Lead Dioxide Titanium Anode Manufacturer and Supplier
As a manufacturer of customized lead dioxide titanium anodes in China, Wstitanium has rich experience and technical strength in design, customized specifications, manufacturing, quality inspection and application.
- Mesh lead dioxide titanium anode
- Tube lead oxide titanium anode
- Plate lead oxide titanium anode
- Rod lead oxide titanium anode
- For Wastewater Treatment
- For Electroplating
- For Perchlorate
- For Chromate
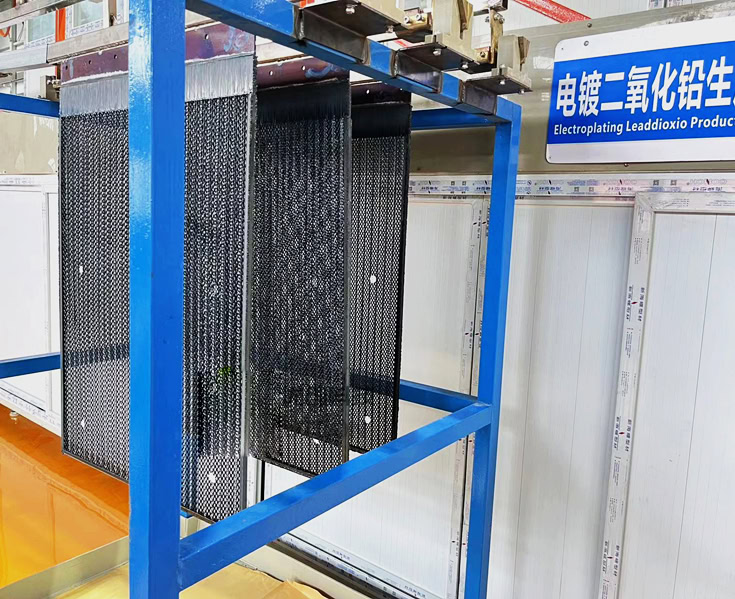

Trustworthy Lead Dioxide Factory-Wstitanium
In today’s industrial field, with the continuous improvement of the pursuit of high efficiency, environmental protection and sustainable development, advanced materials and technologies have become the key force to promote the progress of various industries. Lead dioxide titanium anode plays a vital role in many fields such as electroplating, electrolytic refining, organic synthesis, and wastewater treatment due to its unique performance advantages. As a Chinese lead dioxide titanium anode manufacturer, Wstitanium has established a good reputation in the industry with its excellent quality, advanced technology and professional services, and has become your trusted preferred supplier.
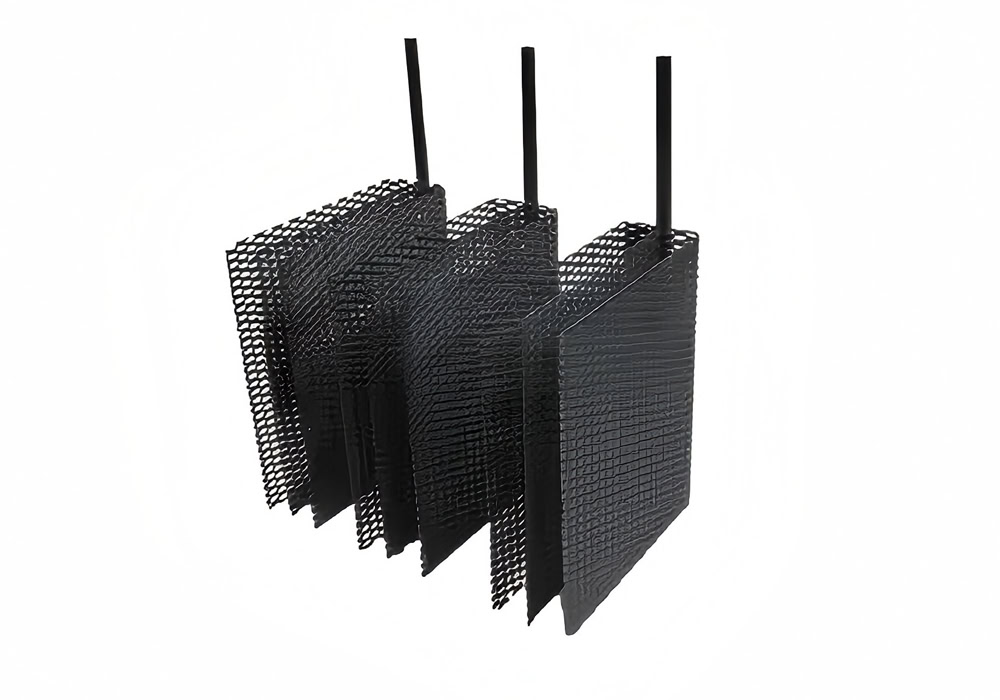

Customized Lead Dioxide Anode
A variety of titanium substrate material (Gr1, Gr2, etc.) options. Customized various shapes, such as plate, mesh, tube, coating thickness, etc.
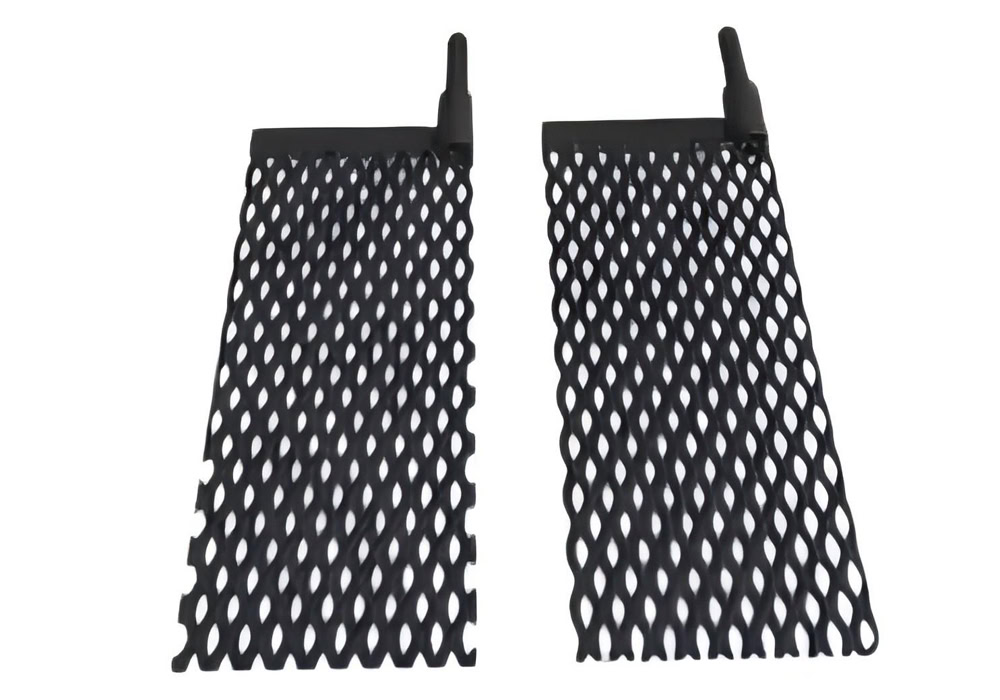

Mesh Lead Dioxide Anode
Titanium mesh substrate (pore size 0.1-5mm), β-PbO₂ coating thickness 0.2-0.5mm. The effective surface area is increased by 300% compared with the flat plate.
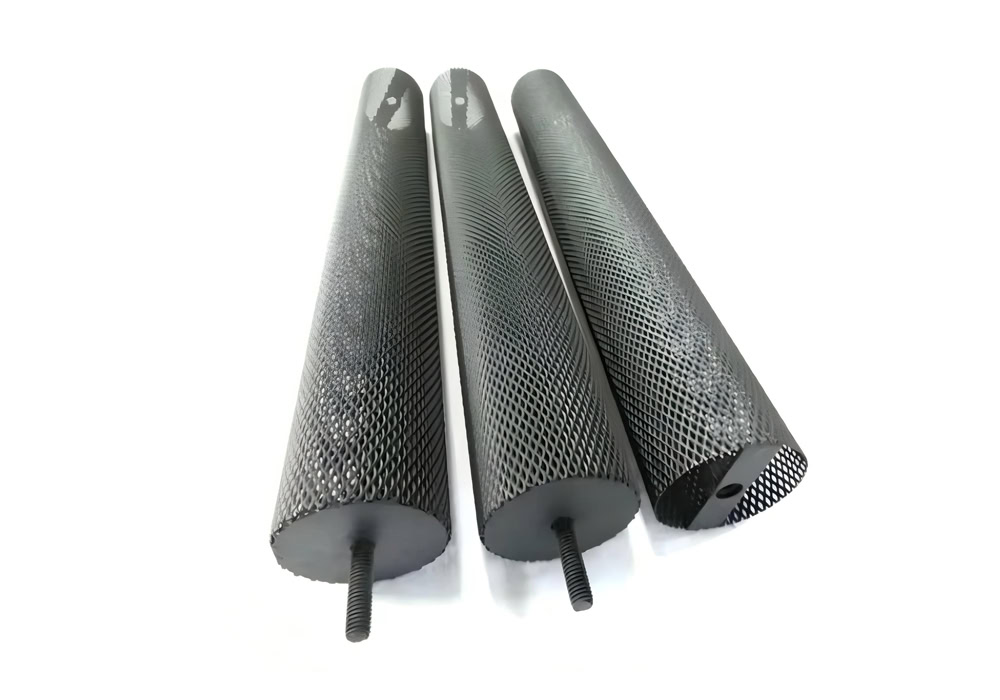

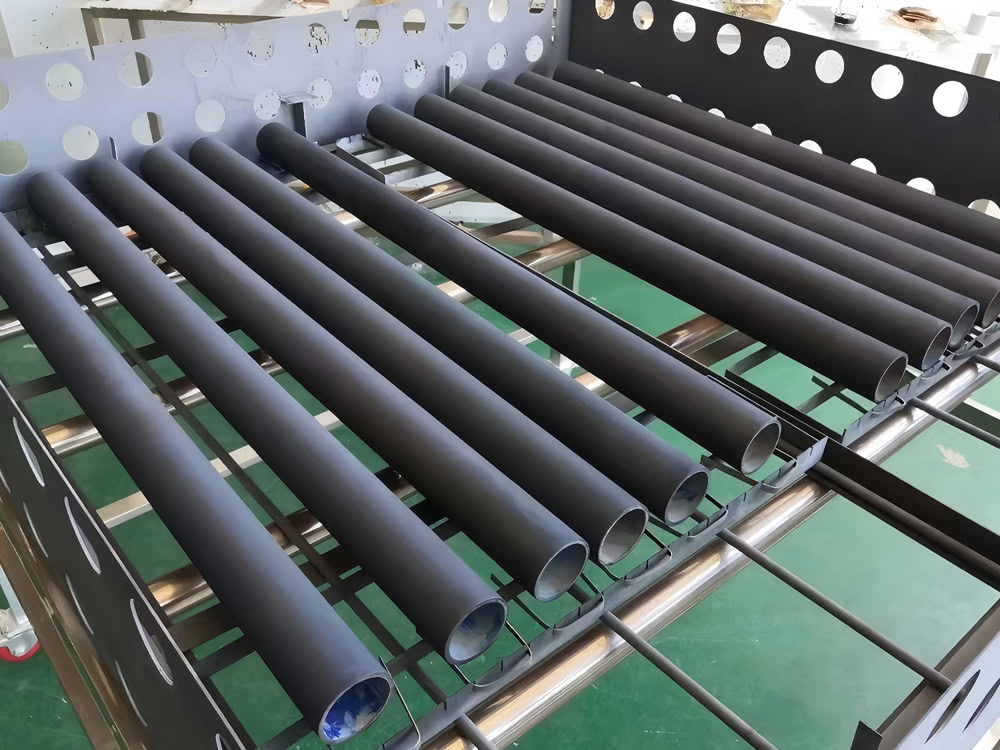
Tube Lead Dioxide Anode
φ10-100mm titanium tube substrate, the inner wall is treated with nano-level roughening (Ra 0.8-1.6μm). The bubble detachment speed is increased by 40%.
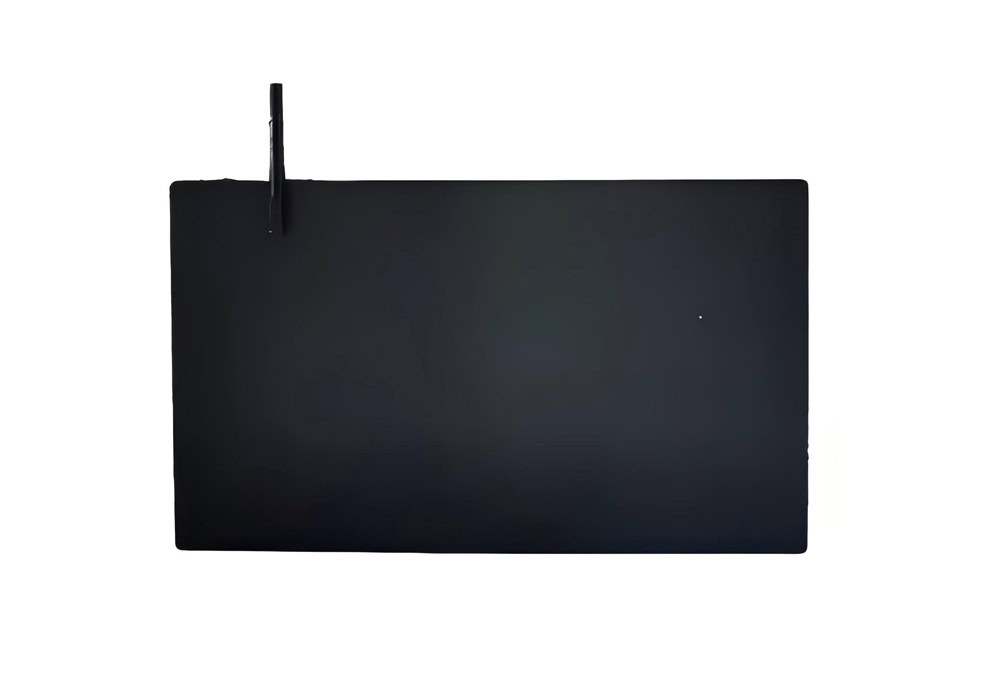

Plate Lead Dioxide Anode
2-5mm thick titanium plate, combined with gradient coating design (bottom layer α-PbO₂/surface layer β-PbO₂), the bending strength reaches 180MPa.
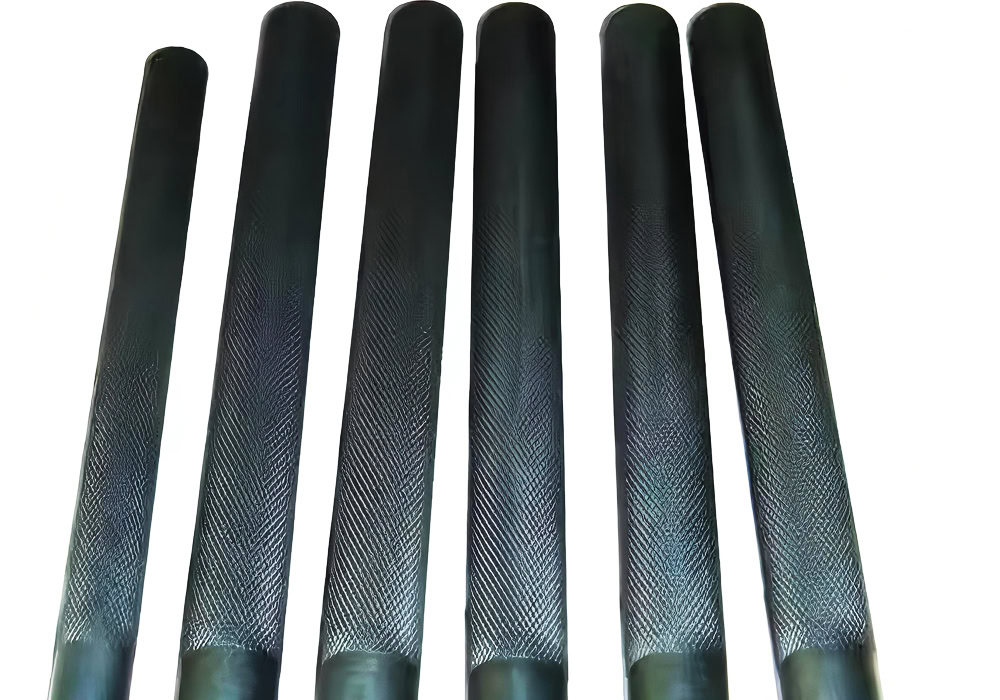

Rod Lead Dioxide Anode
φ5-20mm titanium rod, combined with pulse electrodeposition technology, the coating density is >99.5%. Axial uniformity, resistivity deviation <5%.
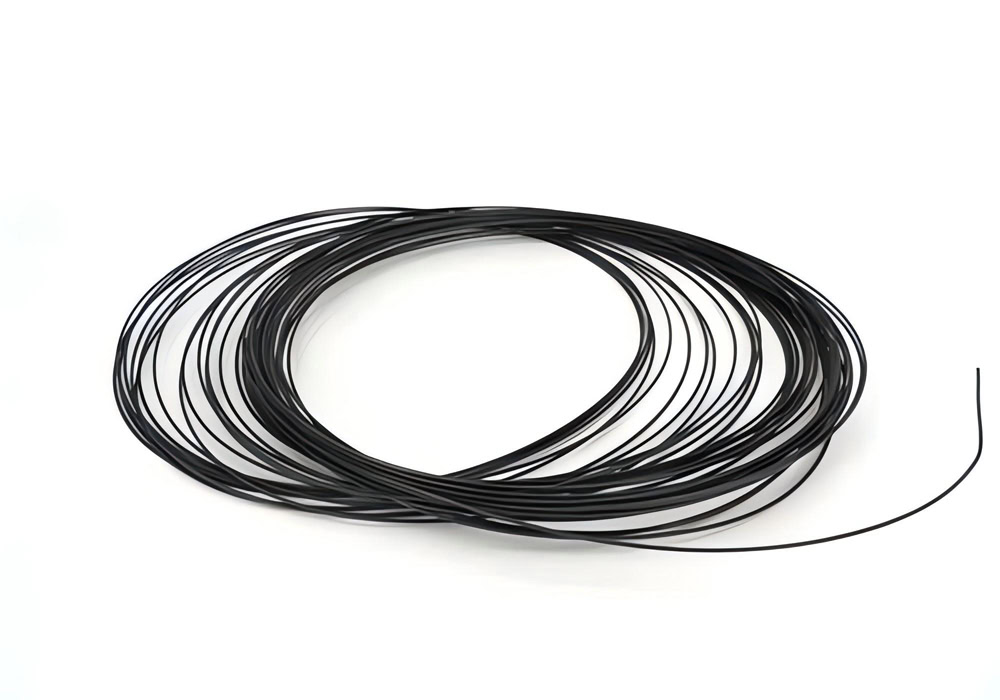

Wire Lead Dioxide Anode
φ0.1-1mm titanium wire, achieving uniform coating thickness of ±5μm. Specially designed spiral winding structure, specific surface area can reach 1500m²/m³.

For Wastewater Treatment
Oxidize heavy metal ions (such as chromium, nickel, copper, lead, etc.) in wastewater to high valence states, making it easier to form precipitation.

For Electroplating
It can accurately control the current density and electrode potential during the electroplating process to obtain alloy coatings with excellent performance.

For Sodium Hypochlorite
Promote electrolysis, and resistance to chlorine precipitation ensures the purity of sodium hypochlorite, making it suitable for disinfection purposes.
Advantages of Wstitanium manufacturing lead dioxide titanium anodes
Wstitanium invests in professionals in the fields of materials science, electrochemistry, etc. They conduct in-depth research on the manufacturing technology, performance optimization and application expansion of lead dioxide titanium anodes, and are committed to developing products with higher performance and wider application fields. For example, a new type of intermediate layer material developed can significantly improve the adhesion and bonding strength between the lead dioxide coating and the titanium substrate, effectively extending the service life of the electrode.
High Oxygen Evolution Overpotential
The lead dioxide titanium anode manufactured by Wstitanium has an extremely high oxygen evolution overpotential. In acidic media, its oxygen evolution overpotential is usually 0.1-0.3V higher than similar products, which more effectively inhibits the occurrence of oxygen evolution side reactions. For example, in wastewater treatment, high oxygen evolution overpotential can enable the electrode to preferentially oxidize organic pollutants, improve degradation efficiency, and reduce costs.
Good Electrocatalytic Activity
By optimizing manufacturing technology and coating structure, the lead dioxide titanium anode is endowed with excellent electrocatalytic activity. The active sites on the electrode surface are rich, which can quickly adsorb and activate reactant molecules, reduce the activation energy of the reaction, and accelerate the reaction rate. For example, in the synthesis process of certain drug intermediates, the use of Wstitanium’s lead dioxide titanium anode can increase the reaction yield by 10%-20%.



High Current Efficiency
Due to its high oxygen evolution overpotential and good electrocatalytic activity, Wstitanium’s lead dioxide titanium anode maintains a high current efficiency. In the electroplating industry, high current efficiency means that high-quality coatings can be obtained in a shorter time. Using Wstitanium’s lead dioxide titanium anode for electroplating, the current efficiency can be increased by 15% – 25%, greatly reducing production costs.
High Hardness and Wear Resistance
Wstitanium further improves the hardness and wear resistance of the coating through a special preparation process. Its Mohs hardness can reach 5.5 – 6.5. During long-term use, it can effectively resist mechanical friction and wear and maintain the stability and performance of the electrode. In processes such as electrolytic machining and electrolytic rust removal, this high hardness and wear resistance allows the electrode to operate stably for a long time.
Strong Acid and Alkali Resistance
Whether in acidic or alkaline media, Wstitanium’s lead dioxide titanium anode exhibits excellent chemical stability. In strong acidic media, such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, etc., the electrode can resist acid corrosion for a long time, and will not dissolve or chemically react, ensuring the normal use of the electrode. In alkaline media, the electrode also has good corrosion resistance and can adapt to various alkaline electrolyte environments.
Diverse Specifications
Wstitanium can provide a variety of lead dioxide titanium anode product specifications. Customize electrodes of different shapes, sizes and coating thicknesses according to customer requirements. Whether it is a conventional flat electrode, a tubular electrode, or a special-shaped electrode. The thickness of the lead dioxide coating is precisely controlled between 0.1-2.0mm to meet the requirements of electrode performance in different application scenarios.
Comparing Lead Dioxide Anodes and MMO Anodes
Lead dioxide titanium anode is suitable for organic electrosynthesis, acid electroplating, etc. MMO titanium anode is mostly used in modern electrochemistry such as chlor-alkali industry and water electrolysis to produce hydrogen. The life of lead dioxide titanium anode is relatively short, and the coating needs to be checked regularly. MMO titanium anode has a long life and simple maintenance. The initial cost of lead dioxide titanium anode is low, but the operating energy consumption is slightly higher. In short, according to specific needs, if you pursue high oxidation capacity and the electrolyte is acidic, you can choose lead dioxide titanium anode; if you need low overpotential and high stability, choose MMO titanium anode.
| Aspect | Lead Dioxide Anode | MMO Anode |
| Material Composition | Primarily consists of lead dioxide (PbO2). | Titanium substrate coated with mixed metal oxides, often ruthenium oxide (RuO2) and iridium oxide (IrO2). |
| Durability and Lifespan | Generally has a shorter lifespan, especially in chlorinated environments. | Known for long operational life, especially in chlorine-rich environments. More durable and stable. |
| Overpotential | Higher overpotential for chlorine evolution. | Lower overpotential for chlorine evolution, making them efficient in processes like electrochlorination. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Potential to corrode, especially in acidic environments. | Highly corrosion-resistant due to titanium substrate and mixed metal oxide coating. |
| Applications | Used in electrowinning, electroplating, and other electrochemical processes. | Widely used in water treatment, cathodic protection, and various industrial electrochemical applications. |
| Environmental Concerns | Lead content poses environmental risks if released or improperly disposed. | Less environmental risk, but precious metals like ruthenium and iridium in coatings can impact cost. |
Customized Manufacturing of Lead Dioxide Titanium Anode
In response to your special applications and requirements, Wstitanium gives full play to its R&D advantages to provide customized lead dioxide titanium anode solutions. From in-depth communication with you about your needs, to designing exclusive electrode structures and coating formulas, to later quality inspection and optimization, every link is closely centered on your needs. With its mature manufacturing technology and efficient supply chain, Wstitanium provides a competitive price system to reduce your procurement costs.
The lead dioxide titanium anode is mainly composed of two parts: titanium matrix and lead dioxide coating. Industrial pure titanium (such as TA1, TA2, etc.) is usually selected as the matrix material. Titanium has the advantages of low density, high strength, and good corrosion resistance, and can provide good mechanical support and corrosion resistance for the anode. Its surface is specially treated to enhance the bonding with the lead dioxide coating. Lead dioxide (PbO₂) is the active substance of the anode and is divided into two crystal forms: α-PbO₂ and β-PbO₂. β-PbO₂ has higher electrochemical activity and conductivity and is more commonly used in most applications. Some other elements (such as strontium, barium, etc.) may also be added to the coating as additives to improve its performance.
α-PbO₂ has an orthorhombic crystal structure, which is relatively dense and has high hardness, but relatively poor conductivity; β-PbO₂ has a tetragonal crystal structure, good conductivity, high catalytic activity, and shows better performance in electrochemical reactions. In practical applications, the characteristics of both are often used to form a composite coating. For example, a layer of α-PbO₂ is first deposited on the titanium substrate as a base layer, and its dense structure is used to improve the adhesion between the coating and the substrate and the overall corrosion resistance; then β-PbO₂ is deposited on the α-PbO₂ layer as an active layer, giving full play to its advantages of high catalytic activity and good conductivity to improve the electrocatalytic performance of the anode.
Intermediate Layer Coating Materials
Common intermediate layer coating materials include tin antimony oxide (SnO2−Sb2O3) and the like. Tin antimony oxide has good conductivity and chemical stability, and can play a transition and connection role between the titanium substrate and the lead dioxide coating, improving the adhesion and stability of the coating. The titanium substrate is immersed in the tin antimony oxide sol, and then the sol is evenly coated on the surface of the titanium substrate by pulling, rotating, etc., and after drying and sintering, a dense intermediate layer is formed.
Lead Dioxide Titanium Anode Manufacturing Process

Select Titanium Substrate
Select high-purity titanium materials, such as industrial pure titanium Gr1, Gr2 or titanium alloys, to ensure that they have good corrosion resistance and conductivity.

Forming
According to the design requirements, the titanium materials are processed into the required shape and size through cutting, drilling, bending and other technologies.
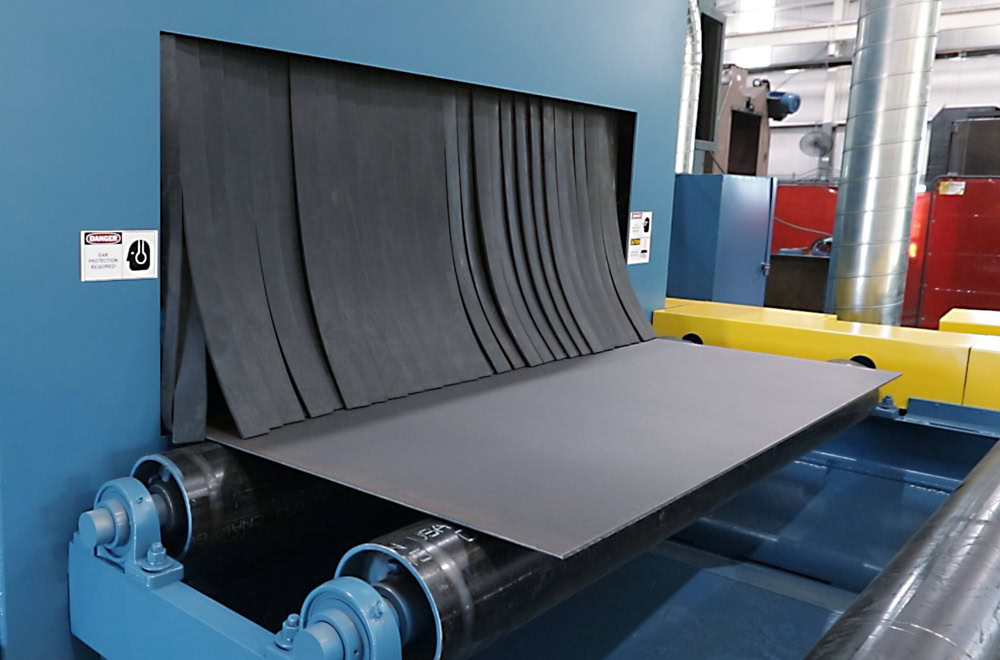

Sand Blasting
Use compressed air to spray sand particles onto the surface of the titanium substrate for impact grinding. The surface forms uniform pitting, improves the roughness, and increases the adhesion of the coating.
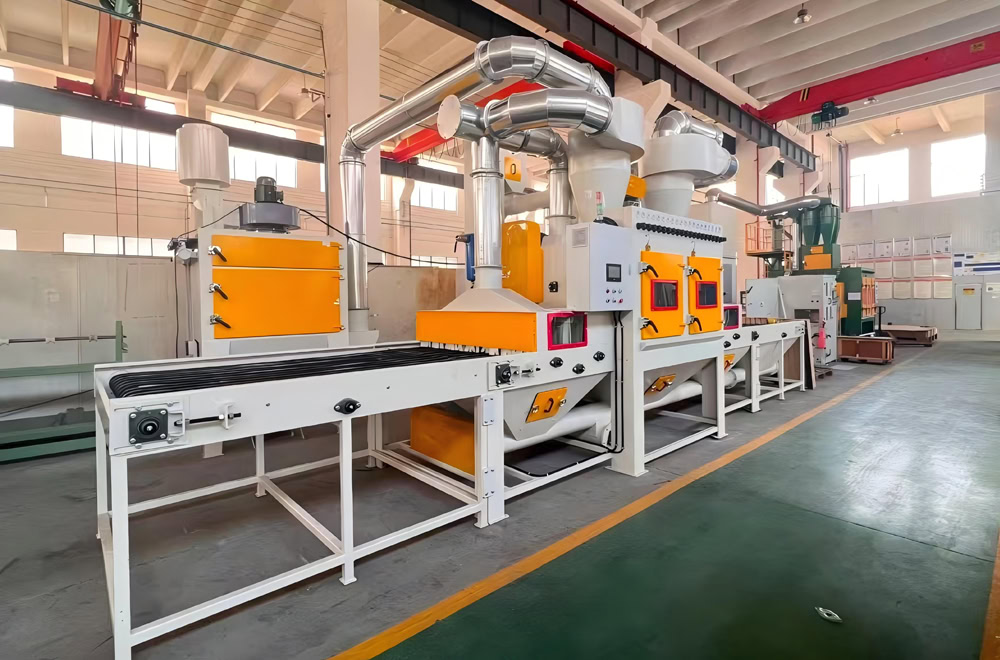

Leveling / Annealing
Heat and shape the titanium material in a furnace at about 500°C, keep it warm for about 2 hours, eliminate the stress inside the material, and improve the material’s organizational structure.
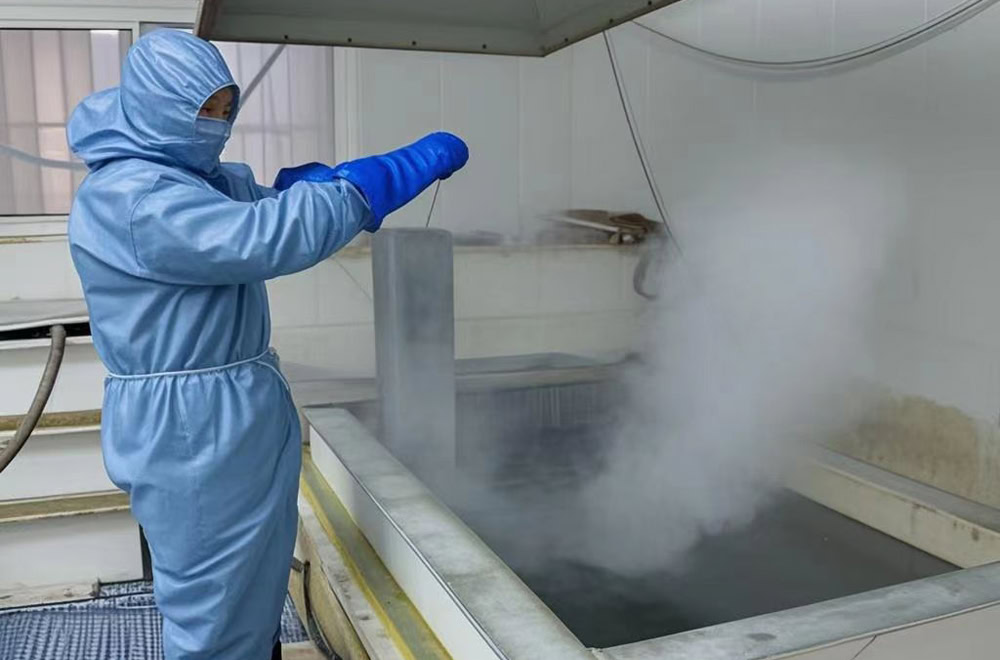

Pickling
Put the titanium substrate into a mixed acid solution composed of sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid for pickling to remove the oxide layer, rust and other impurities on the surface.

Liquid Preparation
Commonly used lead nitrate, lead acetate, lead methanesulfonate, etc. These lead salts can provide lead ions in the electrolyte and are important raw materials for electrodeposition of lead dioxide.

Coating
Use a brush or spray gun to evenly apply or spray the prepared coating solution on the surface of the pretreated titanium substrate. The thickness and uniformity of the coating should be controlled during operation.

Drying
The coated titanium substrate needs to be placed in a high-temperature furnace for sintering. The sintering temperature is generally between 450-550℃, and the sintering time is 10-20 minutes.

Quality Inspection
The composition and crystal structure of the coating are detected by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy spectrum analysis (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), etc.
Specification of Lead Dioxide Anodes
| Parameter | Specification |
| Substrate | Gr1/Gr2 Titanium |
| Coating Type | Lead dioxide |
| Dimension & Shape | Plate, mesh, rod, or customized |
| Voltage | < 1.13V |
| Current Density | < 3000A/M^2 |
| Work Time | 80-120 hours |
| Noble Metal Content | 8-13g/㎡ |
| Coating Thickness | 1-15μm |
Lead Titanium Dioxide Anode Application
As an important electrochemical electrode material, lead dioxide titanium anode is widely used in many fields such as electroplating, hydrometallurgy, sewage treatment, chemical synthesis, etc. By rationally selecting titanium substrate and lead dioxide coating materials, and implementing effective performance optimization strategies, lead dioxide titanium anode with high electrocatalytic activity, good stability and low internal resistance can be manufactured. In practical applications, according to different industry needs and working conditions, the appropriate anode type and design scheme are selected to give full play to the advantages of lead dioxide titanium anode.
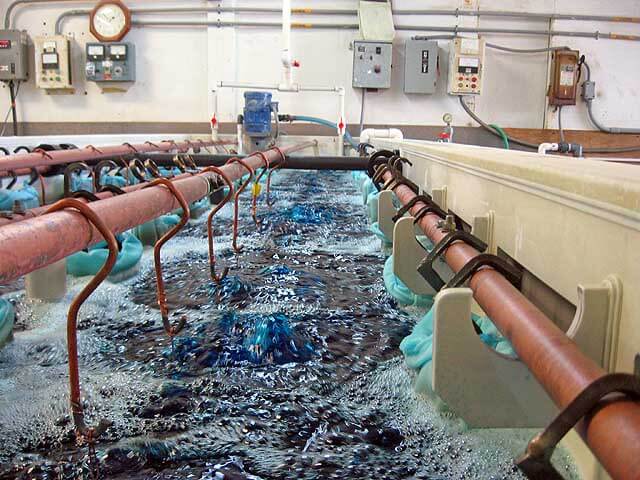
Electroplating Copper
The copper plating process of traditional lead-based anodes has problems such as poor uniformity of the coating and electrolyte contamination caused by anode dissolution. The lead dioxide titanium anode replaces the traditional lead-based anode. It uses a flat structure and the titanium substrate is industrial pure titanium TA1. After strict surface cleaning and etching pretreatment, it is coated with a SnO2 −Sb2O3 intermediate layer and a β- PbO2 outer coating. The uniformity of the coating is greatly improved, and the product defect rate is reduced from the original 15% to 1.2%. Since the lead dioxide titanium anode is insoluble, the electrolyte contamination problem is fundamentally solved, reducing the frequency of electrolyte replacement. At the same time, the service life of the anode is also extended from the original 3 months to more than 12 months.

Hydrometallurgy
In the past, lead-silver alloy anodes were used for zinc electrolytic production, which had problems such as large anode consumption, low current efficiency, and serious lead pollution. A mesh-structured lead dioxide titanium anode was used, and the titanium matrix was made of high-strength titanium alloy. A multi-layer composite lead dioxide coating was prepared through a special coating process, in which the bottom layer was α-PbO2 and the active layer was fluorine-doped β-PbO2. After the improvement: the anode consumption rate was significantly reduced from about 10kg per square meter per year to 2kg. The current efficiency was increased from the original 80% to about 88%. The lead pollution problem was effectively solved, and the product quality of zinc was improved.

Wastewater Treatment
The wastewater discharged from the printing and dyeing factory contains a large amount of organic dyes and heavy metal ions that are difficult to degrade. The titanium matrix of the rod-shaped lead dioxide titanium anode is industrial pure titanium that has undergone special strengthening treatment. The lead dioxide coating on its surface adopts bismuth-doped modification technology to enhance the catalytic degradation ability of organic dyes. Actual operation results: The decolorization rate of printing and dyeing wastewater has increased from about 50% to more than 90%, and the COD (chemical oxygen demand) removal rate has increased from 30% to more than 70%. The removal effect of heavy metal ions has also been significantly improved.

Electrolytic Industry
In the chlor-alkali industry, which produces caustic soda, chlorine and hydrogen by electrolyzing brine solutions, lead dioxide titanium anodes can replace traditional graphite electrodes, etc., with advantages such as small loss, low chlorine evolution potential, and stable size and shape. They can improve product quality, reduce energy consumption, and increase chlorine purity. In the process of electrolytic extraction of non-ferrous metals such as copper, nickel, cobalt, and zinc, lead dioxide titanium anodes can improve current efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and reduce the impact of anode dissolution on cathode product quality.

Battery
Lead dioxide titanium anode can be used as the negative electrode material of lithium-ion batteries, which can significantly improve the rechargeable capacity and cycle life of lithium-ion batteries and enhance the overall performance of the battery. Due to its good catalytic activity, it can be used as an oxygen reduction reaction catalyst for lithium-air batteries, improving the output efficiency of the battery and enabling lithium-air batteries to perform charge and discharge reactions more efficiently.
Wstitanium’s lead dioxide manufacturing shows unique advantages in material properties and production processes. From the performance point of view, the manufactured lead dioxide has high catalytic activity, which can significantly accelerate the process of various chemical reactions and speed up and increase the efficiency of many industrial reactions. It has strong chemical stability, and can maintain its own structure and properties in different acid-base environments and complex chemical systems, reduce loss and replacement frequency, and save costs. At the same time, the physical properties are also excellent, with high hardness and good conductivity, which not only ensures durability during use, but also facilitates electron transmission and improves the efficiency of electrochemical reactions. In terms of production technology, Wstitanium has high technical maturity and standardized manufacturing processes, which can achieve large-scale stable production and meet the market’s large demand for lead dioxide. Moreover, the production process is environmentally friendly, reduces pollutant emissions, conforms to the current green development concept, and reduces the environmental protection pressure on enterprises.