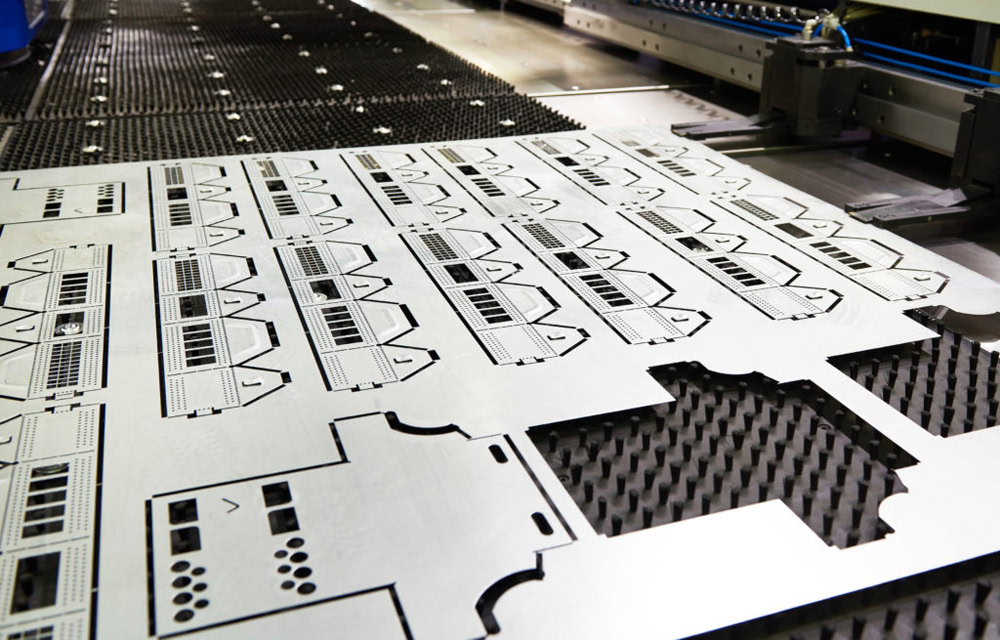
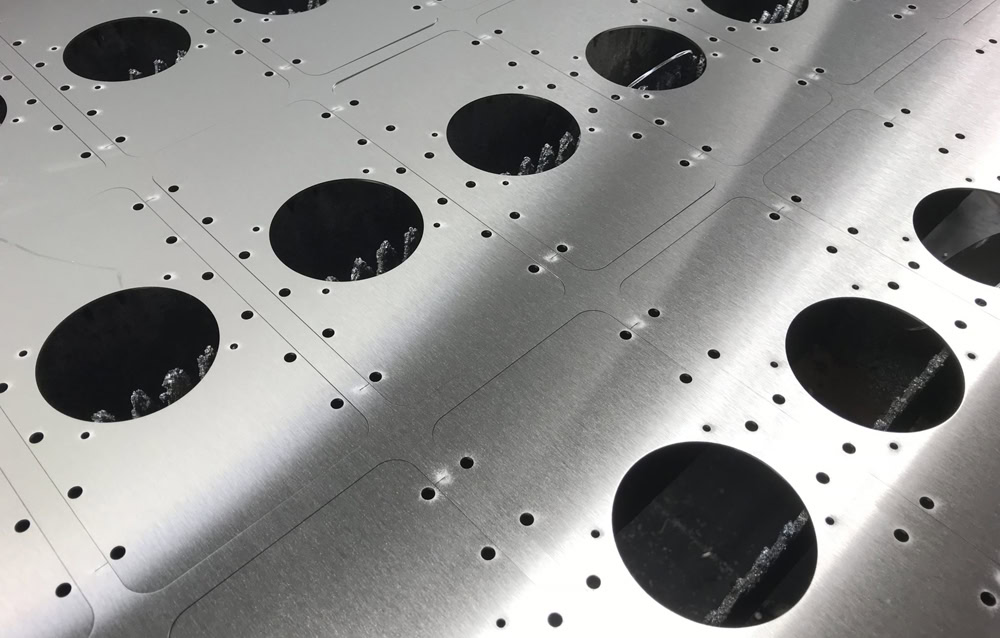
Laser Cutting for Titanium Sheet Metal Fabrication
Wstitanium is one of the leading titanium laser cutting service manufacturers in China, providing you with the best quality titanium precision cutting solutions. Investing in the most advanced laser cutting technology and machinists ensures that the final product meets demanding tolerances and precise specifications.
- ISO9001&ISO13485
- Design and DFM Support
- Tight Tolerances +/- 0.002”
- Minimum Order Quantity: 1
- Full Size Inspection Report
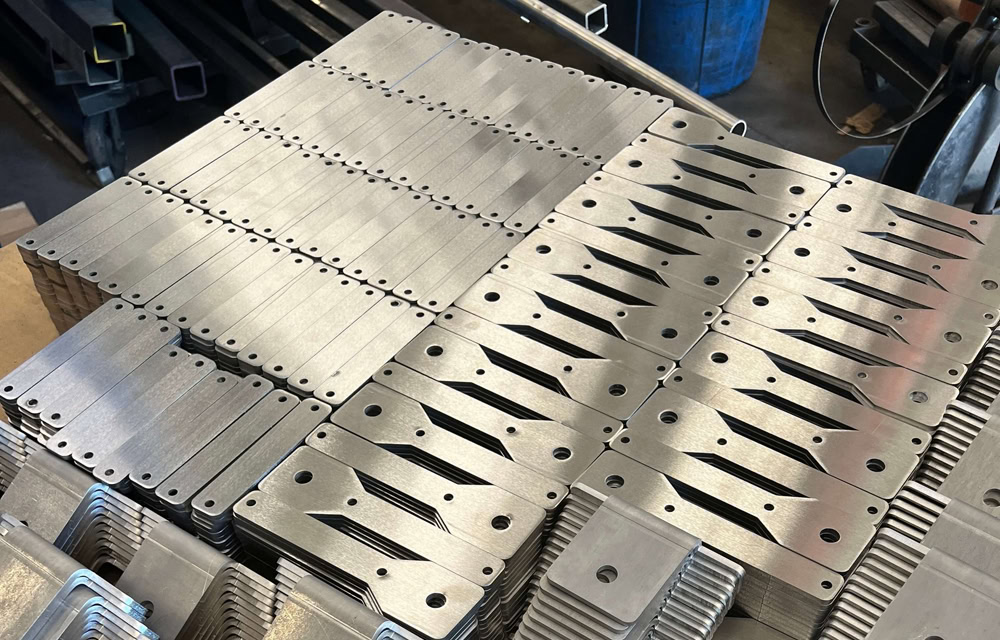
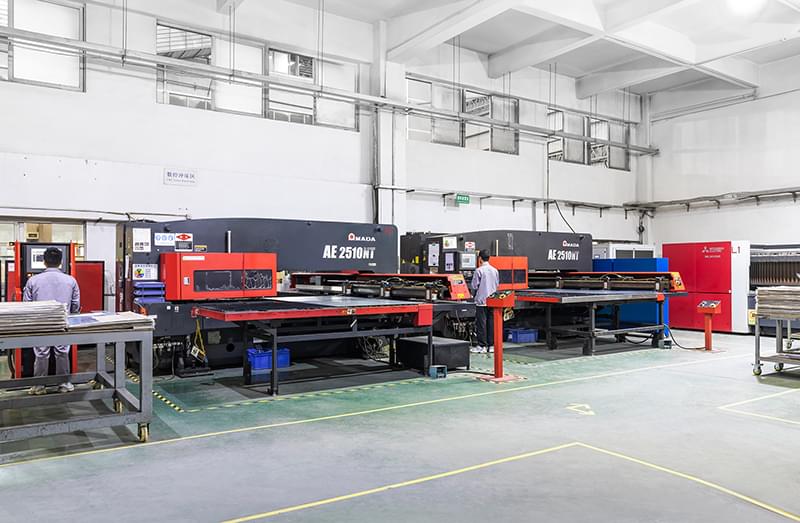
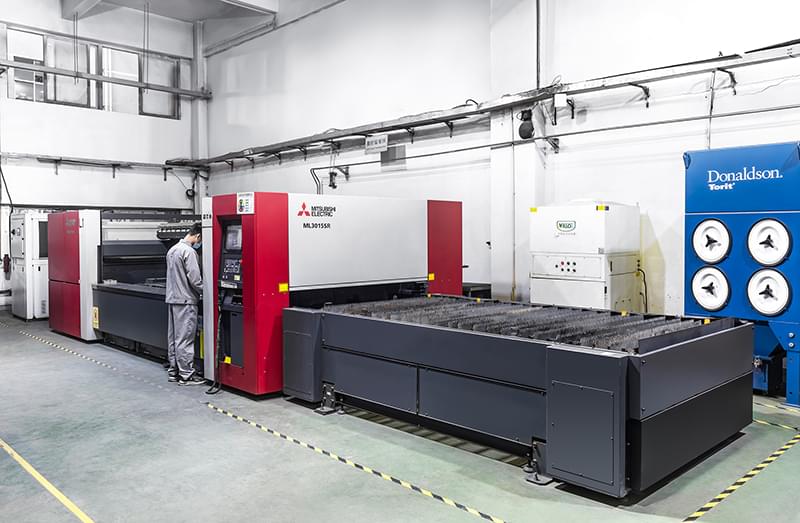
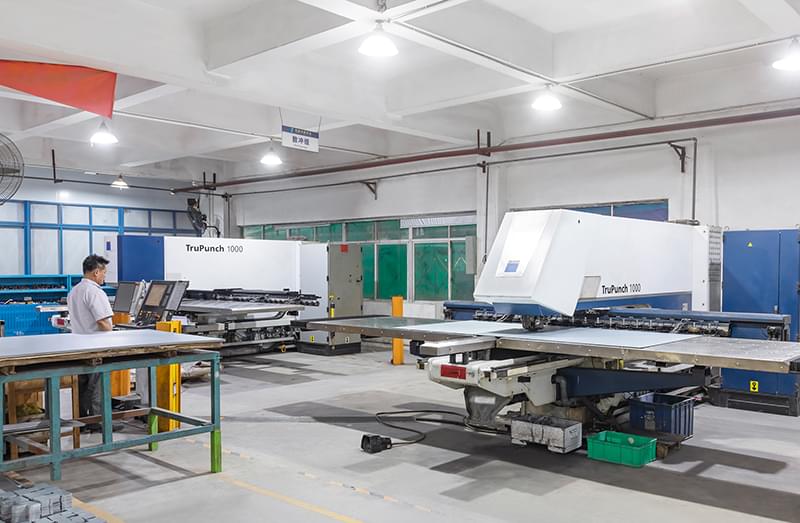
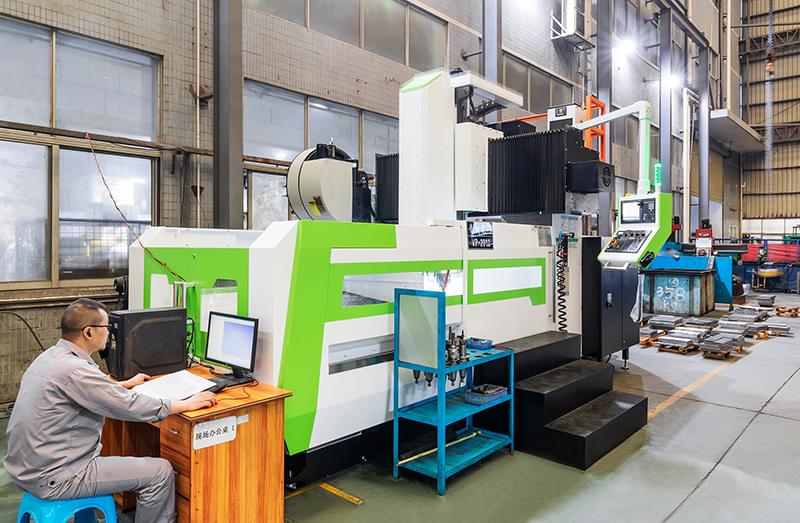
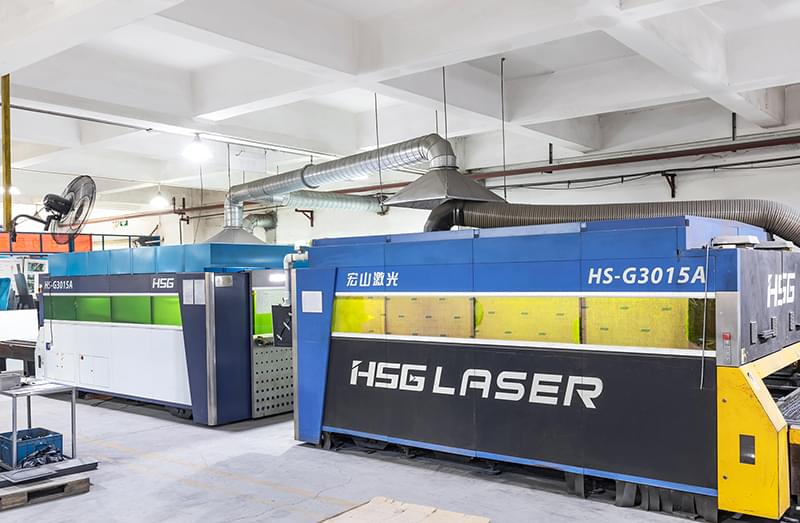
Wstitanium Workshop
Our Powerful Facilities

Laser Cutting - Custom Titanium Parts
Titanium is used in a wide variety of applications due to its optimal strength, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and weldability. Typically, CO2 and fiber lasers are used for laser cutting of titanium. Laser cut titanium alloys are often used in the aerospace industry due to their lightweight and durable parts, especially in applications such as aircraft structures, engine components, and internal components. In the medical industry, laser cut titanium is suitable for implants and surgical instruments. Wstitanium manufactures a variety of complex laser cut titanium parts every day. Years of experience invested in advanced laser cutting machines and machinists to manufacture a variety of complex and unique laser cut titanium products to meet your demanding requirements.
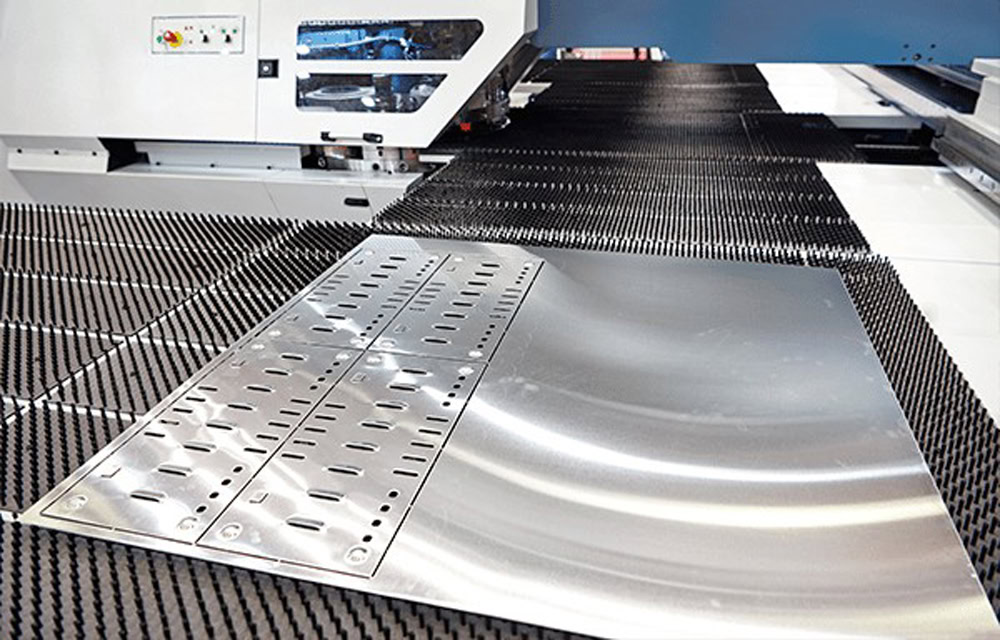
Advanced In-House Laser Cutting Machines
Titanium is sensitive to heat and must be cut at relatively low temperatures to achieve the best results. This way, the titanium alloy is prevented from deformation, discoloration, and contamination, which can lead to defects. Laser cutting is one of the best ways to get the smooth lines and complex cuts required for your project. Wstitanium utilizes CO2 lasers and nitrogen or oxygen to obtain the best surface results for titanium alloys. Professional machinists are well trained to recognize that titanium can melt to a certain extent and will monitor and adjust regularly to ensure that there are no burns and defects on the titanium plates you cut.
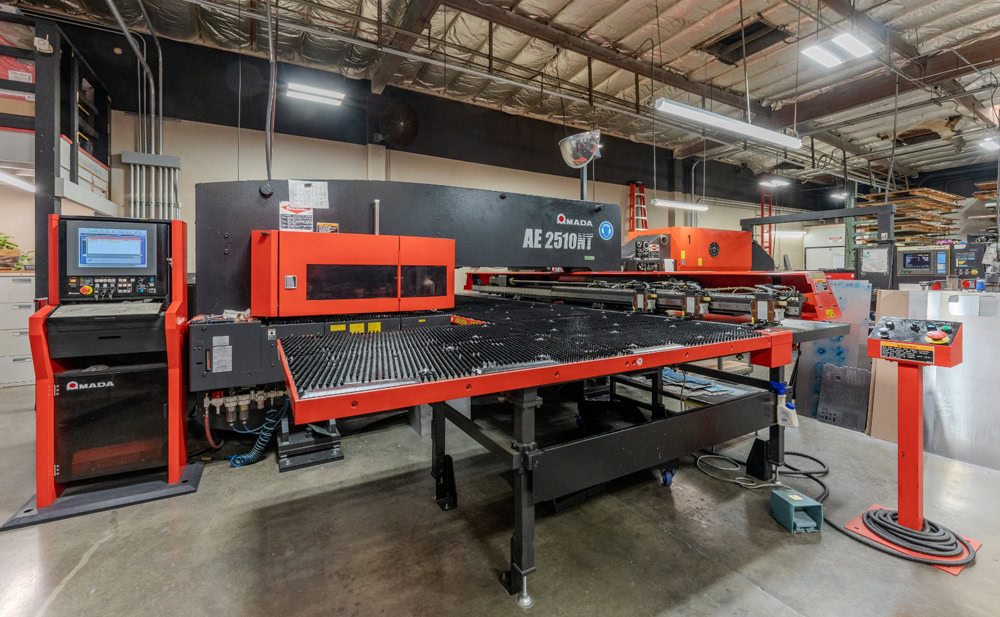

Laser Cutting Machines
- 4 Units
- 3000 W & 6000 W & 12000W.
- Part Thickness: 0.05mm to 10mm.
- Maximum Size: 2500 mm*6000 mm.
Laser Tube-Cutting Machines
- 5 Units
- Round From 5mm to 100mm
- Square From 20mm to 100mm
- Wall Thicknesses From 0.8mm to 5.0mm
Tolerance
- Vertical tolerance: ±0.05mm
- Surface roughness: Ra<0.1μm
- Dimensional tolerance: ±0.1mm
- Straightness tolerance: ±0.05mm
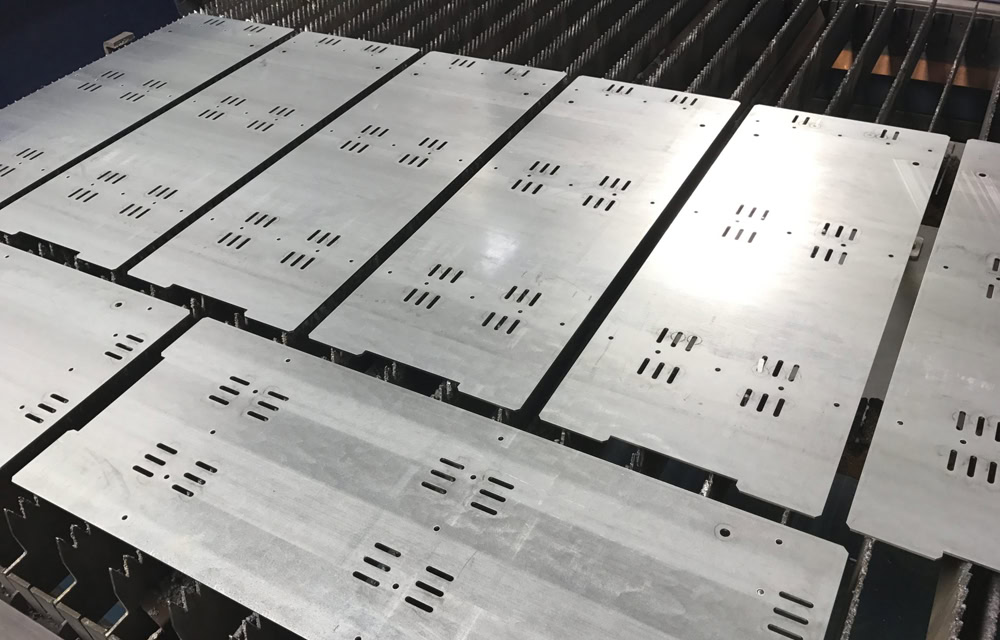
Laser Cutting Workshop
Wstitanium is well known for providing high-quality laser cutting titanium services. Whether it is a CO2 laser cutting machine or a fiber laser machine, titanium can be cut accurately and cleanly. Investing in dozens of advanced machines equipped with advanced technology and excellent beam quality ensures minimal heat-affected zone and excellent edge quality. Wstitanium understands that each titanium metal cutting application is unique and may have specific requirements. Provide customized solutions to meet your specific needs.
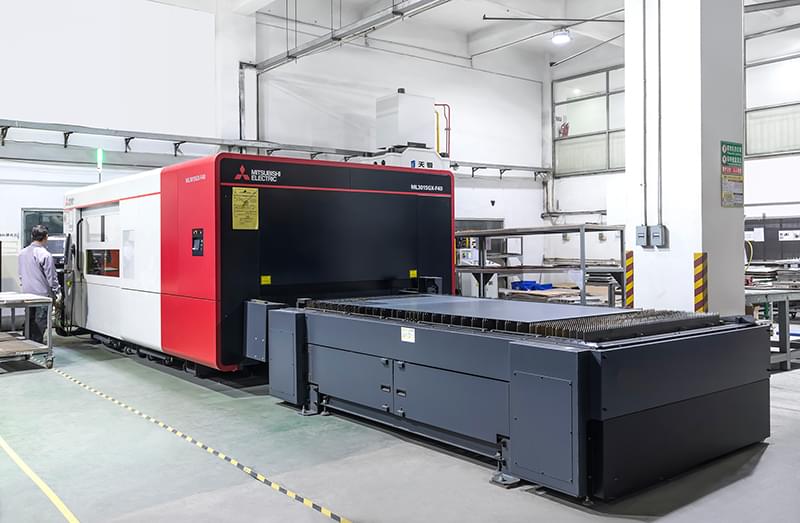






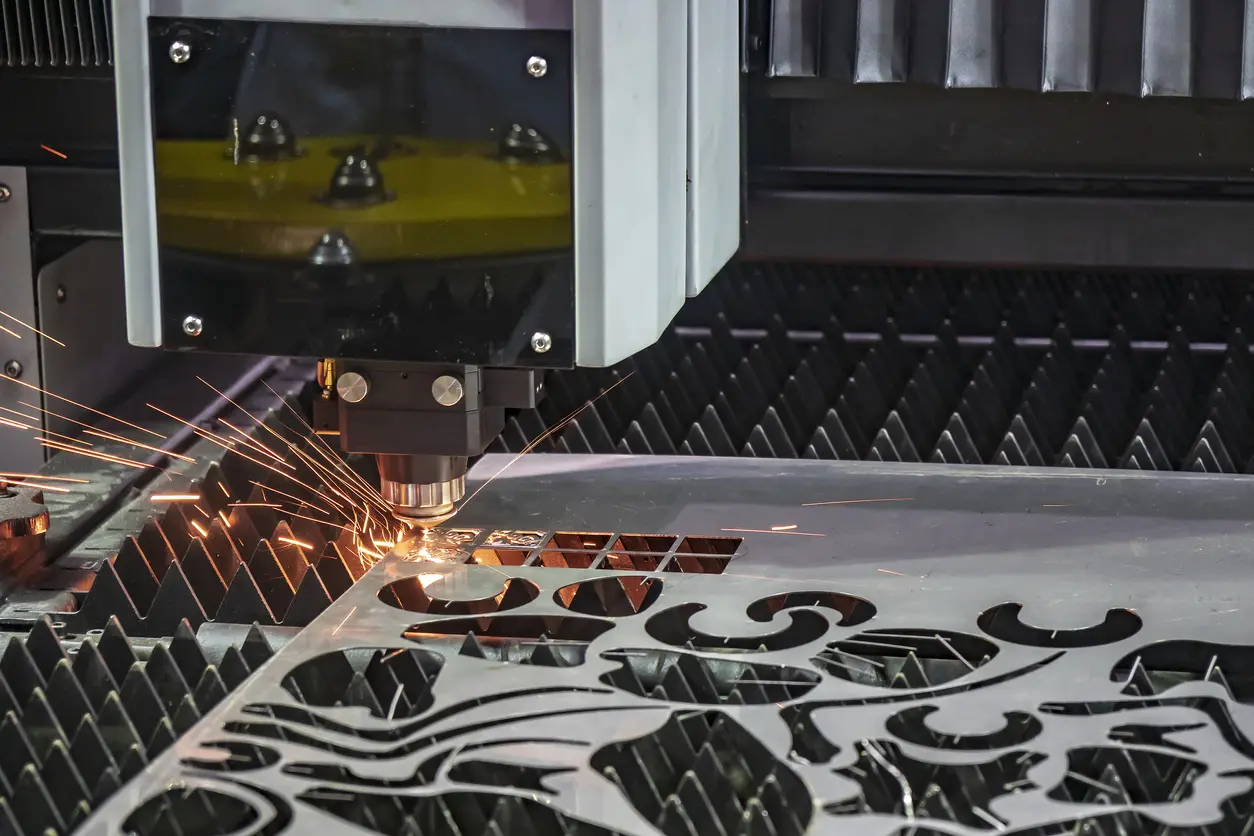
What is Laser Cutting Titanium?
Laser cutting titanium is a specialized technology that utilizes a high-energy laser beam to precisely cut titanium or titanium alloys. It is a non-contact process that offers many advantages over traditional cutting methods, such as: crisp cut edges, smooth lines, intricate cuts, efficiency, and tight tolerances.
Laser cutting titanium is a very delicate process that requires the correct machine settings for best results. Titanium must be cut at low temperatures for best results, as it is a very reflective and heat-sensitive material. The most efficient way to cut titanium sheet metal is with a CO2 laser, with nitrogen or oxygen as the assist gas. Fiber lasers with nitrogen assist gas are also ideal for cutting titanium sheet metal. However, titanium can easily burn from the heat generated by the laser. In some cases, nozzle adjustments and specialized gas mixtures may be required to prevent titanium from burning.

What is the Best Titanium Alloy for Laser Cutting Projects?
There are many types of titanium and titanium alloys. It is important to understand the properties of each type of titanium. This helps to be most cost-effective. As we all know, titanium is not a cheap metal, especially titanium alloys. Choosing a higher grade of titanium alloy means that the metal itself is expensive. Of course, the difficulty of manufacturing will also increase. This adds additional costs to your project.
Pure Titanium
The purest titanium has grades 1, 2, 3, and 4. As the number increases with each higher grade, the tensile strength and yield strength also increase. These grades are classified as pure titanium, which is lighter than steel and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Projects that require these properties will be used in industrial applications such as: medical, aerospace, construction, and chemical.
Grade 5 Titanium Alloy
Grade 5 titanium alloy is the most popular titanium, known as Ti 6-4, Ti 6AL-4V, and Ti6AL4V. Grade 5 titanium sheet has excellent strength, a higher temperature threshold range, and corrosion resistance. It is also used for industrial needs in aerospace, medical implants, and environments where there is potential for corrosion.
Grade 9 Titanium Alloy
Not to be outdone, grade 9 titanium is a titanium alloy that contains aluminum and vanadium. Grade 9 titanium sheet has higher strength, weldability and corrosion resistance. Providing greater flexibility in design for sporting goods, aerospace hydraulic systems, marine environments.
Consult Wstitanium Experts
The best grade of titanium for your project will depend on factors such as: strength to weight ratio, temperature threshold, environment the part will operate in, corrosion resistance, is welding required? A consultation with a Wstitanium expert prior to design and fabrication will help guide the best material selection.
Titanium Laser Cutting Considerations?
Because titanium is reactive to oxygen, it is susceptible to microcracks during the laser cutting process. These microcracks can render parts unusable for aerospace and medical applications. Therefore, Wstitanium must avoid this damage at all costs. For example, we utilize high-pressure nitrogen and specially calculated cutting speeds to prevent microcracks. Another challenge with titanium laser cutting is thickness. Our team of experts considers multiple factors before starting any work. Such factors include optical focal length, gas pressure, speed, power, and nozzle size. These factors will help ensure that you choose the most suitable manufacturing method and achieve the best results.
Power output: Titanium is a tough material, so a laser cutting machine with sufficient power is essential. Higher laser power can cut titanium faster and more efficiently.
Beam quality: The beam quality of the laser is essential to achieve precise and clean cuts in titanium alloys. Laser cutting equipment with high-quality beams will result in better edge quality and minimal heat-affected zones.
Laser settings: Determine the appropriate laser parameters such as focus, power, and speed based on the grade and thickness of the titanium. The correct settings ensure clean and accurate cuts.
Accurate CAD Design: Take the time to create an accurate and detailed CAD design as it directly affects the final cut quality. Check the design for errors and confirm that it meets the application specifications before the cutting process begins.
Gas Assist: Gas assist, such as nitrogen or argon, is often used during titanium laser cutting to prevent oxidation and improve cut quality. Make sure your laser cutter has a gas assist system or the ability to integrate one.
Careful Material Handling: Manage titanium sheets carefully to avoid surface damage or contamination that can affect cut quality. Ensure the sheet is free of debris and clean before cutting.
Compatibility of Thickness and Grade: Make sure the laser cutter you choose is compatible with the specific thickness and grade of titanium you will be using. Different alloys may require different settings or techniques to achieve the best results.
Quality Control: Establish a comprehensive quality control process throughout the manufacturing process. Inspect the cut titanium pieces for potential defects, edge quality, and precision, and make adjustments as needed to maintain high quality standards.
Laser Cutting vs Water Jet Cutting vs Plasma Cutting
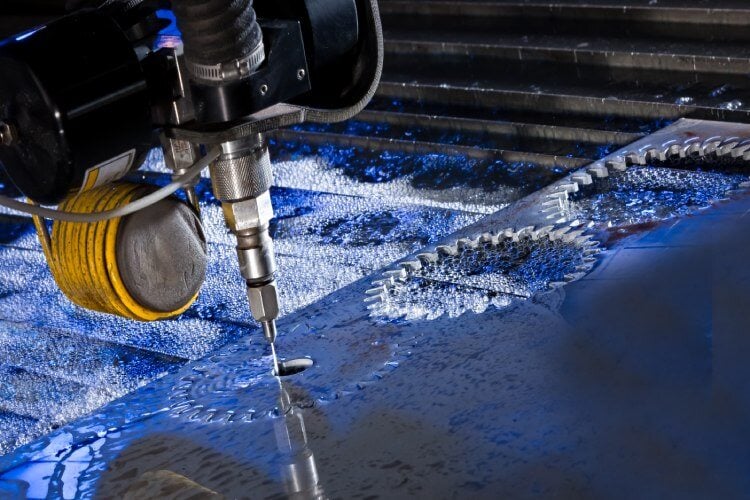

Water jet cutting
Water jet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through materials. It is suitable for cutting titanium and other materials, including thick materials or heat-sensitive materials. Water jet cutting provides good precision and can handle complex shapes.
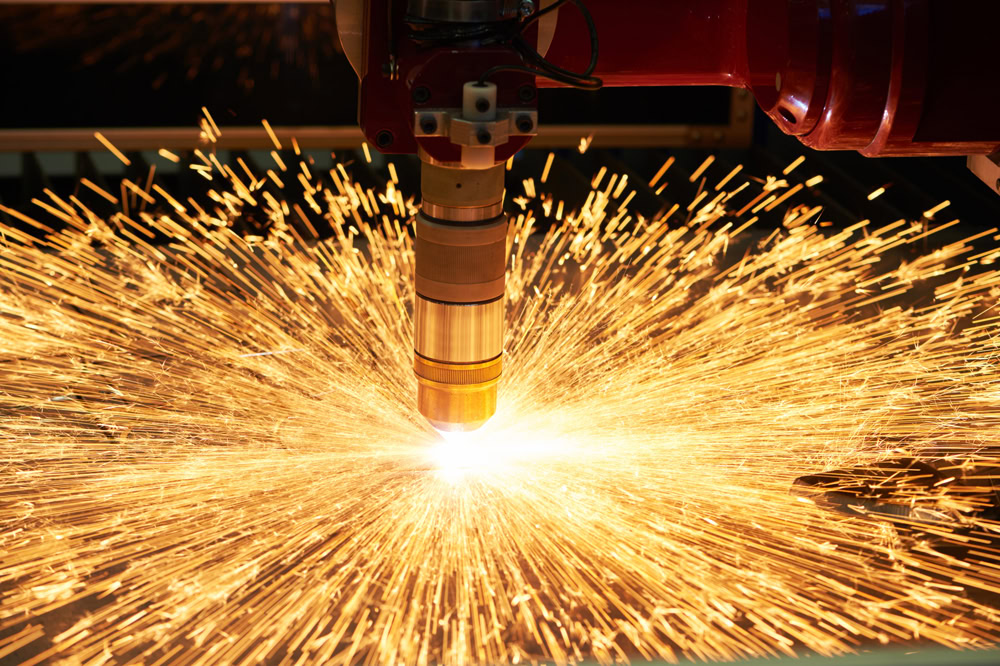

Plasma cutting
Plasma cutting uses a high-temperature plasma arc to melt and cut titanium. It is often used to process thick titanium plates and provides high cutting speeds. Plasma cutting is an effective straight-line cutting method, but it may result in a wider heat-affected zone compared to laser cutting.
Feature | Plasma Cutting | Water Jet Cutting | Laser Cutting |
Working Principle | Uses high-temperature plasma arc to melt metal, removing it with high-speed air. | The technique of cutting materials with high pressure water and abrasives (aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, silica sand and garnet). | Uses a focused high-power laser beam to rapidly melt or vaporize metal, removing molten material with high-speed airflow. |
Cutting Speed | Can achieve speeds 5-6 times faster than flame cutting for thin sheets. | Cutting titanium plates may take longer. | High speed for thin sheets; efficiency may decrease with thicker materials compared to plasma cutting. |
Applicable Materials | Suitable for various conductive metals like stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium. | The material range is roughly the same as that of laser cutting: metals, plastics, and ceramics. | Can cut a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, wood, and glass. |
Economic Efficiency | Generally the most cost-effective method for cutting medium-thick metal plates. | Cutting thin titanium sheets is more cost-effective. | Initial investment and maintenance costs are usually higher than plasma cutters. |
Accuracy | Lower precision (especially on thin sheets) may lead to warping. | No heat damage, poor surface finish of cut parts. Can easily cut different patterns. | High precision with smooth edges, requiring minimal post-processing. |
Environmental Impact | Generates significant noise and dust, negatively affecting the environment. | Waterjet cutting is a very clean process with no toxic fumes and dust to worry about. | Produces less harmful dust and noise, more environmentally friendly. |
Limitations | Only cuts conductive materials; not suitable for non-conductive materials like wood or plastics. | The failure rate during cutting is high and it is not suitable for cutting thicker titanium plates. | Sensitive to thickness; efficiency may drop when cutting thick plates. |
Waterjet, plasma cutting, and laser cutting all work well for cutting titanium sheets and plates. However, there may be reasons to choose one over the other. For example, waterjet cutting titanium sheets makes more sense when cutting simple shapes because it will be a more cost-effective and efficient method, but the process will take a long time. In this case, laser cutting is a better choice.
The initial cost of laser cutting may be higher. Due to the high precision that laser cutting can achieve. Therefore, laser cutting will be a better idea when cutting very small holes in titanium sheets or plates. It’s not that waterjet cutting can’t achieve this goal, but it will be more difficult and may not meet tight tolerances. For titanium sheets greater than 5mm thick, plasma cutting is a good option.
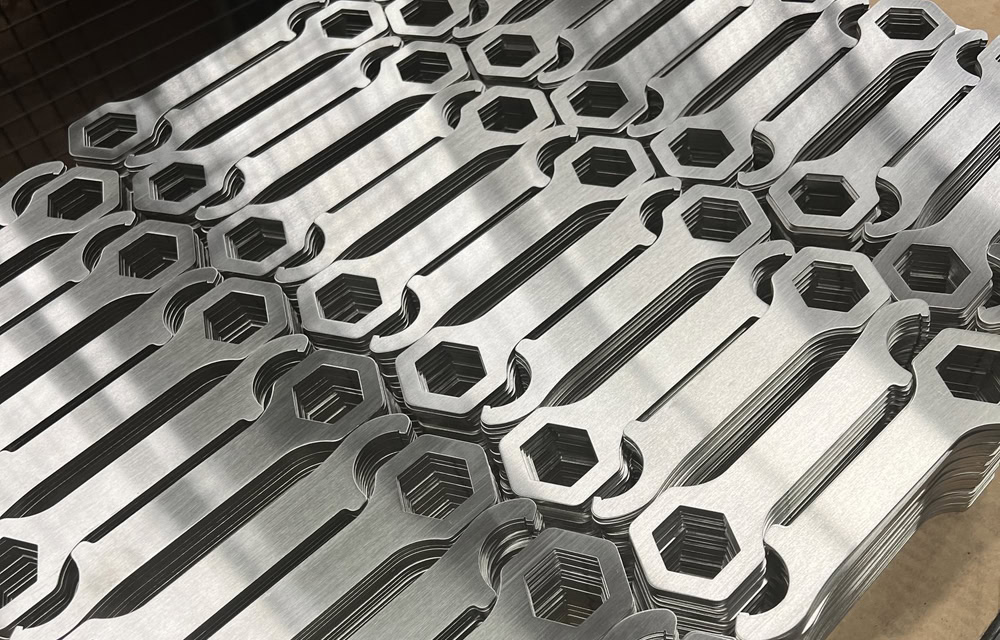
Laser Cut Titanium Parts Gallery