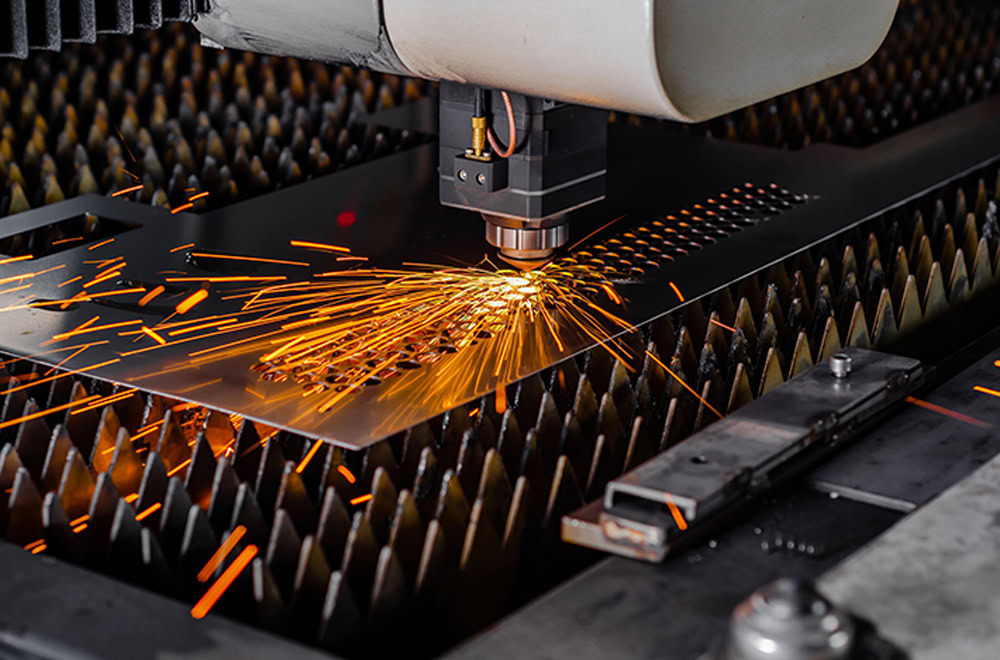
Forming
According to the requirements of the drawings, use cutting equipment (such as plasma cutting machine, laser cutting machine, etc.) to cut the titanium materials into the required shape and size. During the cutting process, attention should be paid to controlling the accuracy to ensure that the dimensional error of each component is within the allowable range. For larger-sized tank parts, it may be necessary to cut in blocks and then splice them. The cut titanium parts need to be formed to make them conform to the designed shape. For the main part of the tank body, bending, rolling and other operations may be required.

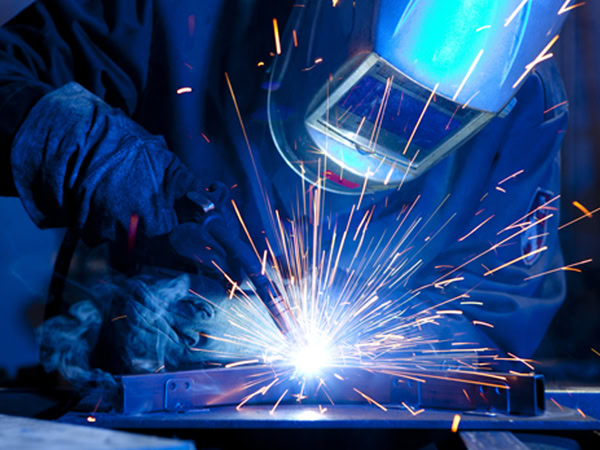
The formed titanium parts need to be welded and assembled to form the overall structure of the tank body. Titanium welding usually uses inert gas shielded welding (such as tungsten inert gas welding) to effectively prevent titanium from being oxidized and contaminated during welding. During welding, welding parameters such as welding current, voltage, welding speed, etc. must be strictly controlled to ensure the quality of the weld. After welding, the weld needs to be inspected, such as appearance inspection, non-destructive testing (such as radiographic testing, ultrasonic testing, etc.) to ensure that the weld is free of defects such as cracks, pores, and slag inclusions.

After the tank body is assembled, it is also necessary to seal it to prevent electrolyte leakage. The sealing material can be made of corrosion-resistant materials such as rubber and polytetrafluoroethylene, and the sealing method can be bolt sealing, welding sealing, etc.
Preparation of Active Coating
In order to improve the electrocatalytic performance of the electrode, it is necessary to apply an active coating (ruthenium iridium, iridium tantalum, platinum, etc.) on the surface of the electrode substrate. There are mainly thermal decomposition method, electrochemical deposition method, spraying method, etc. The thermal decomposition method is to apply a solution containing a substance to the surface of the electrode substrate, and then decompose it at high temperature to form an active oxide coating; the electrochemical deposition method is to deposit active metal ions to form a coating by electrochemical methods. The spraying method is to make the active coating material into powder, and then attach it to the surface of the electrode substrate by spraying equipment or brushes.
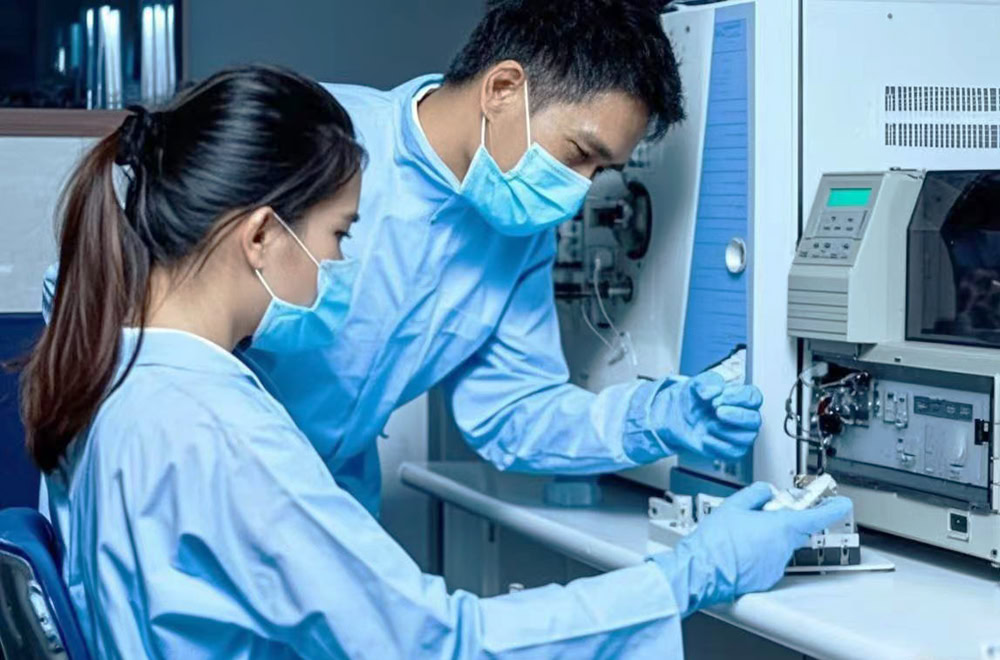

After the active coating is prepared, the electrode needs to be tested for performance, such as electrode potential test, current efficiency test, etc., to ensure that the performance of the electrode meets the design requirements.
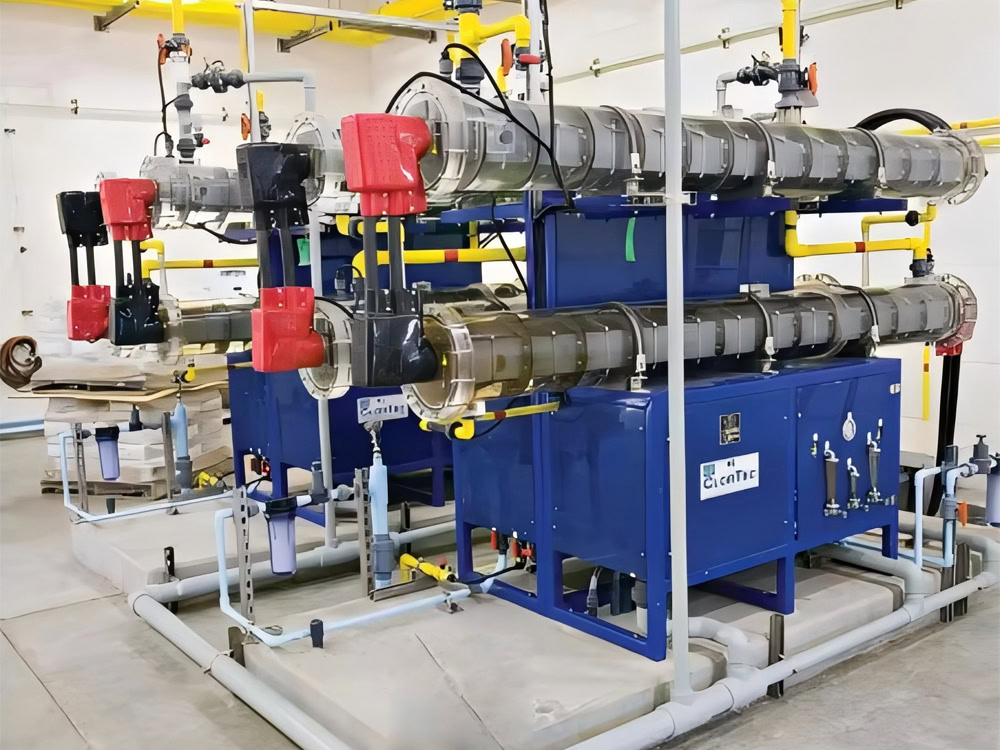
Electrolyte Circulation System
The electrolyte circulation system includes pumps, pipes (transparent PVC, CPVC or UPVC), valves, filters and other components. First, install the pump according to the design requirements, select the appropriate pump type and specifications to ensure that it can provide sufficient flow and pressure. Then, install the pipes and valves. The pipe connections should be firm and well sealed to avoid leakage. Installing filters can remove impurities in the electrolyte and prevent impurities from affecting the electrodes and the electrolysis process.
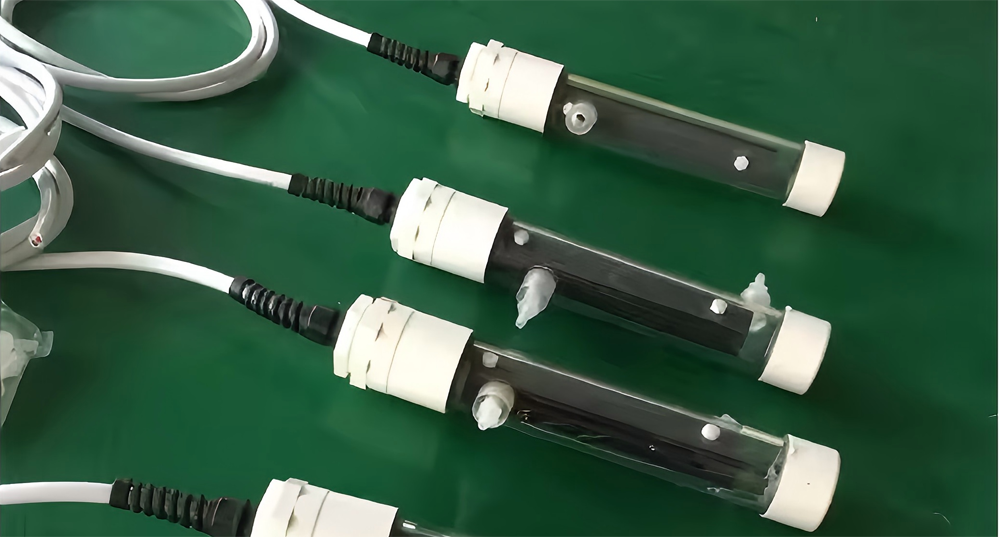

Electrical System
The electrical system includes power supply equipment, conductive bars, electrode connectors, control systems, etc. The conductive bars are generally made of materials with good conductivity such as copper or aluminum, and their cross-sectional area should be selected according to the current size to ensure that they can withstand sufficient current. The installation of the control system includes temperature control, current and voltage control, electrolyte circulation control and other parts. After the installation is completed, electrical performance tests such as insulation test and grounding test are required.
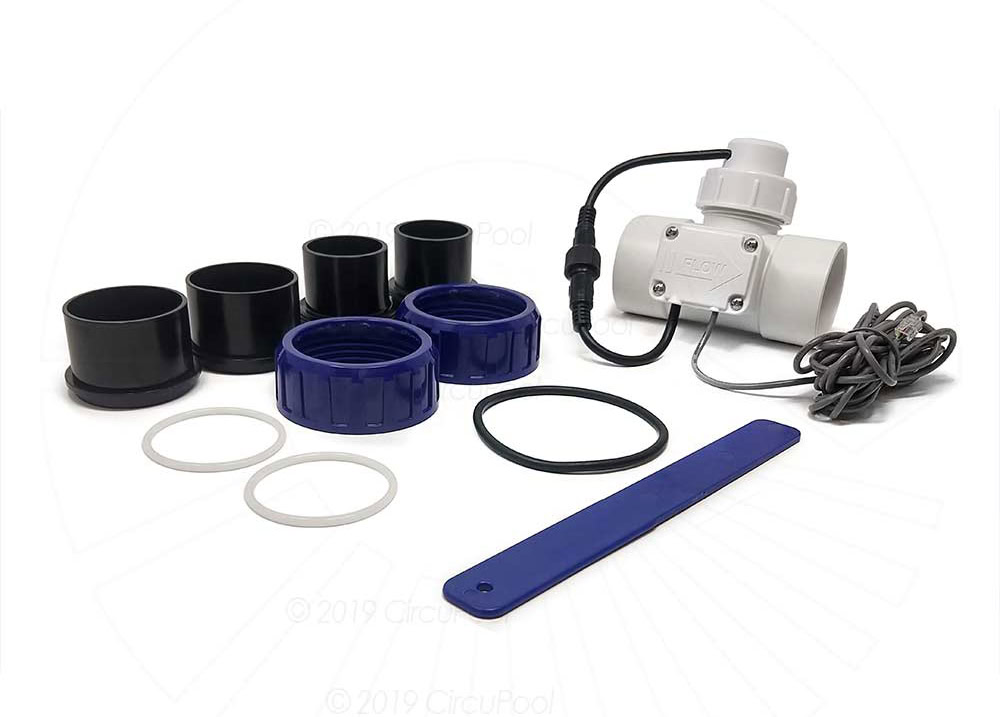

Quality Inspection
After the titanium electrolytic cell is manufactured, it needs to be debugged and inspected as a whole. Including injecting electrolyte into the electrolytic cell, starting the power supply equipment, adjusting parameters such as current, voltage, temperature, and observing the operation of the electrolytic cell. During the debugging process, it is important to check whether the electrolyte circulation is normal, whether the electrode has abnormal heating, sparks, etc., and whether the various parameters are stable within the design range.
The inspection content includes appearance inspection, dimension inspection, performance test, etc. The appearance inspection mainly checks whether the surface of the electrolytic cell has defects such as damage, cracks, and leakage; the dimension inspection mainly checks whether the dimensions of the cell body, electrodes and other components meet the design requirements; the performance test mainly tests the current efficiency, voltage drop, product quality and other indicators of the electrolytic cell.
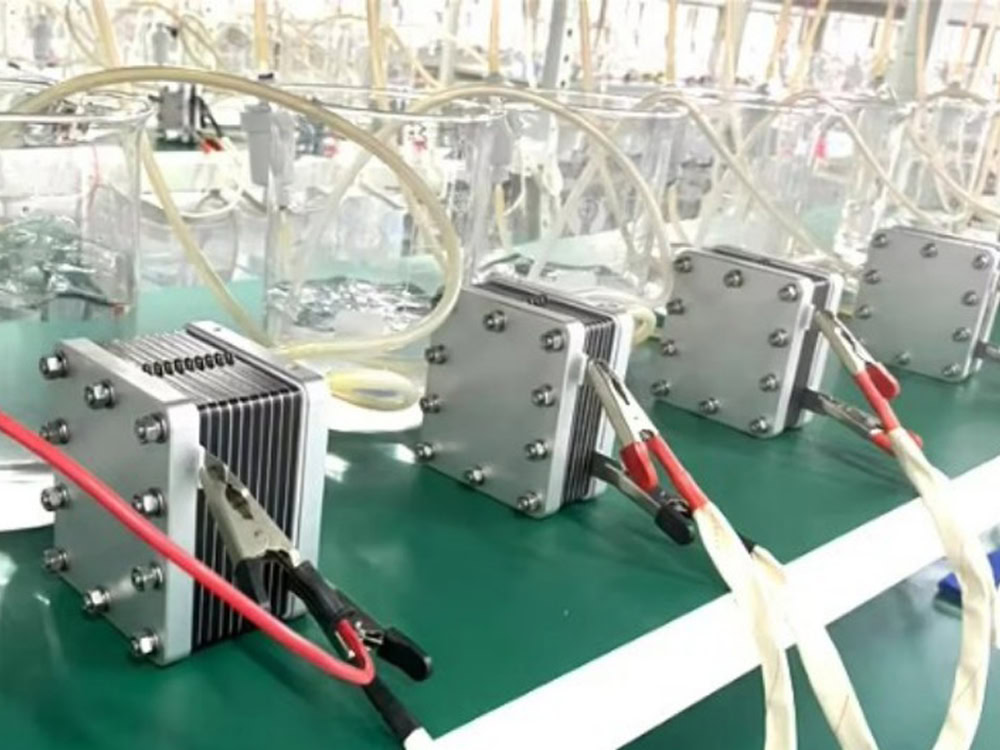
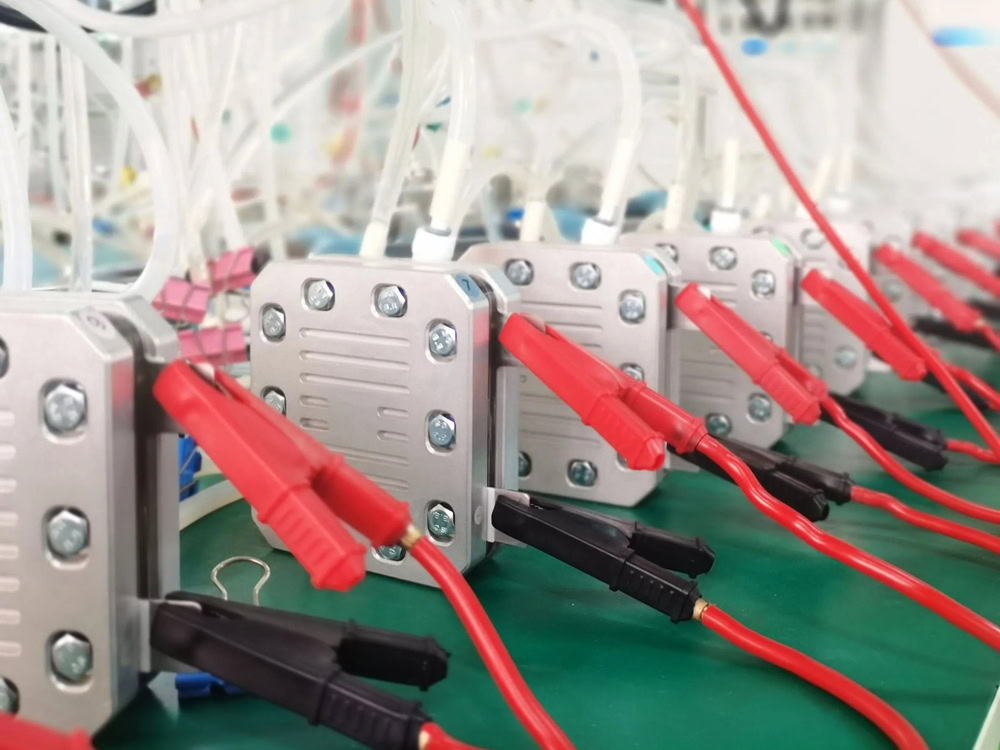
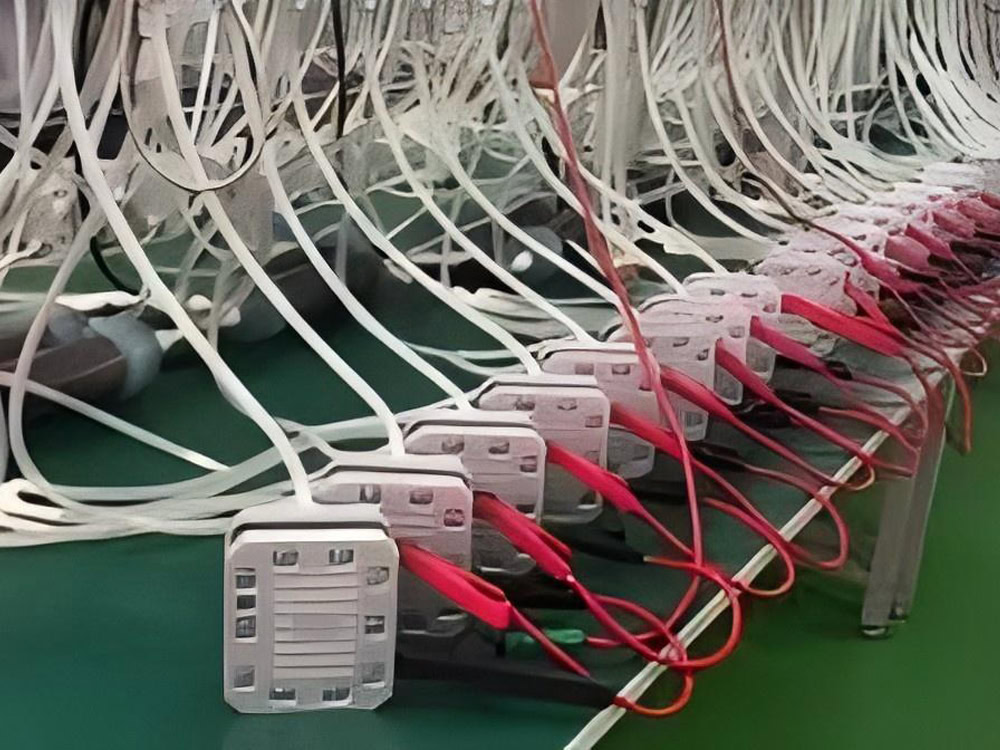



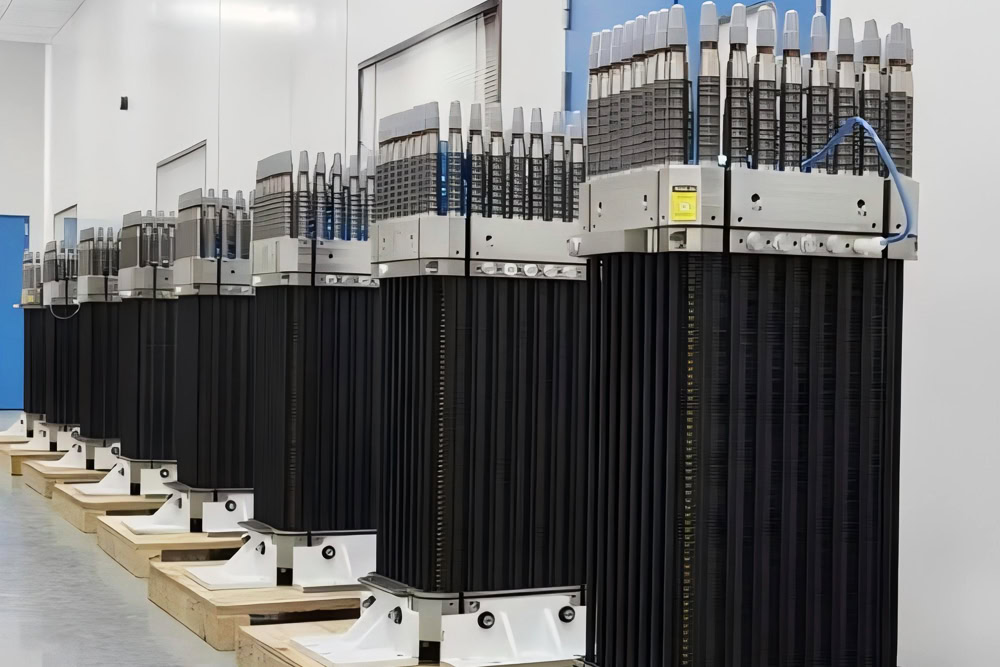
Wstitanium Titanium Electrolytic Dimensions
As a manufacturer of titanium electrolyzers for chlorination systems, Wstitanium offers a variety of size options to meet a variety of needs in seawater electrochlorination and brine electrochlorination applications. Whether you need a standard size or a custom solution, Wstitanium’s expertise and manufacturing capabilities ensure that expected results are exceeded.
Seawater Electrochlorination Electrolyzer
Applicable to power plants, refineries, fertilizer plants, and desalination facilities. It controls biological activity in circulating cooling systems that rely on seawater cooling. Seawater electrochlorination systems are cost-effective in remote areas where other disinfection methods are difficult to implement.
| Model | Production (kgCl2/h) | Amount of Seawater to be treated at 2ppm (m3 /h) | Output Concentration (ppm) | Seawater Flow Rate (m3/h) | Electricity Consumption (kWh/kgCl2) |
| HL-SW-5.0 | 5 | 2500 | 2000 | 2.5 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-10 | 10 | 5000 | 2000 | 5 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-20 | 20 | 10000 | 2000 | 10 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-40 | 40 | 20000 | 2000 | 20 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-60 | 60 | 30000 | 2000 | 30 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-80 | 80 | 40000 | 2000 | 40 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-100 | 100 | 50000 | 2000 | 50 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-140 | 140 | 70000 | 2000 | 70 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-180 | 180 | 90000 | 2000 | 90 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-200 | 200 | 100000 | 2000 | 100 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-400 | 400 | 200000 | 2000 | 200 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-800 | 800 | 400000 | 2000 | 400 | 4.5 |
| HL-SW-1000 | 1000 | 500000 | 2000 | 500 | 4.5 |
Brine Chlorination Electrolyzers
Brine electrochlorination electrolyzers provide hypochlorous acid for disinfection. They are installed on land and produce large quantities of sodium hypochlorite for storage, ensuring continuous disinfection capacity in situations where seawater is not available or for drinking water chlorination.
| Model | Production (kgCl2/h) | Amount of Water to be treated at 1ppm (m3 /h) | Output Concentration (ppm) | Brine Flow Rate (lit/h) | Electricity Consumption (kWh/kgCl2) |
| HL-BR-0.1 | 0.1 | 100 | 8000 | 12.5 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-0.5 | 0.5 | 500 | 8000 | 62.5 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-1.0 | 1 | 1000 | 8000 | 125 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-5.0 | 5 | 5000 | 8000 | 625 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-10 | 10 | 10000 | 8000 | 1250 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-20 | 20 | 20000 | 8000 | 2500 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-30 | 30 | 30000 | 8000 | 3750 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-40 | 40 | 40000 | 8000 | 5000 | 4.8 |
| HL-BR-50 | 50 | 50000 | 8000 | 6250 | 4.8 |
Titanium Electrolyzer Applications
As an important electrolytic equipment, titanium electrolytic cell is widely used in many fields such as electroplating, hydrometallurgy, chlor-alkali industry, environmental protection, chemical synthesis, etc. Its excellent performance advantages enable it to operate stably in complex chemical environments, providing a strong guarantee for efficient and high-quality production.
Electroplating
Titanium electrolytic cells are widely used in the electroplating process of various metals, such as chrome plating, zinc plating, nickel plating, etc. Taking chrome plating as an example, the chrome plating electrolyte is usually highly corrosive and contains a large amount of chromic acid and sulfuric acid. Titanium electrolytic cells can adapt well to this corrosive environment and ensure the stable progress of the chrome plating process.

Hydrometallurgy
Hydrometallurgy is a method of extracting and separating metals by chemical reactions in solution, and titanium electrolytic cells play a key role in hydrometallurgy. For example, in the hydrometallurgy of copper, sulfuric acid is usually used as an electrolyte to dissolve the copper in the copper ore into copper ions, and then the copper ions are reduced to metallic copper by electrolysis. In addition, titanium electrolytic cells are also widely used in the hydrometallurgy of metals such as zinc, nickel, and cobalt. The electrolytes of these metals are usually also corrosive to a certain extent. The corrosion resistance advantage of titanium electrolytic cells enables it to operate stably in these complex chemical environments.

Chlor-alkali
The chlor-alkali industry is an important industrial sector for the production of caustic soda (sodium hydroxide), chlorine, and hydrogen. In the chlor-alkali production process, the electrolyte is a sodium chloride solution, which is highly corrosive. Titanium electrolytic cells have become ideal electrolytic equipment in the chlor-alkali industry due to their excellent corrosion resistance. In chlor-alkali electrolytic cells, the anode usually uses a titanium-based coated electrode, such as a ruthenium titanium coated electrode, which has good corrosion resistance and chlorine evolution performance and can operate stably at high current density. The cathode is generally made of titanium, and the surface can be specially treated to improve the hydrogen precipitation efficiency.

Environmental Protection
Titanium electrolytic cells are used in wastewater treatment, sewage treatment and other aspects. For example, in the electrocoagulation method for treating wastewater, by applying current to the titanium electrode, metal ions are generated on the electrode surface, and these metal ions react with pollutants in the wastewater to flocculate, thereby removing the pollutants. Titanium electrolytic cells can ensure the continuous electrocoagulation reaction in wastewater treatment and improve the effect of wastewater treatment.

In addition, in the electrochemical oxidation method in sewage treatment, organic matter, ammonia nitrogen and other pollutants in sewage can be oxidized and decomposed into harmless substances through electrochemical oxidation.
Chemical Synthesis
Titanium electrolytic cells can meet the requirements of these special chemical synthesis reactions. For example, in organic electrochemical synthesis, titanium electrolytic cells can be used to synthesize some organic compounds, such as organic acids, organic bases, etc. In these reactions, the composition of the electrolyte and the reaction conditions are often complex, and the corrosion resistance and stability of the electrolytic cell are required to be high. Titanium electrolytic cells can operate stably in such a complex environment to ensure the smooth progress of the reaction.
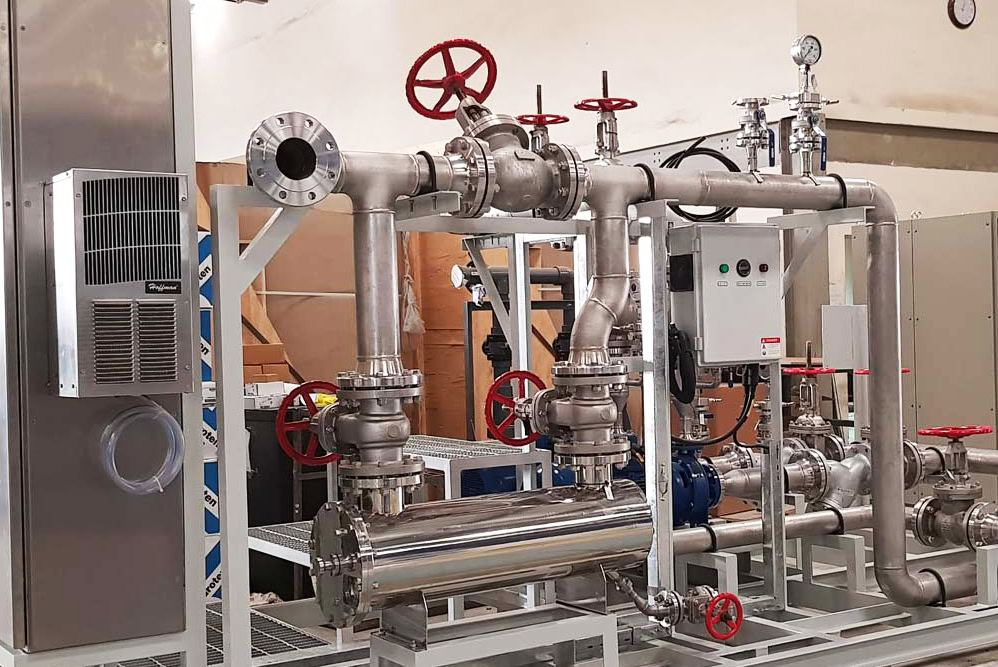

Titanium electrolytic cells meet the diverse requirements of different industrial production with their excellent corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio, good thermal stability, long service life, low pollution and machinability. During the manufacturing process, Wstitanium strictly follows the processes of raw material inspection and preparation, cell body processing, electrode manufacturing, electrolyte circulation system installation, electrical system installation, overall commissioning and inspection to ensure that the quality and performance of titanium electrolytic cells meet the design standards. In the future, titanium electrolytic cells will develop in the direction of high performance, greenness and intelligence, continuously meet the needs of various industries for efficient, environmentally friendly and intelligent production, and make greater contributions to promoting the sustainable development of industry.