Reliable ICCP Anode Supplier & Manufacturer In China
As an efficient anti-corrosion solution, impressed current cathodic protection system has been widely used in many fields. With its profound accumulation in materials science and electrochemistry, Wstitanium is committed to manufacturing high-quality, high-performance ICCP anodes to provide reliable corrosion protection solutions for customers around the world.
- Mixed Metal Oxide Anode
- Platinum Coated Anode
- Ferrosilicon Anode
- Graphite Anode
- ICCP Tube Anode
- ICCP Strip Anode
- ICCP Rod Anode
- ICCP Disk Anode
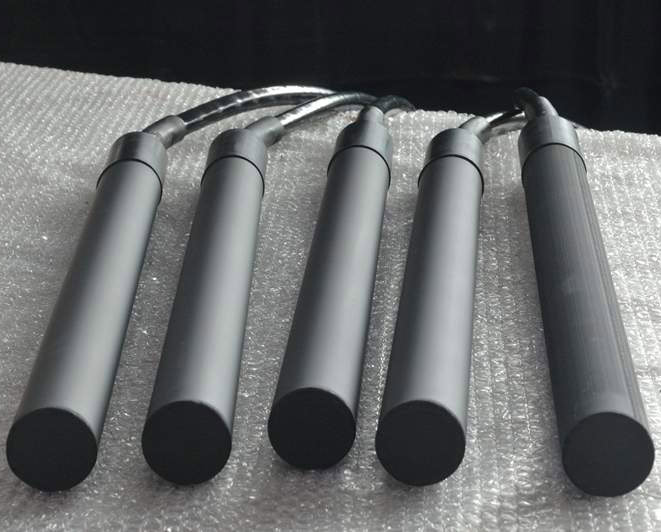

Your One-Stop ICCP Anodes Partner-Wstitanium
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) system plays a vital role in preventing corrosion of metal structures and is widely used in marine engineering, port facilities, ships, bridge foundations and other fields. Wstitanium will be your reliable partner in the field of ICCP anode manufacturing with advanced technology, strict quality control and rich practical experience.
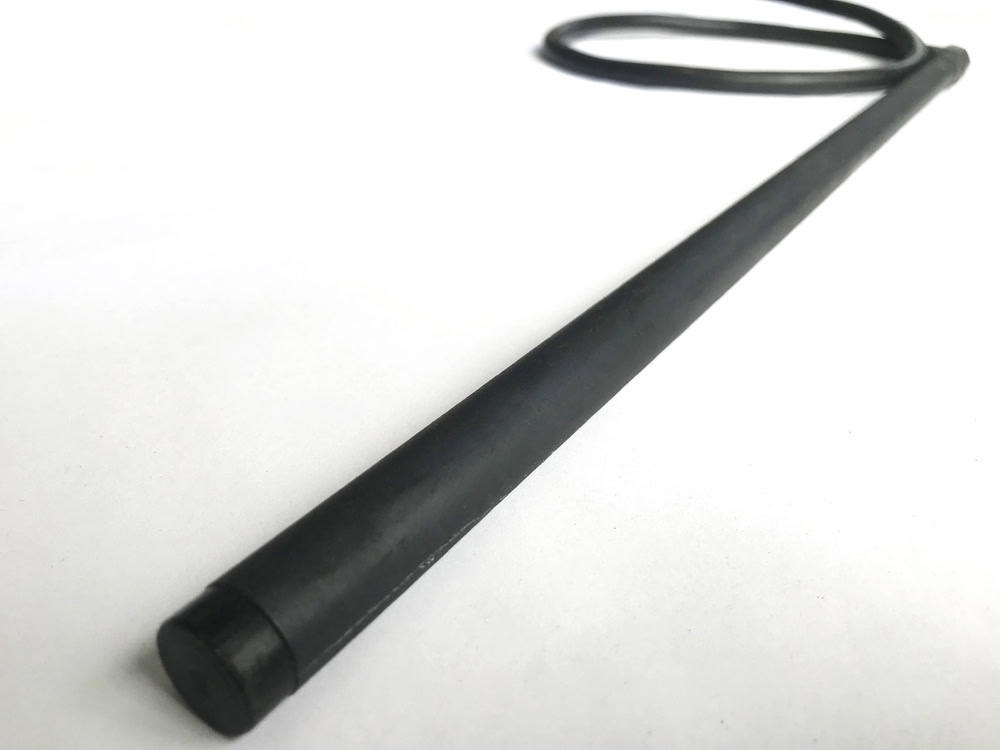

Mixed Metal Oxide Anode
A mixture of ruthenium, iridium, titanium and other oxides is coated on the titanium surface. It is light in weight and highly corrosion-resistant, suitable for soil, fresh water and seawater environments. It is used in deep well beds, offshore platforms, and reinforced concrete structures.
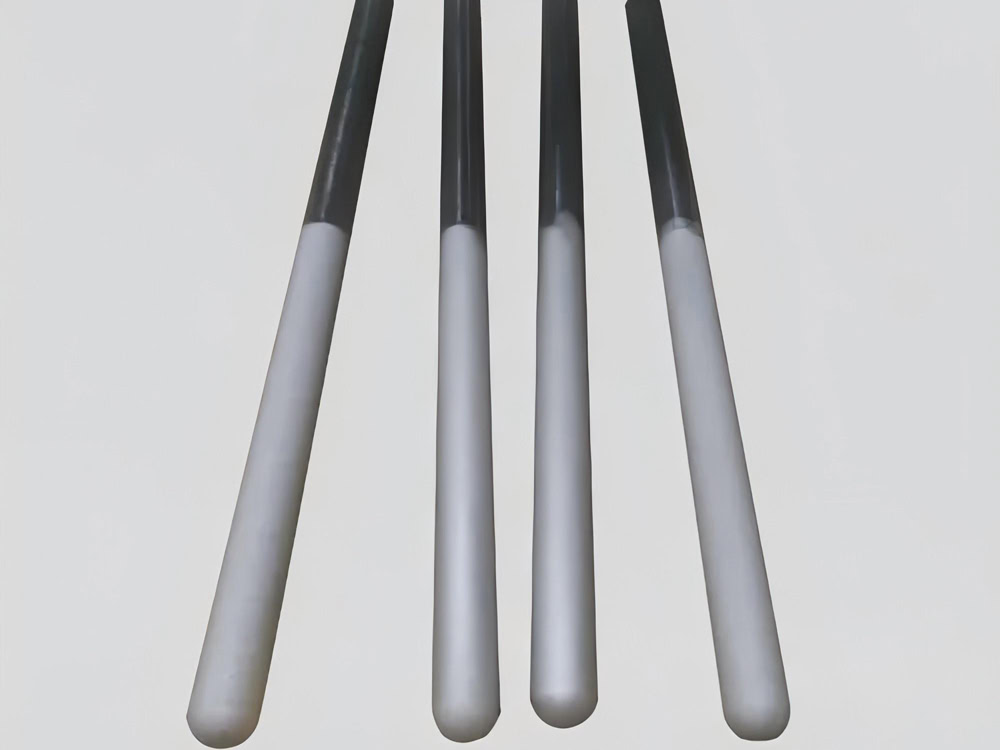

Platinum Coated Anode
With titanium, niobium or tantalum as the substrate, a layer of platinum (usually 0.1~20μm thick) is coated on the surface of the substrate by electrodeposition or thermal decomposition. It has high conductivity and corrosion resistance, and is stable in fresh water, sea water and soil environments.
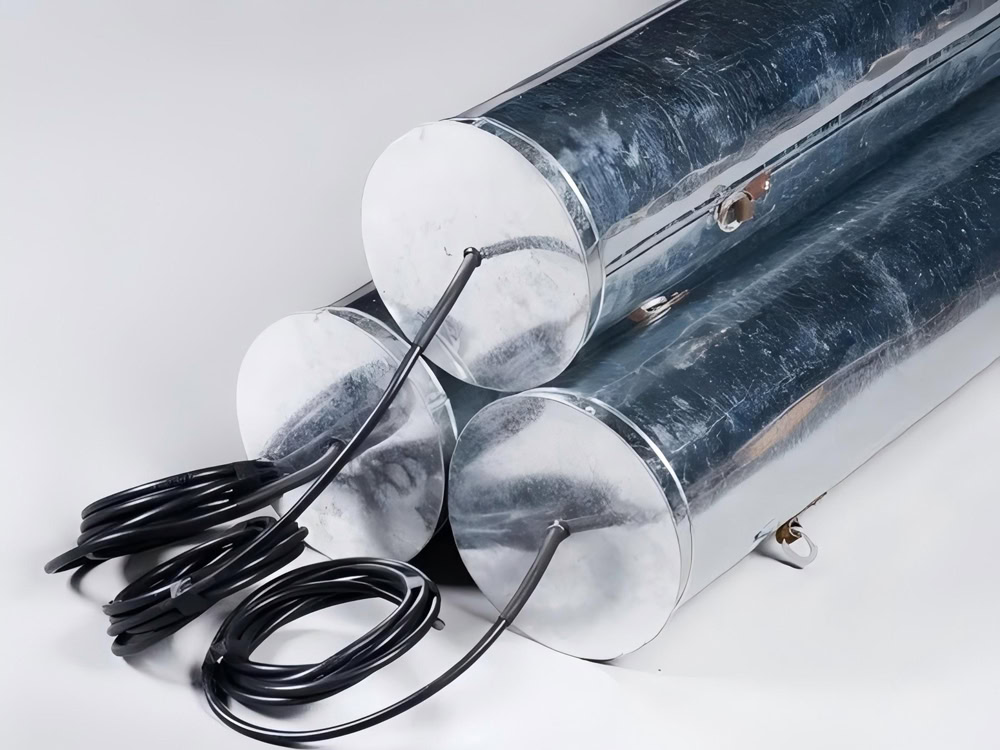

Ferrosilicon Anode
High silicon cast iron anode is cast iron with a silicon content of 14~17%, with some elements such as chromium and molybdenum added. It has good conductivity and strong corrosion resistance, and is suitable for high resistivity soils. It is used in deep wells and long-distance pipelines.
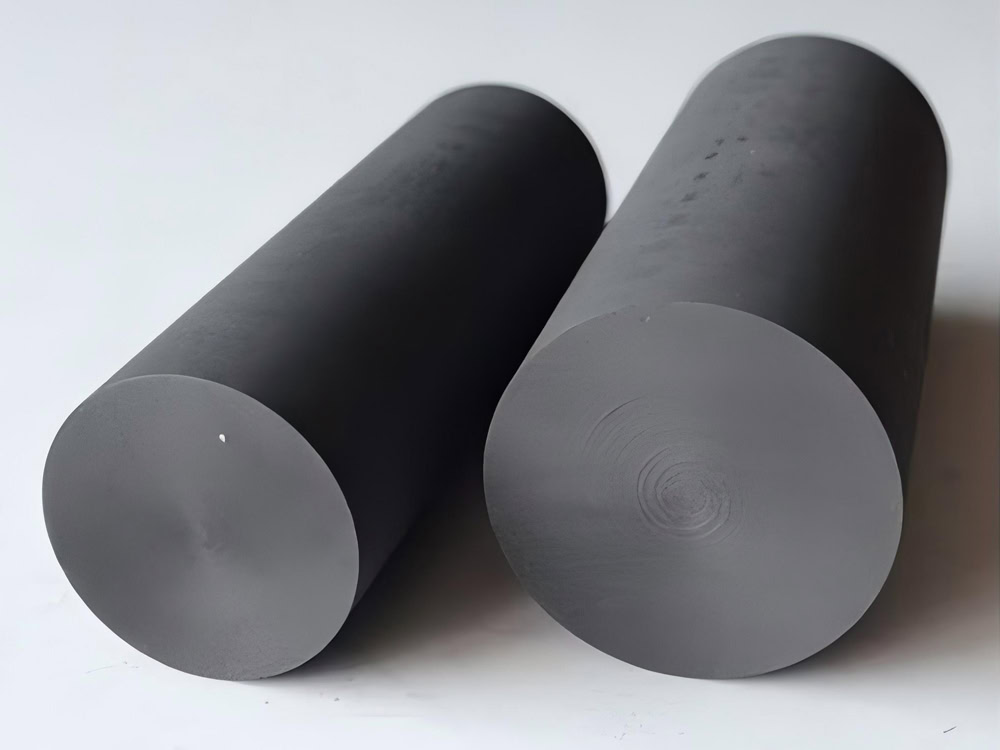

Graphite Anode
Graphite anode has good conductivity and is resistant to acidic environments, but it is easy to become brittle. It has a high consumption rate and requires regular maintenance. It is gradually being replaced by MMO anodes.
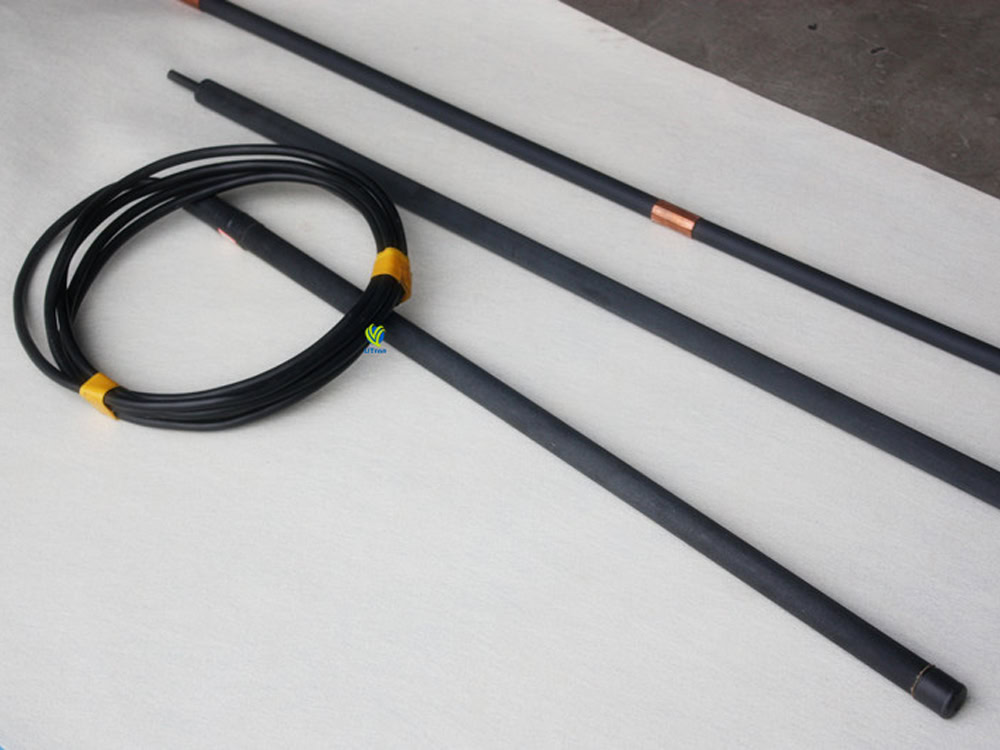

Customized ICCP Anode
Metal oxide coating, platinum iridium ruthenium, has both corrosion resistance and good conductivity, and has plate, tubular, strip, etc. It is used for corrosion protection in ships, offshore platforms, chemical industries and other fields.
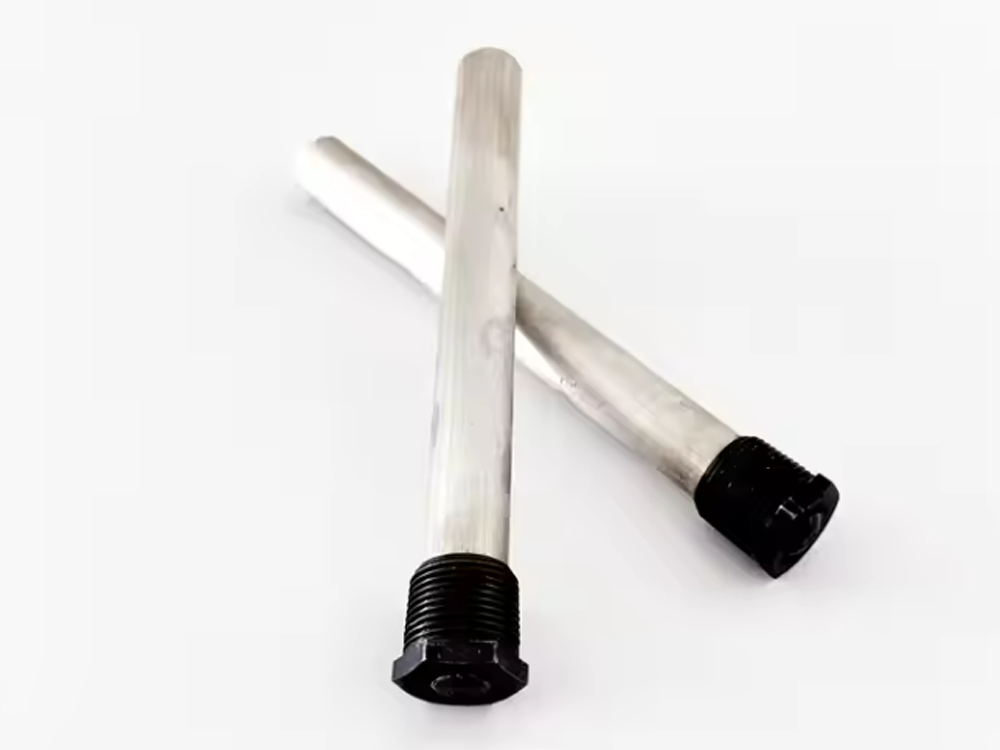

Power Water Heater Anode
ICCP electric water heater anodes are efficient and actively protect the inner tank. The current output can be flexibly adjusted to adapt to different water qualities. It is environmentally friendly and energy-saving, and does not produce harmful substances.
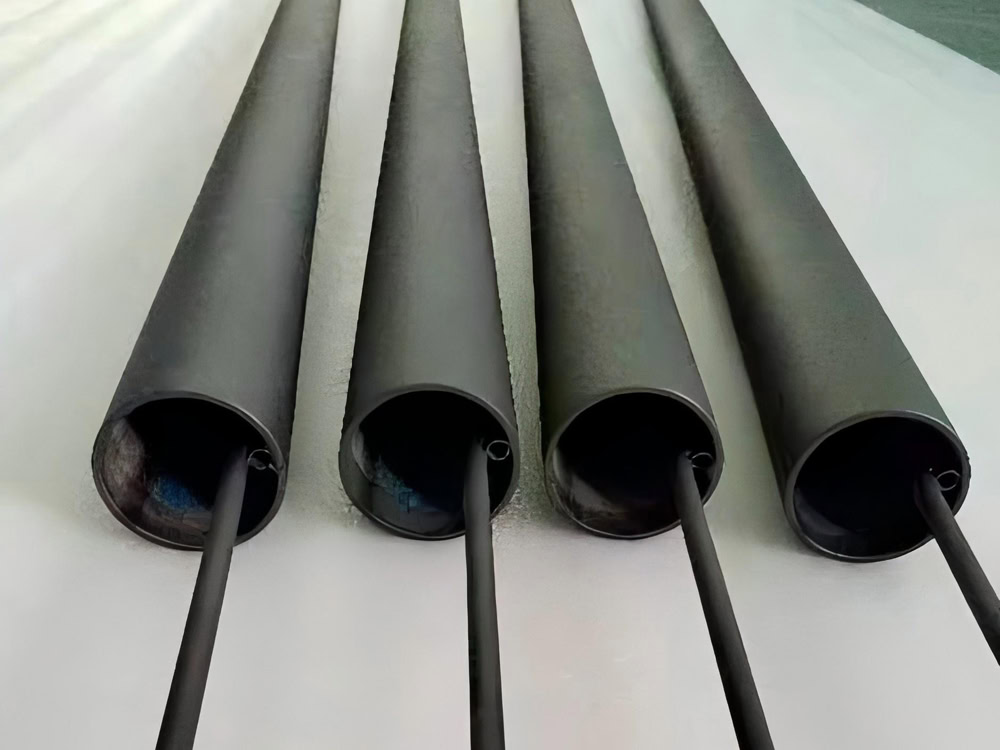

ICCP Tube Anode
ICCP tubular anodes output protection current uniformly and efficiently. The materials are mostly corrosion-resistant titanium-based coated with ruthenium-iridium-platinum oxide. Used for cathodic protection of ships, large water storage tanks, etc.
ICCP Strip Anode
ICCP strip anodes have good flexibility and can flexibly fit the surface of complex structures to achieve all-round and precise protection. Lightweight and easy to install, suitable for cathodic protection scenarios such as oil and gas pipelines and ships.
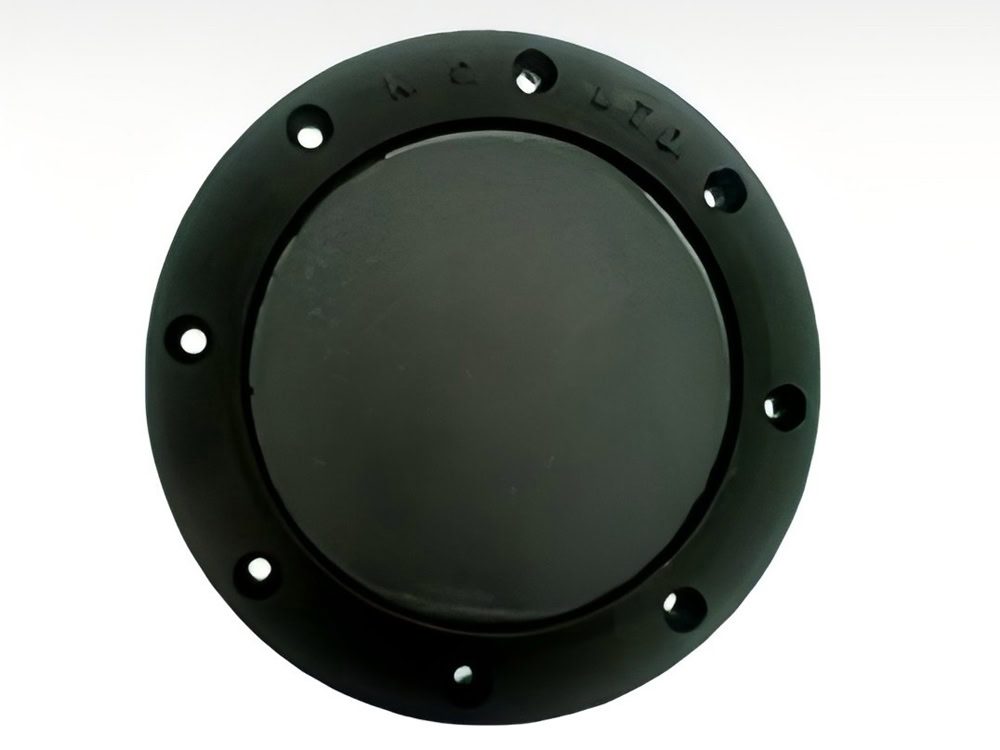

ICCP Disk Anode
ICCP disc anodes have a compact structure and release protection current uniformly and densely, providing efficient protection for specific areas. It is often used in cathodic protection scenarios of small storage tanks and special structures.
Working Principle of ICCP Anode System
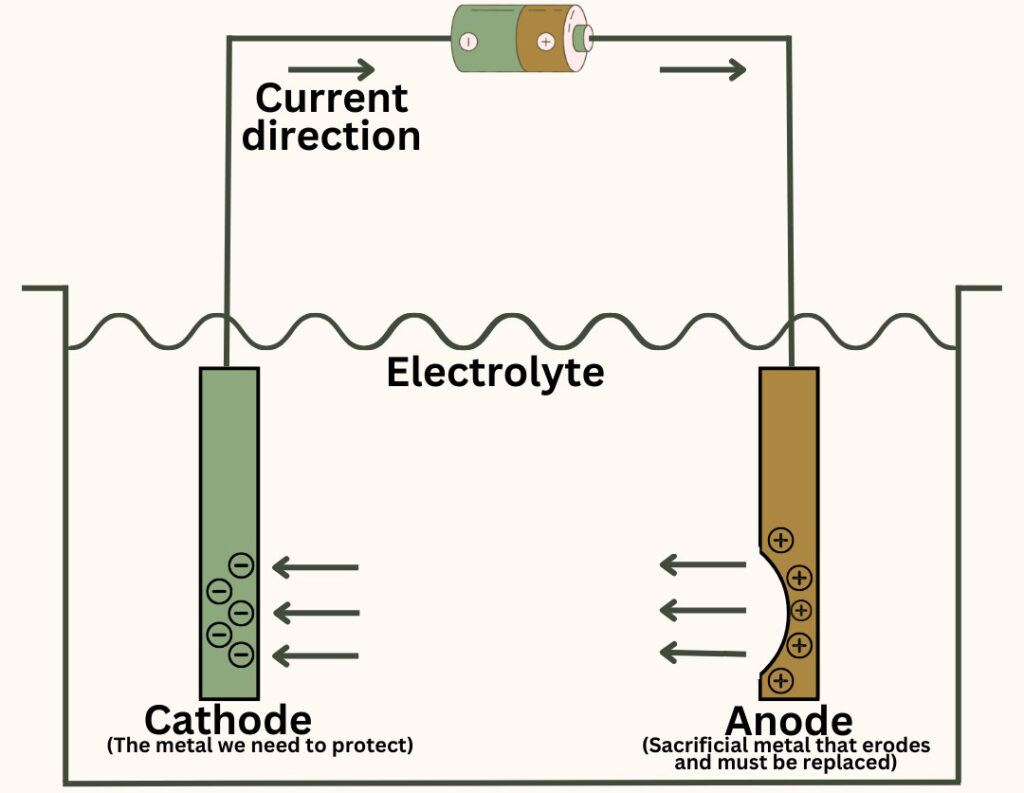
ICCP anode system is mainly composed of a DC power supply, anode, cathode (protected metal structure), reference electrode and connecting cable. The DC power supply provides external current, which flows from the anode, passes through the electrolyte (such as seawater, soil, etc.), and flows to the protected cathode metal. In this process, the anode undergoes an oxidation reaction, consuming its own material (soluble anode) or causing the ions in the electrolyte to undergo an oxidation reaction (insoluble anode), while the cathode metal surface undergoes a reduction reaction, mainly the reduction of oxygen (in a neutral or alkaline aerobic environment) or the reduction of hydrogen ions (in an acidic environment). The reference electrode is used to monitor the potential of the protected metal in real time, provide a basis for adjusting the DC power supply output, and ensure that the protected metal is always within the effective protection potential range.
Comparison of Different ICCP Anodes
Common ICCP anodes include steel anodes based on metal materials, high silicon cast iron anodes, mixed metal oxide (MMO) anodes with special coating technology, platinum-coated anodes, and graphite anodes made of non-metallic materials. Steel anodes are low in cost and can provide a large current output in the early stage, but they are consumed quickly. High silicon cast iron anodes rely on their good corrosion resistance and relatively low consumption rate. MMO anodes utilize mixed metal oxide coatings on titanium substrates to provide efficient current distribution and corrosion resistance. Although platinum-coated anodes are expensive, they have extremely high stability and extremely low consumption rates. Graphite anodes play a role in specific environments due to their good conductivity and acid resistance.
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Applications |
| MMO Anode | Highly corrosion – resistant, uniform current distribution | Coating may peel off in high – temperature environments | Offshore platforms, concrete structures |
| Platinum – coated Anode | High stability, low consumption rate | High cost | Ships, water treatment facilities |
| Flexible Anode | Strong adaptability, flexible installation | Long – term stability is slightly inferior to rigid anodes | Complex pipe networks, storage tanks |
| Silicon – iron Anode | Resistant to high – resistivity soil, low cost | Heavy weight, requires regular maintenance | Deep well ground beds, long – distance pipelines |
| Graphite Anode | Good electrical conductivity, resistant to acidic environments | Prone to embrittlement, high consumption rate | Early cathodic protection systems |
Advantages of ICCP anode
ICCP anodes have an indispensable position in the field of modern industrial corrosion protection due to their advantages such as high efficiency protection, long life, high adaptability, flexible adjustment, environmental sustainability and significant economic benefits.
- Powerful Current Output Capability
ICCP anode is connected to an external DC power supply to output a stable and powerful current. For example, in large ships, the large metal shell has a large area and a high risk of corrosion. The ICCP anode can provide sufficient current to ensure that the entire hull surface can obtain enough electrons, effectively inhibiting the oxidation corrosion of the metal.
- Precise Protection Range Control
For the complex structure of the piers of the cross-sea bridge, which are immersed in seawater for a long time and partially exposed to the atmosphere, the current distribution can be accurately adjusted for different corrosion environment areas to enhance the protection of the underwater parts that are prone to corrosion.
- High-Quality Materials
ICCP anodes are mostly made of high-performance materials such as titanium-based platinum plating and mixed metal oxides. They have excellent corrosion resistance and can remain stable for a long time in harsh environments, such as marine\chemical high acid and alkali environments.
- Environmentally Friendly
ICCP anodes do not use or rarely use substances that are harmful to the environment. During its operation, it will not release toxic and harmful heavy metal ions into the surrounding environment, and will not pollute the soil, water and atmosphere, which is in line with modern environmental protection concepts.
- Improve Efficiency
For industrial production equipment, such as chemical reactors, oil storage tanks, etc., the effective protection of ICCP anodes ensures stable operation of the equipment, reduces equipment failures and downtime caused by corrosion, ensures production continuity, and thus improves efficiency.
- Compatible With Variety Of Metals
Applied to metal structures of different materials such as steel, aluminum, and copper for corrosion protection. In the aerospace field, ICCP anodes prevent key aluminum parts from being corroded under complex climatic conditions. Some key steel parts in cruise ships can also benefit from ICCP anodes.
Shaps of ICCP Anodes
Each ICCP anode shape has its own unique characteristics and application scenarios, including tubular, strip, can, mesh, rod, flexible and hull anodes. Each form provides targeted anti-corrosion protection, and users can choose the most suitable solution according to the specific needs of the project. In practical applications, it is necessary to comprehensively consider environmental factors, the characteristics of the protected metal structure, economic costs and system performance requirements, and reasonably select the ICCP anode type to achieve the best cathodic protection effect.
ICCP MMO Tubular Anode
ICCP MMO tubular anodes are based on titanium tubes coated with mixed metal oxide (MMO) coatings, such as mixtures of metal oxides such as ruthenium, iridium, and platinum. These coatings have excellent electrochemical catalytic activity and chemical stability.
Features: high current output capability, uniform current distribution, strong corrosion resistance, and high mechanical strength.
Applications: Tubular anodes are ideal for protecting critical infrastructure such as oil and gas pipelines, communication cables, drainage systems, water tanks, and marine structures.

ICCP MMO Strip Anode
ICCP MMO Strip Anode is a flat strip structure, usually with titanium strip as the base and MMO coating on the surface. Its working principle is the same as ICCP MMO tubular anode.
Features: good flexibility, uniform current distribution, easy installation, and meet diverse engineering requirements.
Application: Closely fit the complex structures in the fields of ships, chemical equipment, buildings, etc., and effectively resist corrosion
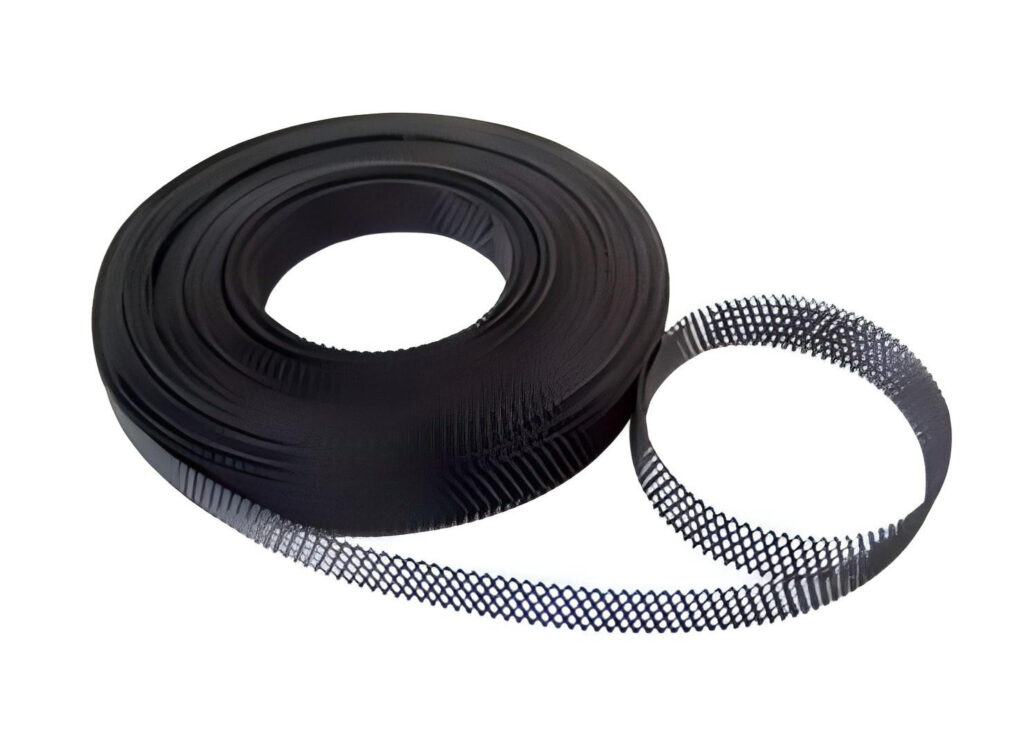

ICCP MMO Canned Anode
ICCP MMO Canned Anode is a structural form that encapsulates MMO anode material in a special can. The can is usually made of corrosion-resistant materials such as plastic, fiberglass, etc., filled with MMO anode blocks or anode cores, and surrounded by conductive media such as coke, graphite powder, etc.
Features: The can protects the internal MMO anode, reduces the direct contact between the anode and the external environment, reduces the risk of mechanical damage and chemical corrosion to the anode, and thus improves the stability and service life of the anode.
Application: Canned anodes are very suitable for protecting oil and gas pipelines, communication systems, drainage systems, water tanks and marine structures.

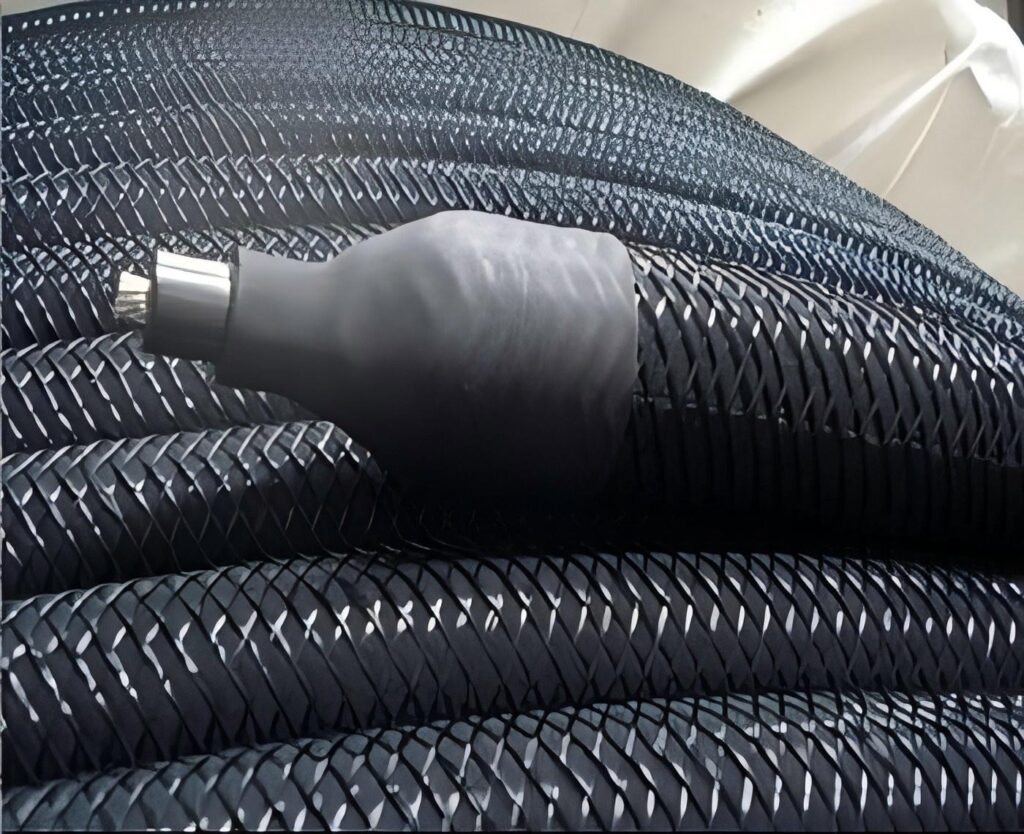
MMO Flexible Anode
MMO flexible anode is a new type of ICCP anode, which is based on a flexible conductive core, usually a copper core or copper-plated steel core, and is coated or wrapped with a layer of electrochemically active MMO material. This structure makes the anode both flexible and highly efficient in electrochemical performance.
Features: Uniform current distribution, strong anti-interference ability, bends and winds like a cable, and can adapt to various complex terrains and structural shapes, such as pipelines crossing mountainous areas, industrial pipeline systems with complex bends, etc.
Application: Flexible anodes are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines, drainage systems, and marine structures. Their flexibility and adaptability make them suitable for installation in harsh environments.

ICCP Hull Anode
ICCP hull anode is specially designed for ships. The core is still based on MMO technology, with corrosion-resistant metal as the base and MMO coating.
Features: Adapt to complex hull surfaces, resist seawater scouring and corrosion, low magnetic interference characteristics, and adapt to ship navigation conditions.
Application: ICCP hull anodes are widely used in container ships, tankers, bulk carriers, etc. in the marine industry. They are also effective in protecting other underwater structures, such as submarine pipelines and buoys, from seawater corrosion.
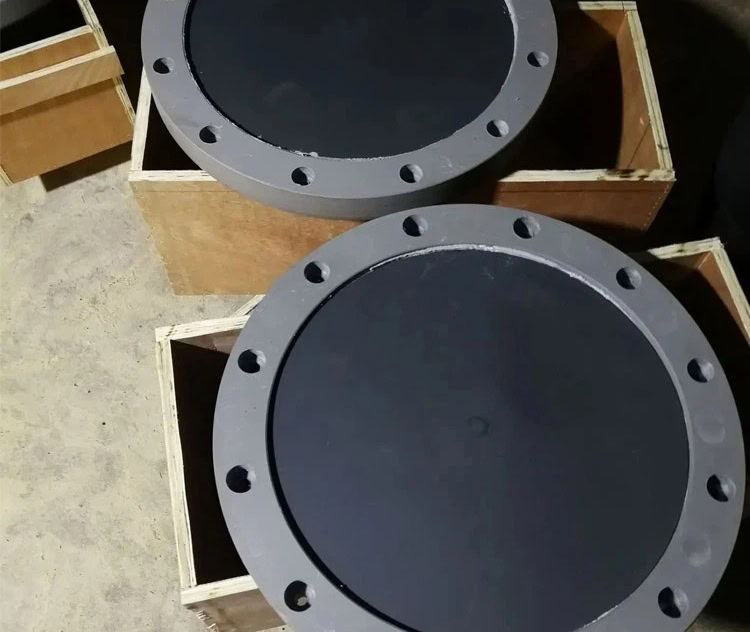

Customized ICCP Anodes: For Optimal Cathodic Protection
Customizing ICCP anodes is a complex and systematic project, involving multiple links such as evaluation, type selection, design and manufacturing, installation and commissioning, maintenance and management. It is also necessary to fully consider the characteristics of the protected object, the service environment, budget and other factors, and comprehensively apply knowledge of materials science, electrochemistry, engineering design, etc. to ensure that the customized anode can meet the requirements of efficient and reliable cathodic protection. Through strict quality control and scientific maintenance management, the service life of the anode can be extended, the operating cost of the system can be reduced, and a strong guarantee can be provided for the long-term safe operation of metal structures.
Anode Size Design
The size of the anode mainly includes length, diameter (or thickness), etc., which needs to be determined according to factors such as the required protection current, the current output capacity of the anode, and the service life. Generally speaking, the larger the surface area of the anode, the greater the protection current it can provide. The surface area of the anode can be determined by calculating the total protection current required for the protected object and combining the current density parameter (current output capacity per unit area) of the selected anode material. For example, if the protection current required for an underground pipeline is 10A, and the recommended current density of the selected high-silicon cast iron anode is 0.1A/dm², the required surface area of the anode is 100dm².
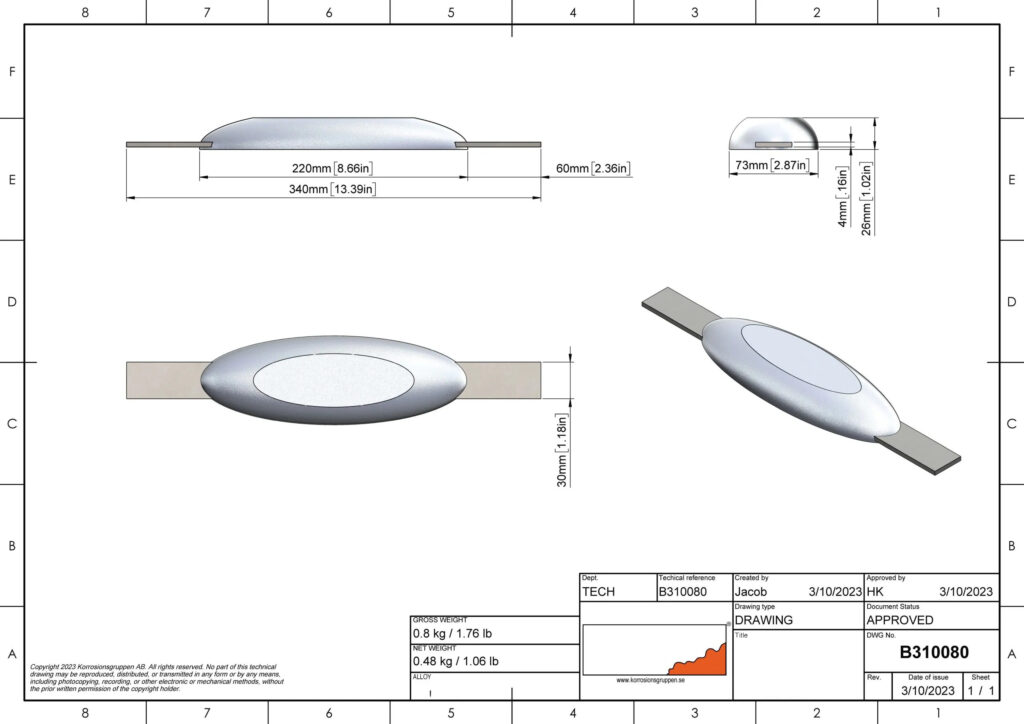
Anode Shape Design
The shape of the anode should be designed according to the structural shape and installation space of the protected object. Common anode shapes include tubular, rod, strip, disc, flat plate, etc. Tubular anodes are suitable for long-distance pipeline protection. Strip anodes have good flexibility and can fit tightly to metal surfaces of complex shapes, such as the hull of a ship, the inner wall of a storage tank, etc. Disc anodes are often used for centralized protection of small equipment or specific areas. Flat anodes are suitable for large-area flat structures, such as the deck of an offshore platform, concrete foundation, etc. When designing the shape of the anode, the uniformity of the current distribution must also be considered to avoid the situation where the local current is too large or too small. For example, for flat anodes, special current distribution auxiliary structures, such as a grid-like conductive layer, can be set on the surface of the anode to improve the current distribution.
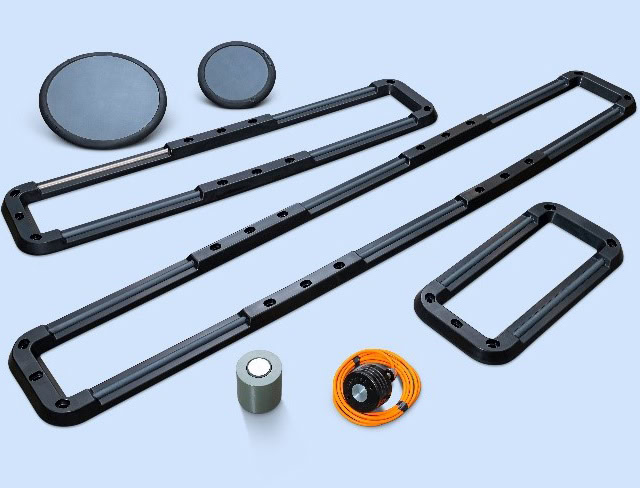

Steel anodes are usually manufactured by casting or forging processes. The steel raw materials are first melted and poured into a mold for molding, and then processed and surface treated. The manufacturing process of high-silicon cast iron anodes is relatively complicated. High-silicon ferroalloys need to be smelted and cast, and then mechanically processed and heat treated to improve their performance. Graphite anodes are generally made by pressing and sintering graphite powder or graphite blocks. The key to the manufacture of MMO anodes lies in the preparation of coatings. Commonly used methods include thermal decomposition and electrochemical deposition. First, one or more layers of mixed metal oxide precursor solution are coated on the surface of the metal substrate, and then heated or electrochemically treated to convert it into a catalytically active oxide coating. The manufacture of platinum-coated anodes mainly adopts electroplating or chemical plating methods to plate a uniform platinum coating on the surface of the metal substrate.
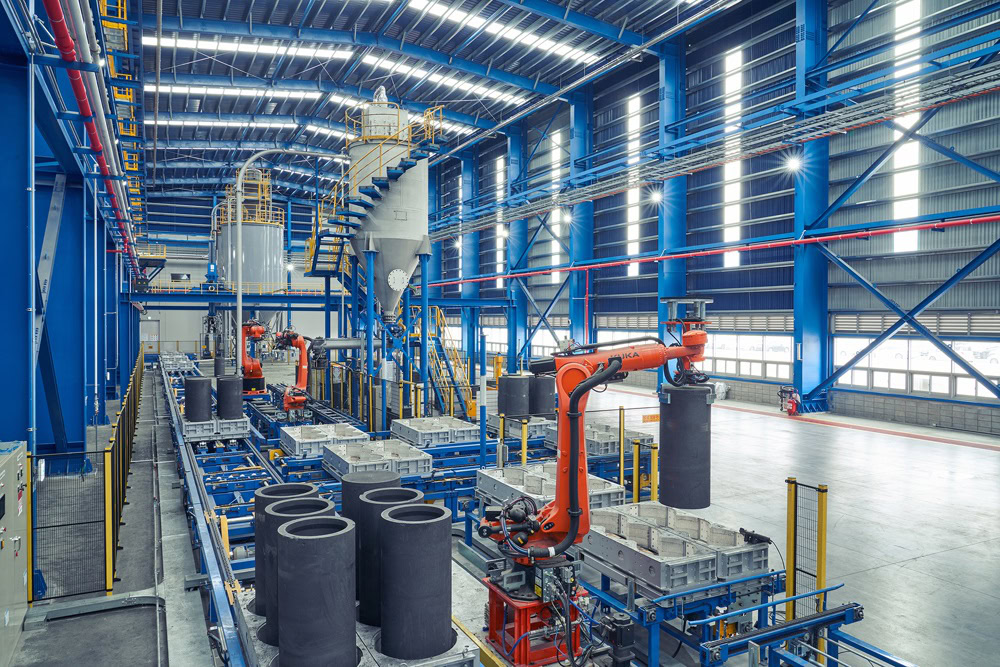

Quality Inspection
In the quality inspection of raw materials, chemical composition analysis, metallographic structure analysis, mechanical property testing, etc. of metal materials are carried out to test whether their composition, organizational structure and mechanical properties meet the requirements. For coating materials, such as mixed metal oxide precursor solutions, platinum salt solutions, etc., their purity, concentration and chemical composition can be tested by chemical analysis, spectral analysis and other methods. After the anode is manufactured, the inspection items include appearance inspection, size measurement, conductivity test, corrosion resistance test, current output performance test, etc.

Cost of ICCP Anode
The cost of ICCP anodes covers many aspects. The cost of raw materials is a key part. Materials such as titanium, which are corrosion-resistant and often used as MMO anode substrates, are relatively expensive. Niobium is even more expensive due to its scarce resources and difficulty in refining. Although steel is cheap, it has poor corrosion resistance. Among coating materials, MMO coatings composed of precious metal oxides such as ruthenium and iridium account for a large proportion of the cost due to metal price fluctuations.
Simple casting has low cost. Although extrusion, precision casting, 3D printing, etc. can achieve complex shapes and high precision, the equipment investment and processing costs are high. When preparing the coating, the thermal decomposition method has simple equipment and relatively low cost, but the coating performance is slightly inferior; the electrochemical deposition method can obtain high-quality coatings, but the cost increases due to equipment and reagent consumption.
| Manufacturing and Processing Cost | Transportation and Installation Cost | Maintenance and Replacement Cost | Overall Cost Characteristics | Cost Advantages in Applicable Scenarios |
| Relatively low, the manufacturing process is relatively simple. | Due to its high density and large weight, the transportation cost may be relatively high; the installation process is not complicated, and the installation cost is moderate. | Relatively high, with poor corrosion resistance, fast consumption rate, frequent replacement is required, and maintenance is frequent with high costs. | Low initial cost, but high overall cost in the long term. | Suitable for short-term temporary projects or environments with low protection requirements and weak corrosion, which can reduce the initial investment. |
| Relatively low, the manufacturing process is not complicated. | Lightweight, with low transportation cost; relatively simple installation, with low installation cost. | Relatively high, with low mechanical strength, easy to crack, high consumption rate, regular replacement is required, and maintenance cost is high. | Low initial cost, but relatively high cost in the long term. | Suitable for scenarios such as the cathodic protection of underground pipelines in areas with low soil resistivity and not strong corrosion, which can control the initial cost. |
| Relatively high, special casting and processing technologies are required, and the manufacturing process is complex. | Large weight, with high transportation cost; professional equipment and technology may be required during installation, with high installation cost. | Relatively low, good corrosion resistance, long service life, low consumption rate, low frequency of maintenance and replacement, and low cost. | High initial cost, but relatively low overall cost in the long term. | Suitable for projects with high requirements for anode performance and allowable installation conditions, such as large water storage tanks and petrochemical plants. It is more economical for long-term use. |
| Relatively high, the manufacturing process is complex, and the composition and thickness of the coating need to be precisely controlled. | The transportation cost varies depending on the shape and weight; the installation cost is high in some complex installation environments, such as the installation on offshore platforms. | Relatively low, with excellent performance, high current efficiency, long service life, low frequency of maintenance and replacement, and low cost. | High initial investment, but low overall cost in the long term. | Suitable for large-scale projects with strict requirements for cathodic protection effects and long-term operation, such as offshore platforms, cross-sea bridges, and urban water supply pipelines. It has a high cost-performance ratio in the long term. |
The performance, selection, installation and maintenance of impressed current cathodic protection systems are crucial to the effectiveness and stability of the entire cathodic protection system. Different types of anodes, such as soluble anodes and insoluble anodes, each have their own characteristics and applicable scenarios. In practical applications, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the characteristics of the protected structure, environmental factors, economic factors, system compatibility and other factors, select the appropriate anode type, and carry out reasonable design, installation and maintenance.