CNC Turning Titanium
From complex CNC turned titanium parts to high volume manufacturing, short lead times and competitive pricing. Tight tolerances of 0.002mm. Lead times as fast as 1 day. Advanced CNC lathes with live tooling to machine features such as axial and radial holes, flats, grooves and slots.
- ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485 Certified.
- 100% Quality Inspection Report
- Tolerances Up to ± 0.002mm
- Parts as Fast as 1 days
- Global Delivery
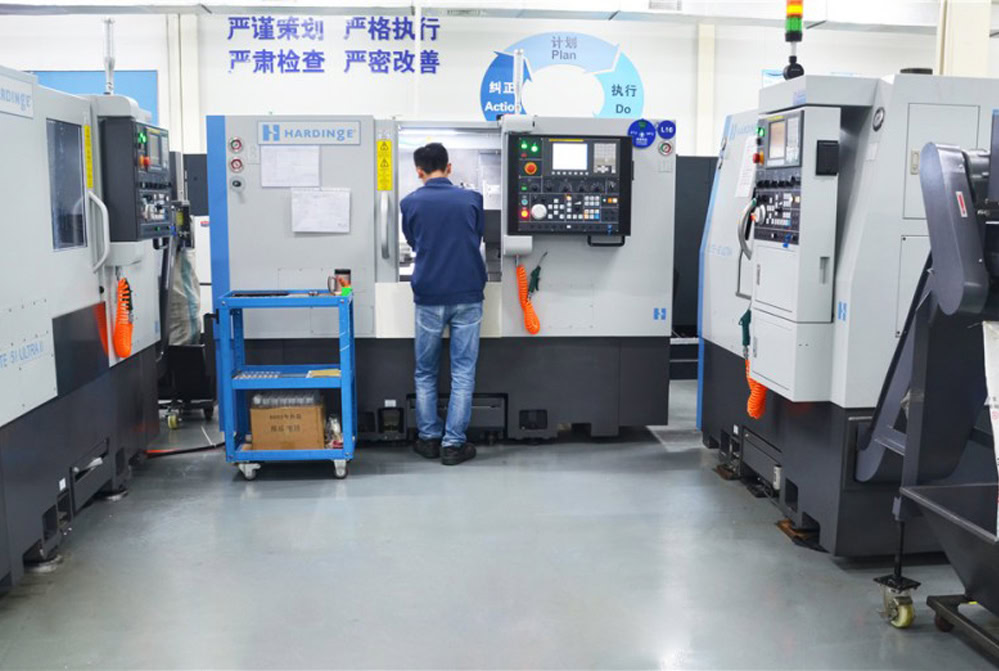
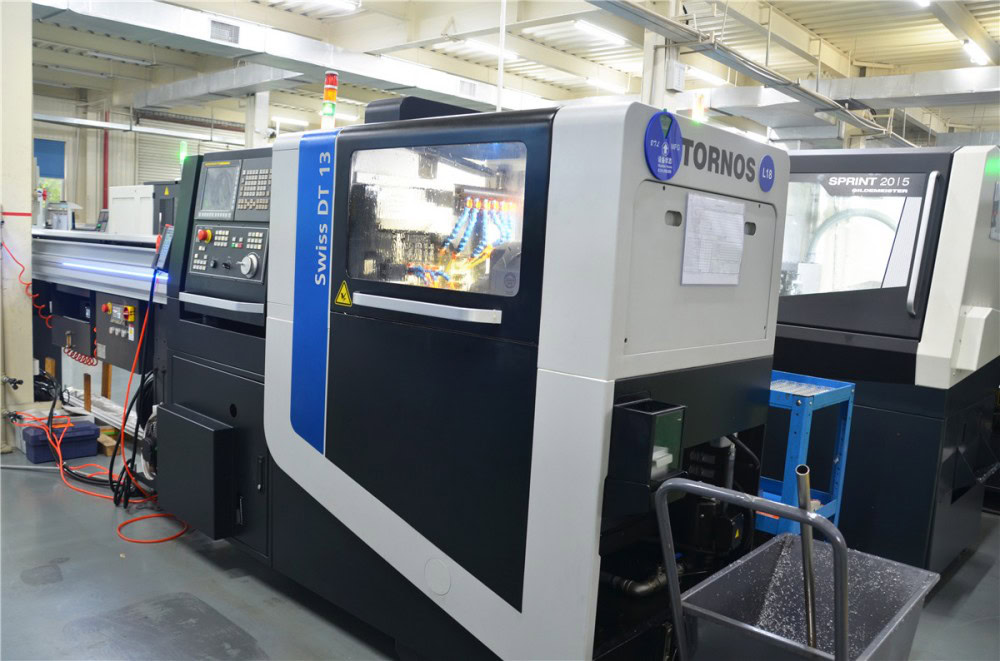
WSTITANIUM Factory
Our Powerful Facilities

Online Customized CNC Turning Titanium Service
Titanium alloys have become important materials in aerospace, medical devices, chemicals and other fields due to their excellent physical properties, such as high strength, low density and excellent corrosion resistance. However, titanium alloys pose great challenges to CNC manufacturing processes due to their high strength, low thermal conductivity and work hardening characteristics. Therefore, it is crucial to choose an excellent CNC turned titanium parts service provider. Wstitanium’s investment in HAAS CNC turning centers is fully capable of manufacturing complex and critical-size custom parts, providing high-quality titanium CNC turned parts for rapid prototyping or low-volume manufacturing.
What is CNC Turning?
CNC turning is a subtractive process that relies on a computer program to remove material from a workpiece and create the desired part. The process starts with you creating a 3D CAD model of the desired part, which is then converted into a G-code (computer program) using Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. The G-code then automatically manipulates the cutting tool and workpiece to create the shape you want. CNC turning is very similar to the CNC milling process. However, unlike CNC milling, which keeps the workpiece fixed while the cutting tool rotates in reverse, the cutting tool in a CNC lathe remains in place while the workpiece rotates in reverse.
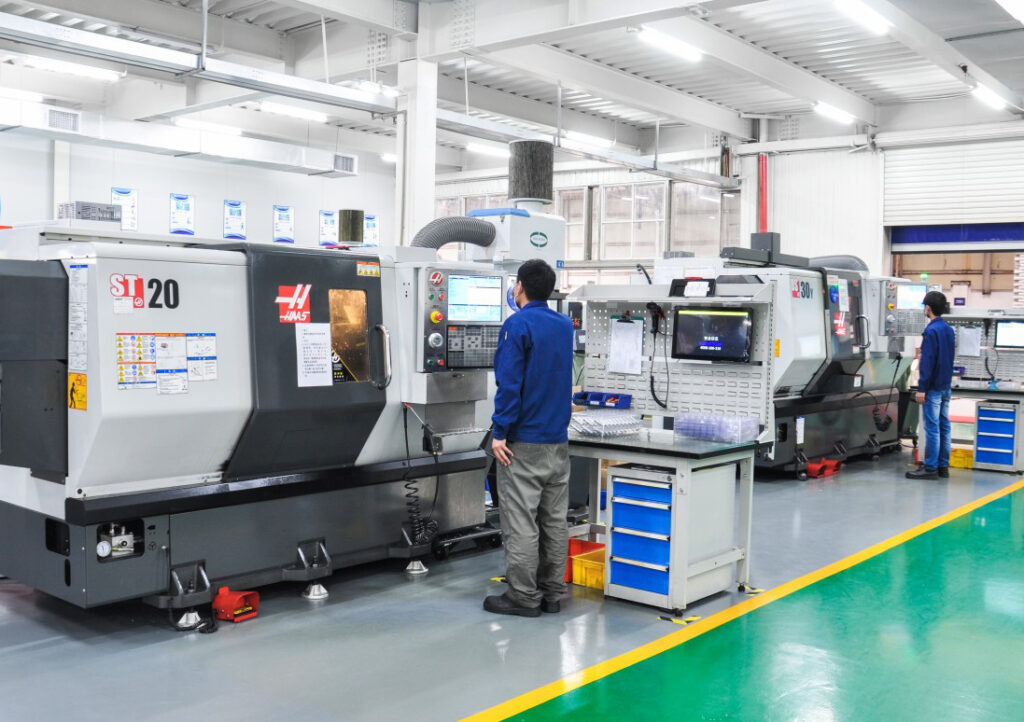

Why Choose CNC Turning Services?
As you can see, CNC turning is the process of removing material from a rotating workpiece using the linear path of the tool on a CNC lathe. In simple terms, the main elements involved in this process are the rotating spindle that clamps the workpiece and the cutting tool mounted on the turret.
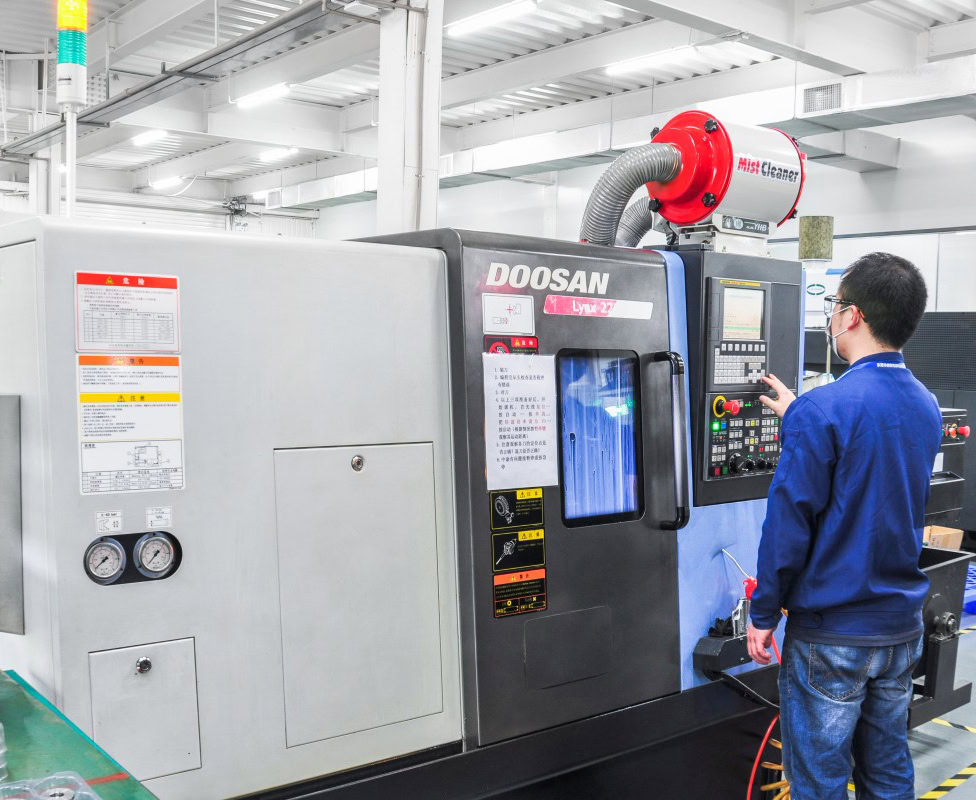

Manufacturing Cylindrical Titanium Parts
CNC turning is ideal for creating cylindrical or axisymmetric titanium parts, such as titanium bars, titanium bolts, titanium rivets, titanium flanges, etc. CNC turning also solves some manufacturing challenges associated with CNC milling. For example, it allows you to easily create undercuts or relief grooves, while CNC milling machines require specialized cutting tools to achieve this.
Allows for a variety of processes
CNC lathes allow you to perform operations such as taper turning, knurling, threading, and cut-off. This subtractive manufacturing process is particularly suitable for rapid prototyping and low-volume production.
Automated and cost-effective
CNC lathes are highly automated, providing efficient products that can reduce labor; CNC turning is highly scalable, which makes the process suitable for both low-volume and high-volume production without much cost.
Wstitanium CNC Turning Capabilities
At Wstitanium, we provide high precision CNC turned titanium parts services to customers in a wide range of industries including aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics and more. We use the latest multi-axis lathes to manufacture complex cylindrical components, producing titanium parts with tolerances up to +/-0.002mm and diameters up to 16.9685 inches (431mm).
- Invest in advanced CNC lathes
We invest in precision CNC lathes such as HAAS ST20 from the United States, Doosan from South Korea, and NEF400 from Germany to meet precise specifications. This ensures high precision and high efficiency in manufacturing of titanium parts, and enables the conversion of single prototypes into mass production quickly, efficiently, and economically.
- Other Value-Added Services
Wstitanium goes to great lengths to provide additional custom manufacturing services to our diverse customers, including secondary processing and surface treatment capabilities. Examples include EDM, wire cutting, anodizing, powder coating, passivation, plating, heat treatment, and final product assembly.
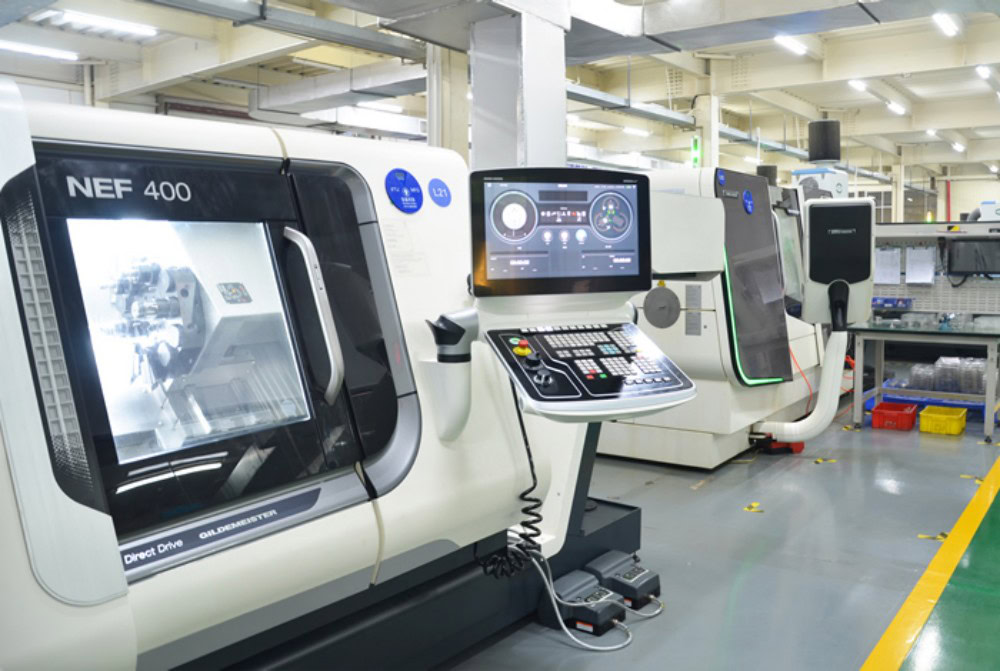
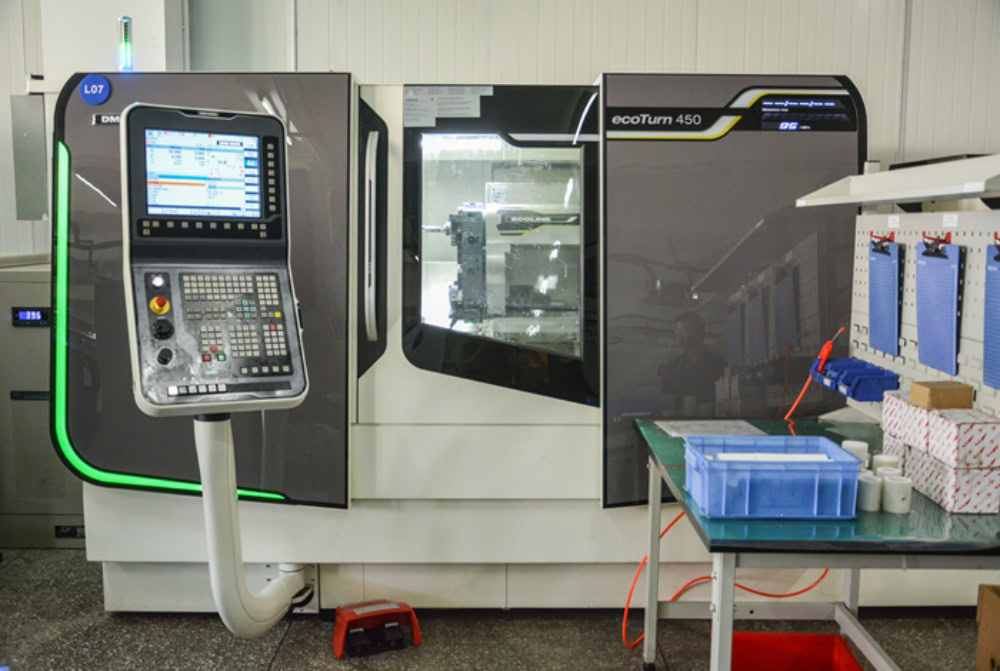
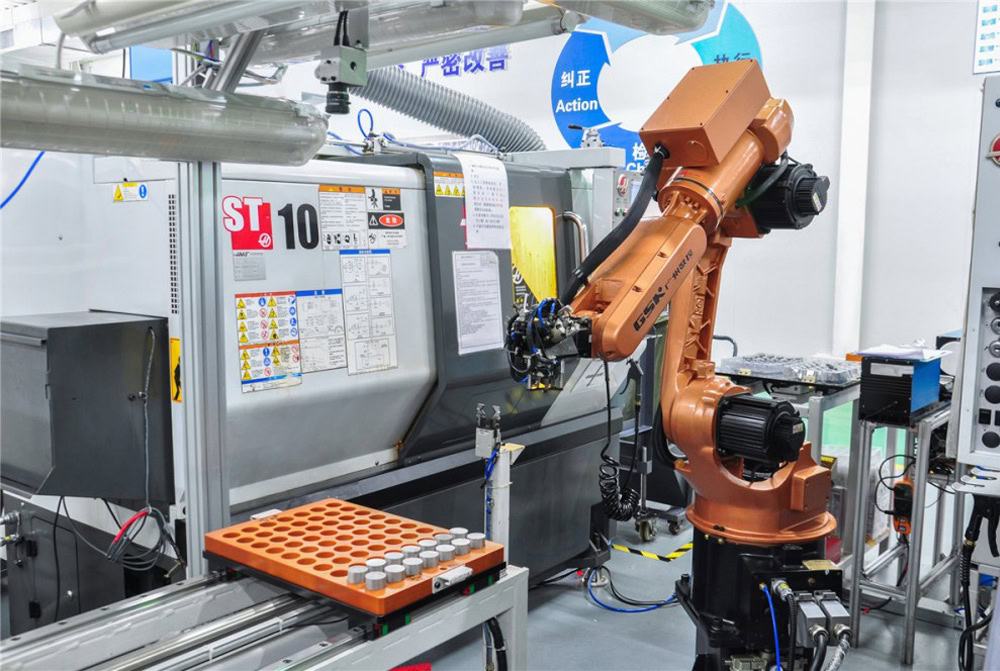





- Experienced Technical Team
Wstitanium’s experienced technical team specializes in manufacturing high-precision titanium prototypes and end-use titanium products for industries with stringent quality standards and tight tolerance requirements.
- Excellent Customer Support
Wstitanium is committed to fully meeting your unique needs by continuously improving CNC turning operations and learning new industry technologies. It is a wise choice to entrust your titanium parts to Wstitanium.
CNC Turning Operations
CNC turning has a wide range of processing, and can create various types of rotating surfaces, such as external turning, internal turning, taper turning, parting, end facing, boring, reaming, drilling, knurling, threading, grooving, etc.
- OD and ID Turning – used to create parts with precise cylindrical features that can continue further machining with visible tool marks.
- Parting and Grooving – used to part off or cut a “groove” profile on the inside or outside of a part.
- Facing – flattening the surface of a workpiece.
- Boring and Reaming – enlarging or finishing an existing hole to a high-precision diameter.
- Drilling – removing material to drill a hole from the inside of a workpiece.
- Threading – turning to create threads, which can be done on the inside or outside of a workpiece.
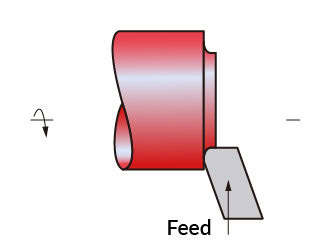
Facing
Facing is a process used for turning flat surfaces that are perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the workpiece. In this process, the facing tool is fed perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the part.
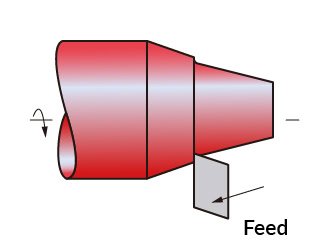
Taper Turning
Taper turning refers to gradually reducing the diameter of a cylindrical material to give the part a conical or tapered shape. The cutting tool can cut the workpiece into the desired angle shape.
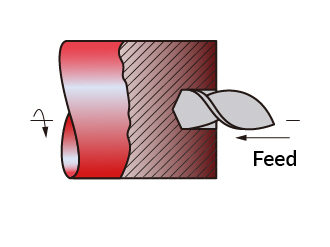
Drilling
CNC drilling refers to the process of drilling holes in parts using computer numerical control (CNC). High precision, accuracy and consistency.
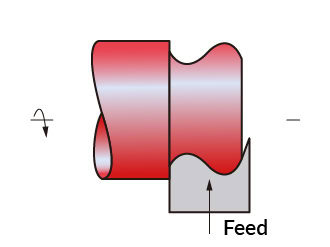
Form Turning
Form turning is used to give any irregular shape on the workpiece using specially ground tools. The tool has a cutting edge that conforms to the desired shape.
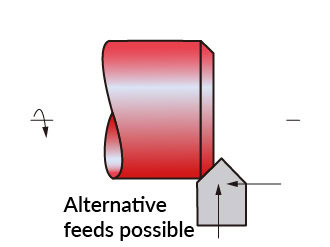
Chamfering
Chamfering is the process of cutting a sharp edge at a 45 degree angle (this is the most common angle, but not the only one).To eliminate sharp edges.
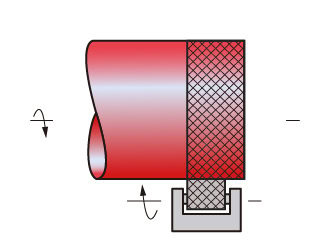
Knurling
Knurling is a manufacturing process that forms straight lines, diamonds or raised ridge patterns on titanium parts through plastic deformation.
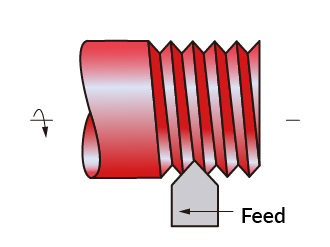
Threading
Threading is used to create external and internal threads of various diameters. Including right-hand and left-hand, male and female threads.
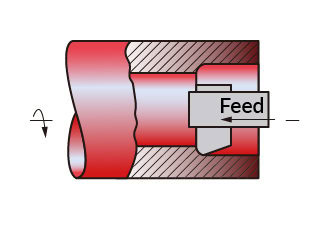
Boring
CNC boring is the process of enlarging an already drilled or cast hole to a specific diameter. Generally, CNC boring is more accurate than CNC drilling.
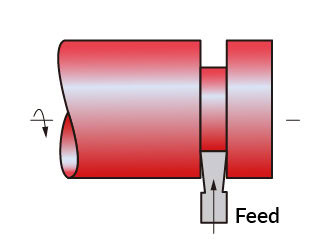
Cutoff
Cutoff is the operation of cutting a groove in a workpiece using a carbide tool. In the grooving operation, the principle is the same, but the cut is shallower.
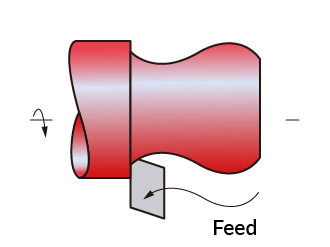
Contour Turning
Contour Turning is the process of creating irregular contours for titanium parts. The cutting tool moves along a predefined contour path, creating the contour shape.
Specifications for CNC Turned Titanium Parts
| US | Metric | |
Maximum Dimensions | Diameter | 17 in. | 431 mm |
Length | 39 in. | 990 mm | |
Minimum Dimensions | Diameter | 0.16 in. | 4.07mm |
Length | 0.05 in. | 1.27mm | |
Wall Thickness | 0.020 in. | 0.51mm | |
Angle | 30° | 30° | |
Tolerances | +/- 0.005 in. | +/- 0.13mm | |
Maximum spindle through-hole | 1.5 in | 40 mm | |
CNC turning design guidelines
Considering effective dimensional planning and reasonable dimensional design in the design is the basis for ensuring the fit and accuracy of CNC titanium parts. The following will introduce some key CNC turning design dimensional guidelines and best practices to achieve the best results in the CNC manufacturing process.
Feature | Recommended size | Feasible size |
Min. feature size | Ø 2.5 mm | Ø 0.50 mm |
Internal edges | R 8 mm | R 0.25 mm |
Minimum wall thickness | 0.6 mm | 0.5 mm |
Holes | Diameter: standard drill bit sizes | Diameter: Ø 0.5 Depth: 10 x diameter |
Threads | Size: M6 or larger Length: 3 x diameter | Size: M2 |
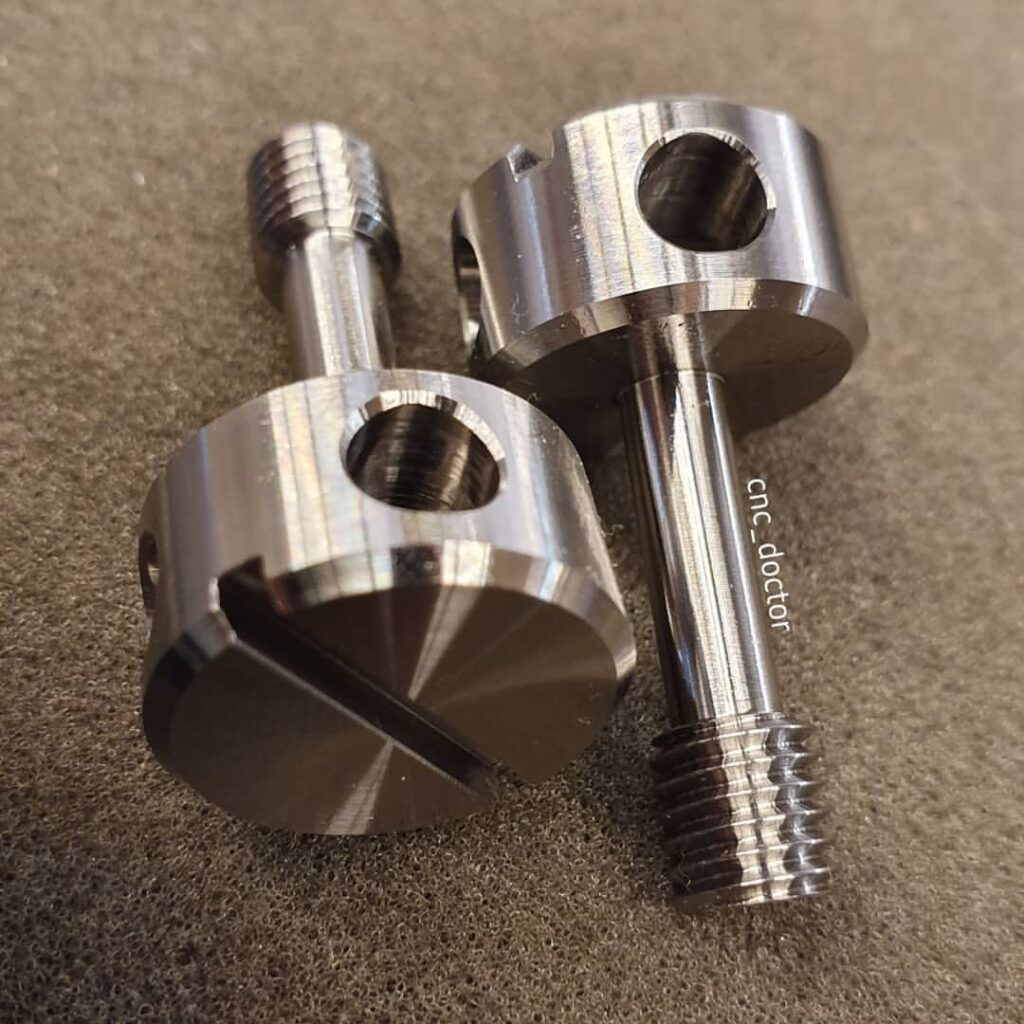
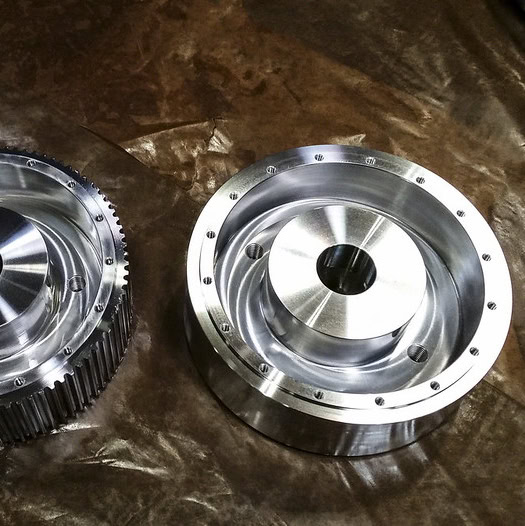
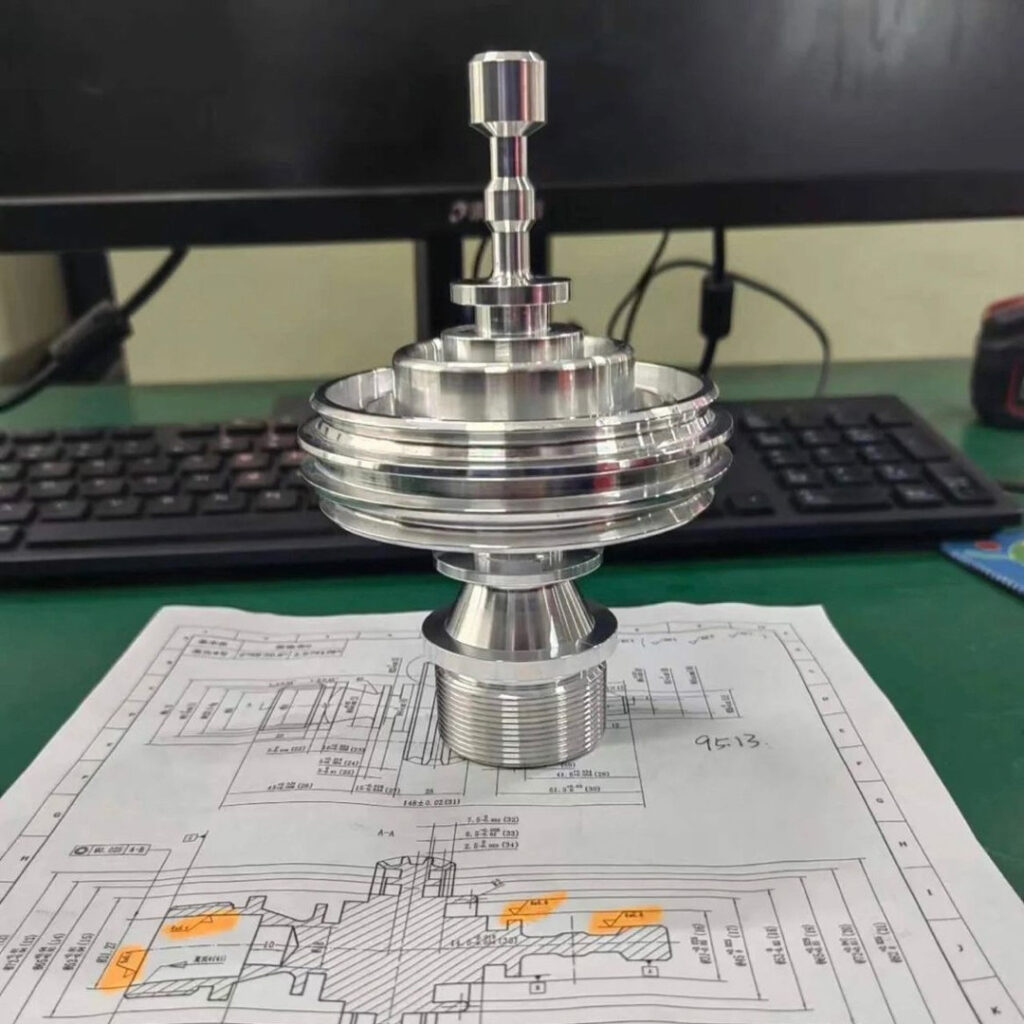
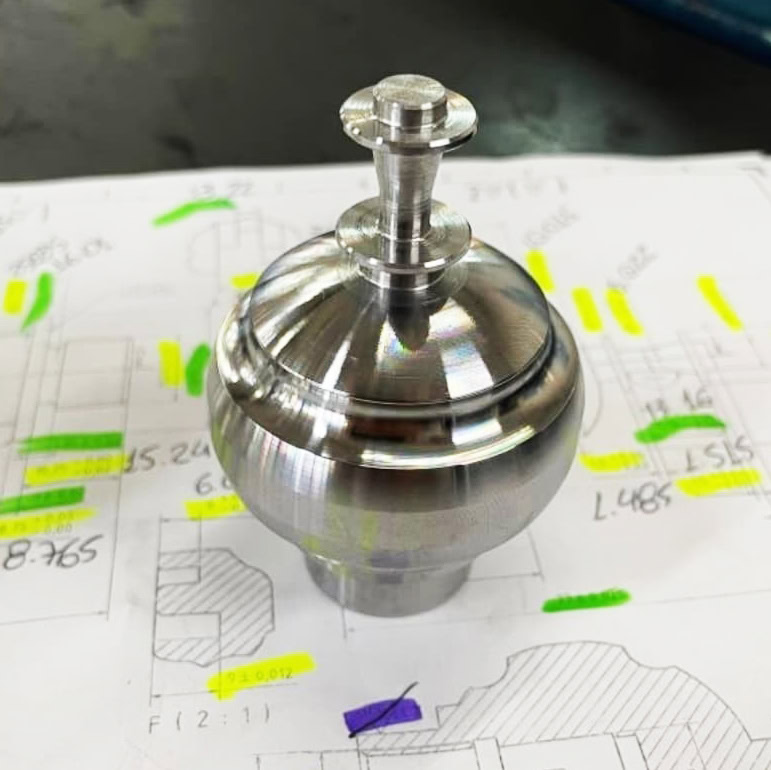
CNC Turned Titanium Parts Gallery





