Platinised Titanium Anodes Manufacturer & Supplier In China
Wstitanium will continue to be committed to the research and development and innovation of platinum titanium anodes, continuously optimize manufacturing technology, improve its quality and performance, provide you with more complete solutions, and promote platinum titanium anodes to play a greater role in more fields.
- Platinum Plating
- Platinum Coating
- Oxygen Evolution
- Chlorine Evolution
- Rod Platinum Titanium Anode
- Plate Platinum Titanium Anode
- Mesh Platinum Titanium Anode
- Tubular Platinum Titanium Anode

Reputable Platinum Titanium Anode Factory-Wstitanium
Wstitanium Manufacturing Platinum-titanium anodes have important applications in many fields such as chlor-alkali industry, sewage treatment, seawater desalination, electronics industry, new energy, metal refining, cathodic protection, food, beverage and pharmaceuticals due to their excellent corrosion resistance, high conductivity, good mechanical properties and outstanding catalytic activity. Diverse manufacturing methods, such as electroplating, thermal decomposition, chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, as well as scientific design guidelines and flexible customized specifications, meet the needs of different application scenarios. A wide range of shape options, including plate, mesh, tubular and other special customized shapes, further expand the application possibilities of platinum-titanium anodes.
Plating Platinum Titanium Anodes
Through electroplating, a dense pure platinum coating is formed on the titanium surface, which is uniformly conductive and has low resistivity.

Coating Platinum Titanium Anodes
Its coating is sintered by platinum compounds, with relatively high resistivity and low cost, but relatively short life, and is used in ordinary industries.
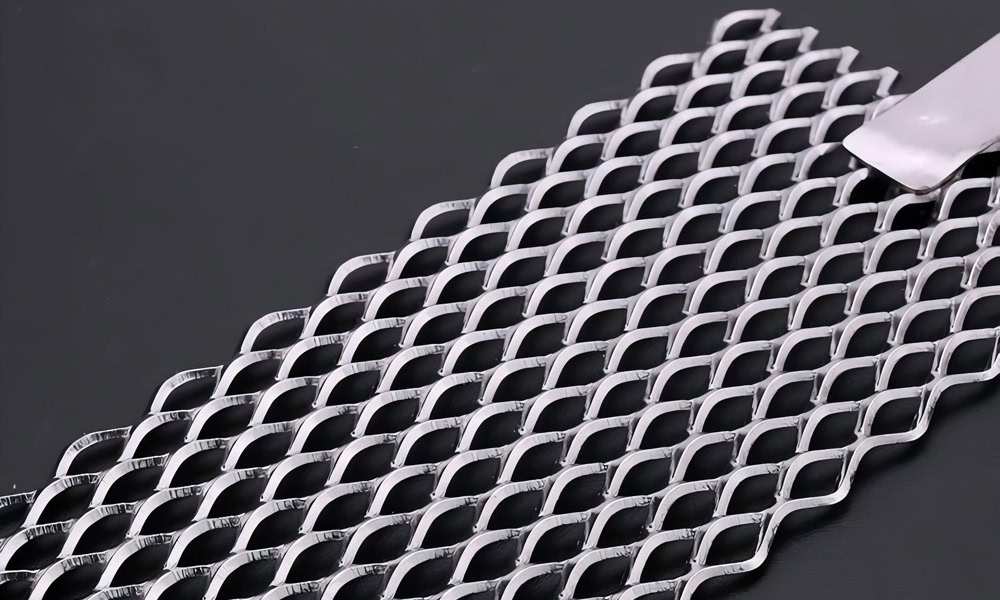
Chlorine Evolution Platinum Anodes
In the electrochemical reaction, chlorine is mainly precipitated, which is suitable for environments with high chloride ion content.
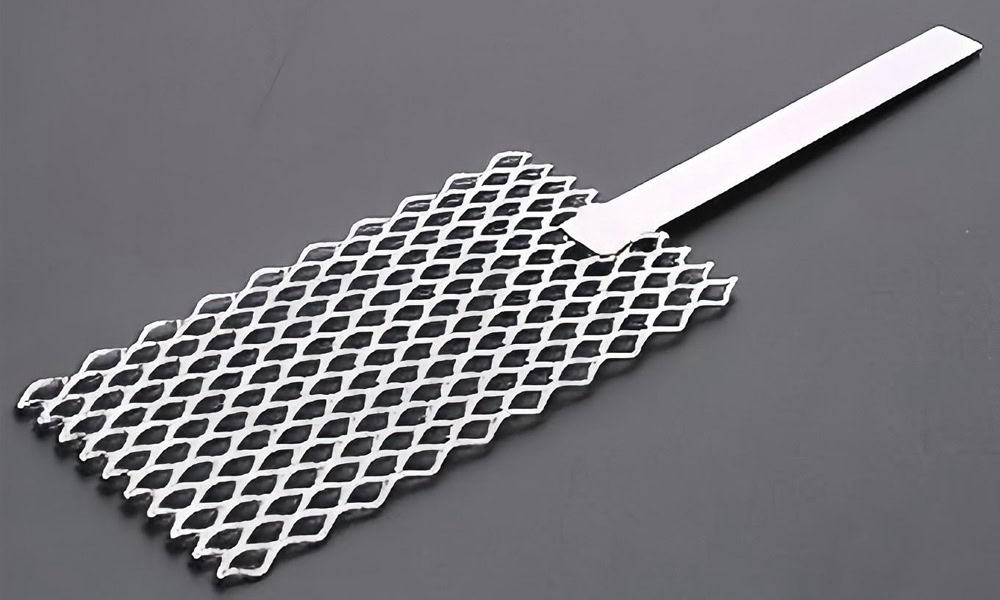
Oxygen Evolution Platinum Anodes
In the electrochemical reaction, oxygen is mainly precipitated, which is generally suitable for environments such as sulfuric acid.

Rod Platinum Titanium Anodes
It is in the shape of a rod, which is suitable for some small electrolytic devices with special requirements for electrode size and shape.

Plate Platinum Titanium Anodes
Flat plate, suitable for some occasions that require large electrode area and uniform reaction, such as anodes in some electrolytic cells.

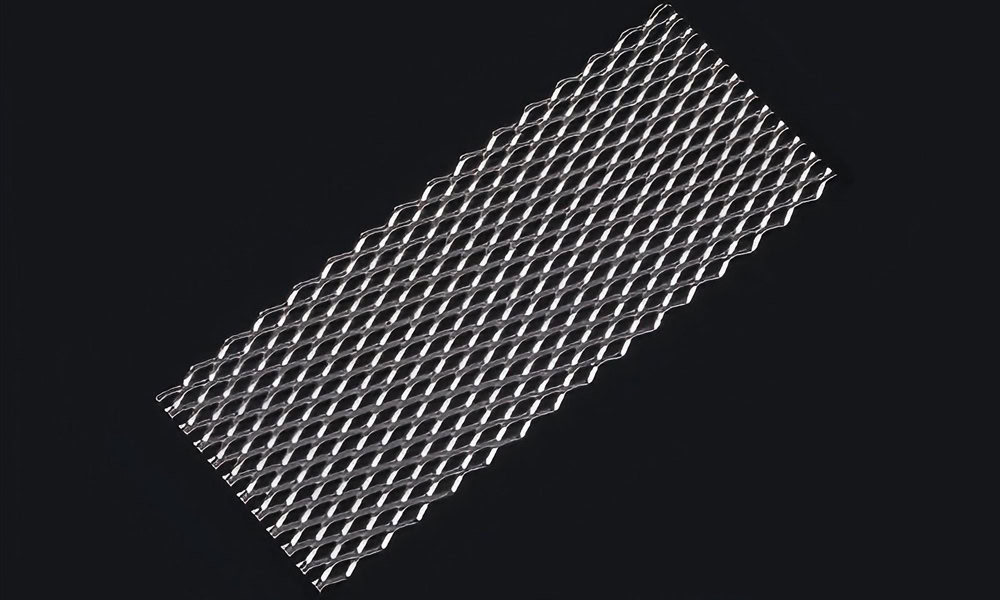
Mesh Platinum Titanium Anodes
It has a large specific surface area and uniform current distribution, which can provide good mass transfer and reaction conditions in electroplating and electrolytic reactions.
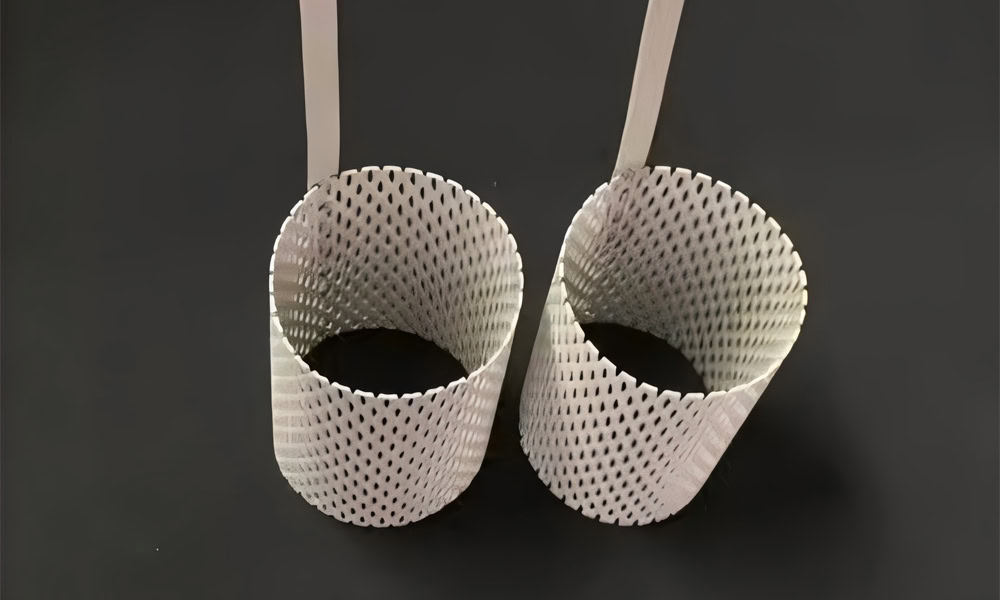
Tubular Platinum Titanium Anodes
It has a tubular structure and can be used in some special electrolytic equipment or occasions where electrochemical reactions need to be carried out in a specific space.
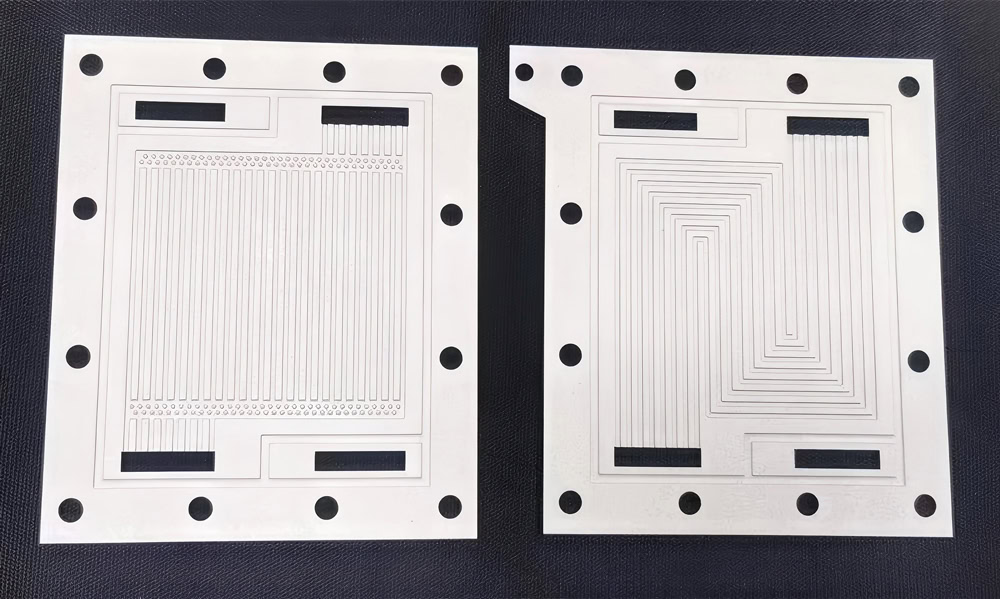
Customized Platinum Anodes
Different titanium matrix options, such as Gr1, Gr2, Ti-6Al-4V, etc. Customized specifications include plate, mesh, tube, etc., as well as surface treatment (sandblasting, polishing), etc.
Customized Platinum Titanium Anode Service
Wstitanium’s custom platinum-titanium anode service has won wide recognition in the electrochemical field with its high-quality product quality, strong technological innovation capabilities and excellent customer service. For companies and projects that require custom platinum-titanium anodes, Wstitanium is a trusted partner.
Evaluation
Wstitanium’s sales team will communicate with you in detail to understand the application areas, technical parameters and other information. For example, for customers in the chlor-alkali industry, it is necessary to understand the specifications of the electrolytic cell, current density, electrolyte composition, etc. For customers in the electroplating industry, it is necessary to understand the type of electroplating solution, coating requirements, electroplating time, etc. The technical team’s evaluation includes whether the design scheme, material selection, and manufacturing of the platinum-titanium anode are feasible, and whether they can meet your performance requirements. If necessary, relevant experiments and simulations will be carried out to verify the feasibility of the design scheme.
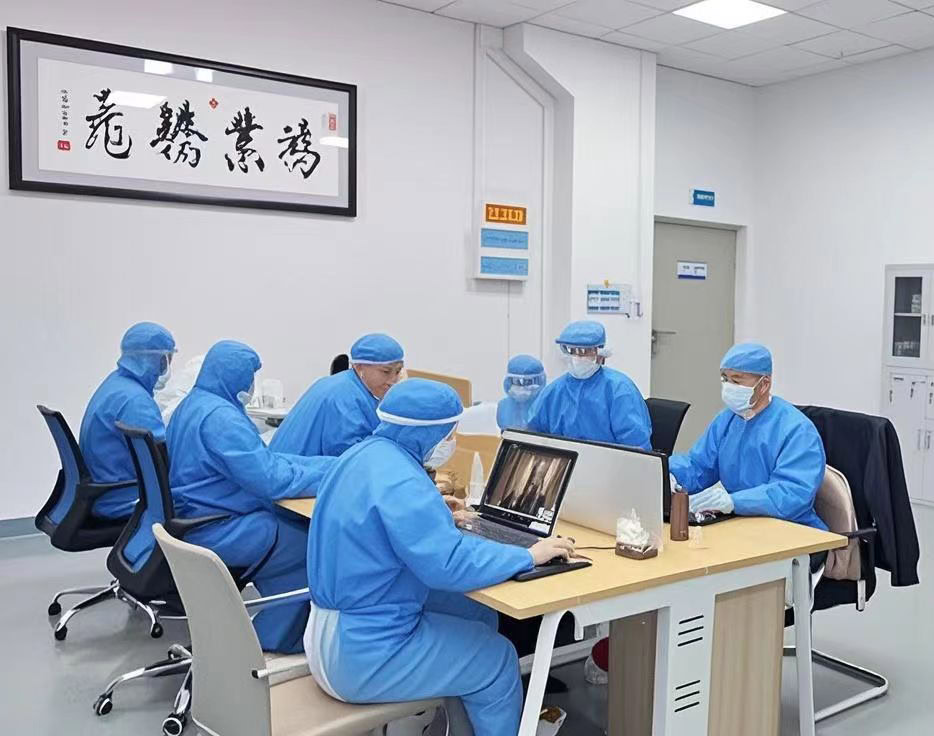

Based on the results of the technical evaluation, Wstitanium’s cost accounting team will budget the cost of customizing the platinum-titanium anode. The cost budget includes raw material costs, manufacturing costs, quality inspection costs, transportation costs, etc. The sales team will feedback the cost budget information to the customer and further communicate and negotiate with the customer to determine the final price and delivery date.
Platinum Titanium Anode Design
The design of platinum titanium anode includes shape, size, structure, coating thickness, etc. For example, for the anode of a large electrolytic cell, it may be necessary to design a mesh structure to improve the uniformity of current distribution. For anodes that require high activity, the thickness of the platinum coating may need to be increased. The selection of titanium substrates needs to consider factors such as its corrosion resistance, mechanical properties and processing properties; the platinum coating needs to consider factors such as its electrochemical activity, stability and cost. Afterwards, the technical team will organize the designed anode scheme and material selection scheme into detailed technical documents, including design drawings, technical specifications, manufacturing processes, etc. These documents will serve as the basis for manufacturing and will also be provided to customers for review and confirmation.

Custom Specifications
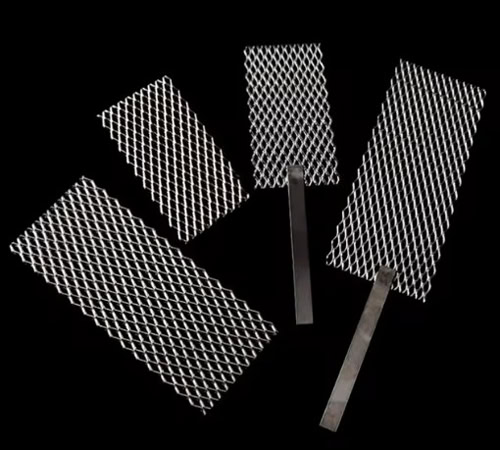
Wstitanium custom platinum titanium anodes include a variety of configurations such as strips, plates (standard, expanded, corrugated or perforated), foils, blocks, wires, rods, discs, bars and tubes to perfectly fit into specific operating spaces.
- Rods: Available in diameters from 10mm to 100mm.
- Wires: Available in diameters from 0.5mm to 15mm.
- Tubes: Available in diameters from 10mm to 200mm.
- Plate: Available in thicknesses from 0.5mm to 5mm.
- Mesh: Available in thicknesses from 0.5mm to 2.0mm.
- Coating: Available in thicknesses from 0.5μm to 5μm.
| Base metal | Gr1, Gr2 titanium |
| Coating material | Pt |
| Temperature range | <80 ℃ |
| Current density | ≤ 5000 A/m² |
| Fluoride content | <50mg / L |
| Precious metal content | ≥20g / m2 |
| Coating thickness | 0.2-10μm |
| PH value | 1-12 |
Coating Thickness
Depending on the application, Wstitanium can customize platinum coatings of different thicknesses for you. In some applications that require a long anode life, such as the chlor-alkali industry, a thicker platinum coating (such as 10-20 microns) may be required to ensure that the anode can maintain good performance during long-term use. In some cost-sensitive applications, such as small electrochemical experimental devices, a thinner platinum coating (such as 1-5 microns) can be selected. Customization of platinum coatings of different thicknesses can be achieved by precisely controlling the parameters of the preparation process such as electroplating, thermal decomposition or chemical plating.
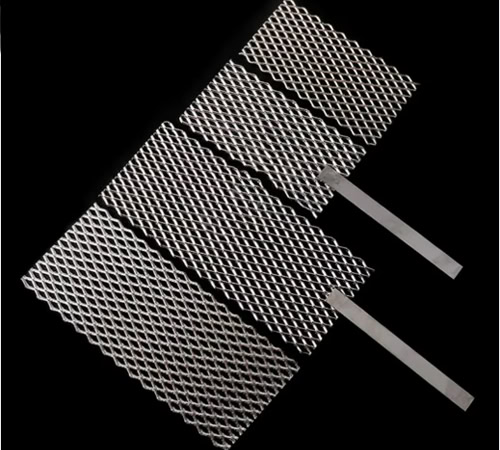
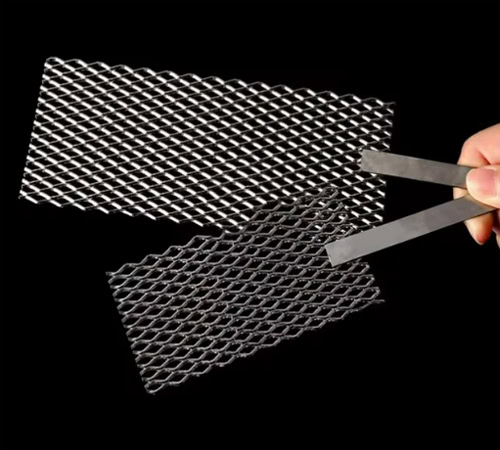

Platinum Titanium Anode Manufacturing
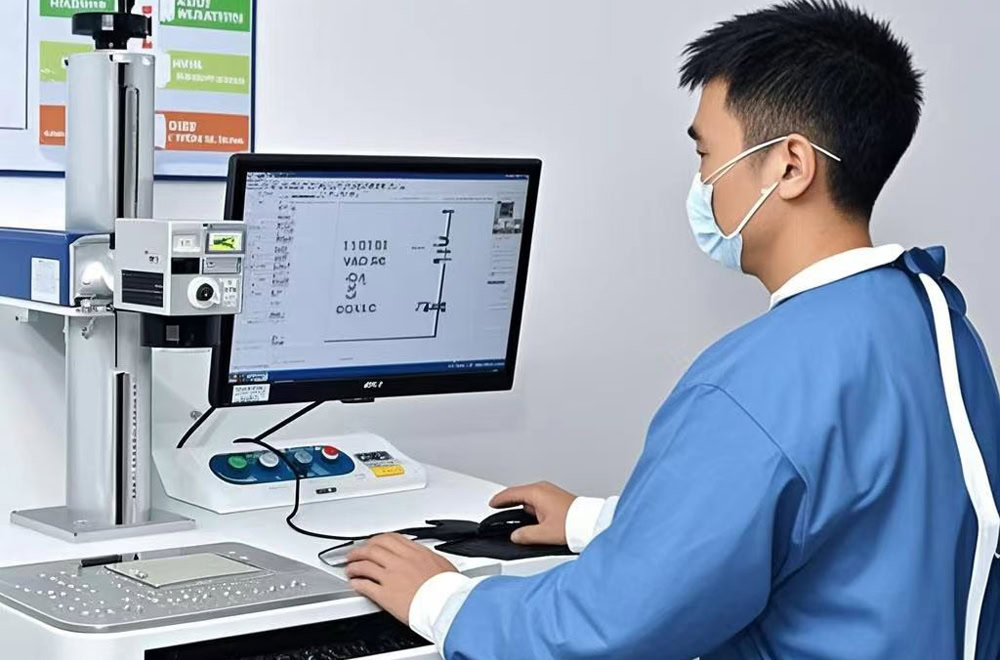

Select Titanium Substrate
Choose pure titanium with a purity of more than 99%, such as Gr1 and Gr2. The purity of platinum should not be less than 99.95%. Auxiliary materials include binders and solvents, such as ethyl cellulose, pine alcohol, or chloroplatinic acid.
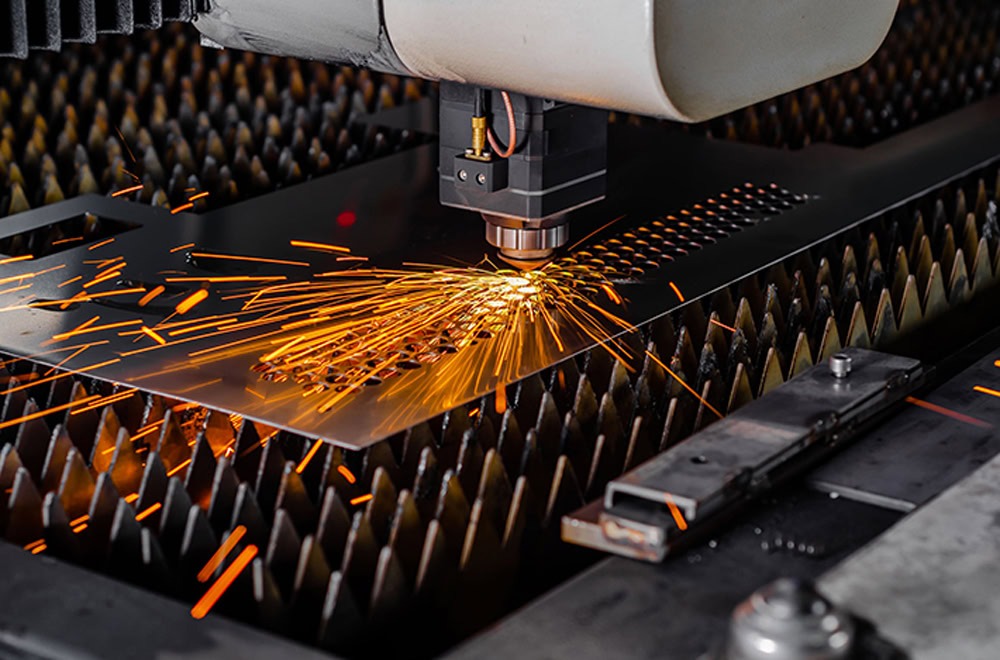

Forming
According to the design, laser cutting machines or CNC machining centers cut titanium into the required shape and size, and then turn, drill, mill, etc. to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface flatness, with a tolerance of ±0.05mm.
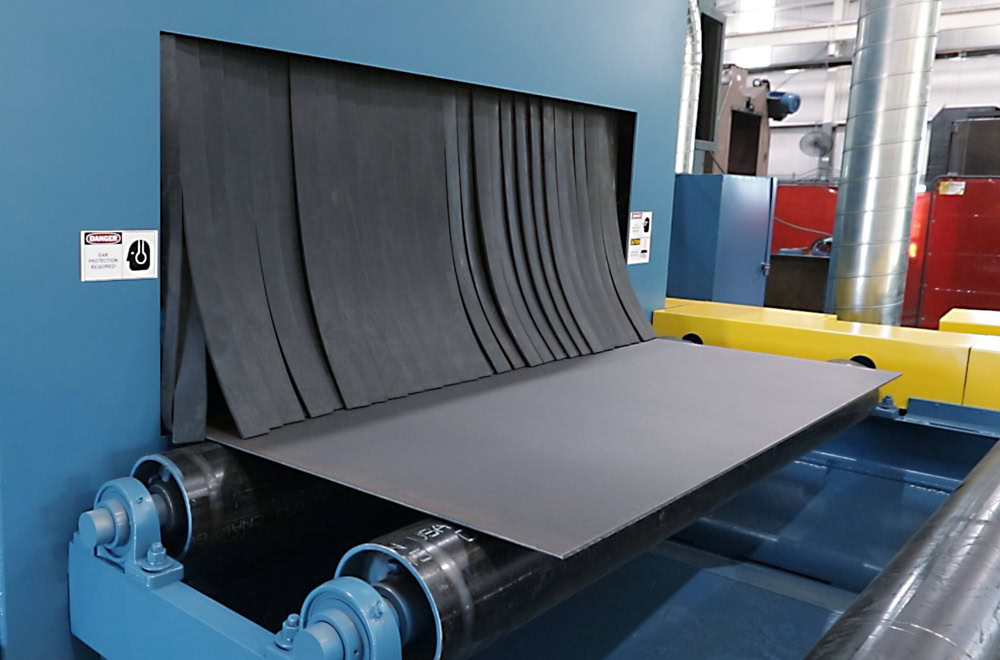

Sand Blasting
Sandblasting will form many tiny concave and convex pits on the titanium surface, and its roughness will increase from Ra0.8μm to Ra3.2μm, providing better adhesion for coatings, plating, etc., and preventing the coating from falling off.
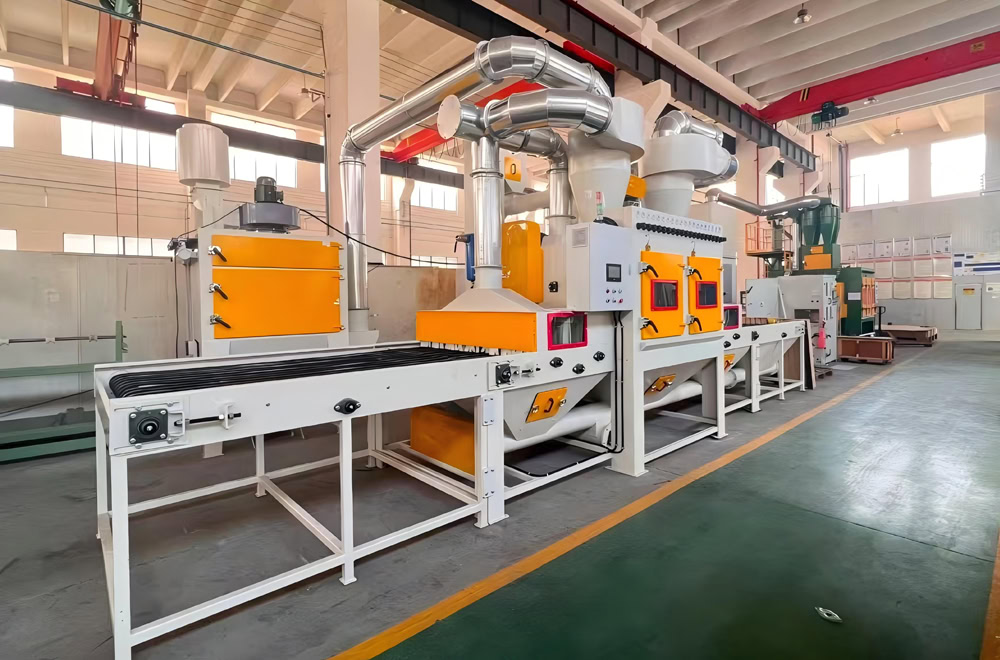

Leveling / Annealing
Leveling can make the titanium flatness reach a higher precision and be controlled within ±0.05mm/m. The leveling process can eliminate some of the internal stress caused by deformation, making the internal structure of the titanium plate more uniform,
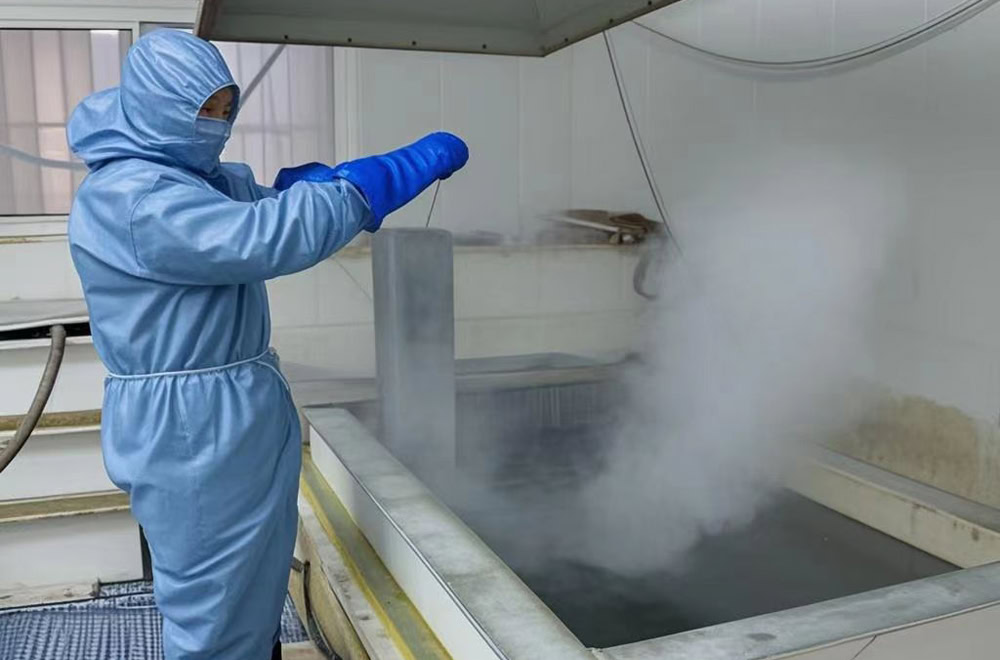

Pickling
Pickling can effectively remove the oxide scale, oil stains and dust on the titanium surface. After pickling, the titanium plate is conducive to chemical reaction and coating adhesion, and enhances the bonding force between the coating and the titanium plate,

Liquid Preparation
According to different platinum coating methods (electroplating, thermal decomposition, physical vapor deposition, chemical vapor deposition), prepare the required 5%-15% concentration of platinum salt, or 99.95% sputtering target.

Coating
Electroplating, thermal decomposition, vacuum coating (physical vapor deposition, chemical vapor deposition) are ways to manufacture platinum coatings. Among them, electroplating and thermal decomposition are relatively low in cost.

Drying
The coating liquid is evenly coated on the surface of the titanium substrate, and dried at 100-120℃ for 10-15 minutes after each coating. Repeat the coating 3-5 times to achieve the required coating thickness. Then thermally decompose at 400-600℃.

Quality Inspection
Measure the thickness of the platinum coating by metallographic microscope, electron microscope or X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. The coating thickness should meet the design requirements and the deviation should be controlled within ±3%.
Coating Preparation Technology
Platinum-titanium anodes have become key components in many electrochemical processes, and the core of their performance depends largely on the platinum coating on the surface. Platinum, as a precious metal with extremely stable chemical properties, hardly reacts with any chemical substances. Platinum has good electrical conductivity and can quickly conduct current and reduce electrode resistance during electrochemical processes. Platinum is also an excellent catalyst with extremely high catalytic activity in many electrochemical reactions. It reduces the activation energy of the reaction, accelerates the reaction rate, and improves the selectivity and yield of the reaction. Different coating preparation methods, such as electroplating, pyrolysis, physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etc., give platinum-titanium anodes different properties to meet the needs of different application scenarios.
Electroplating
The electroplating method is to use the titanium substrate as the cathode and place it in an electrolyte containing platinum salt. Through the external DC power supply, the platinum ions in the electrolyte migrate to the surface of the titanium substrate under the action of the electric field, and obtain electrons on the cathode surface, reducing them to platinum atoms, and gradually depositing to form a platinum coating.
- Anode reaction: H₂O - 2e⁻ → 2H⁺ + 1/2O₂↑
- Cathode reaction: PtCl₆²⁻ + 4e⁻ → Pt + 6Cl⁻
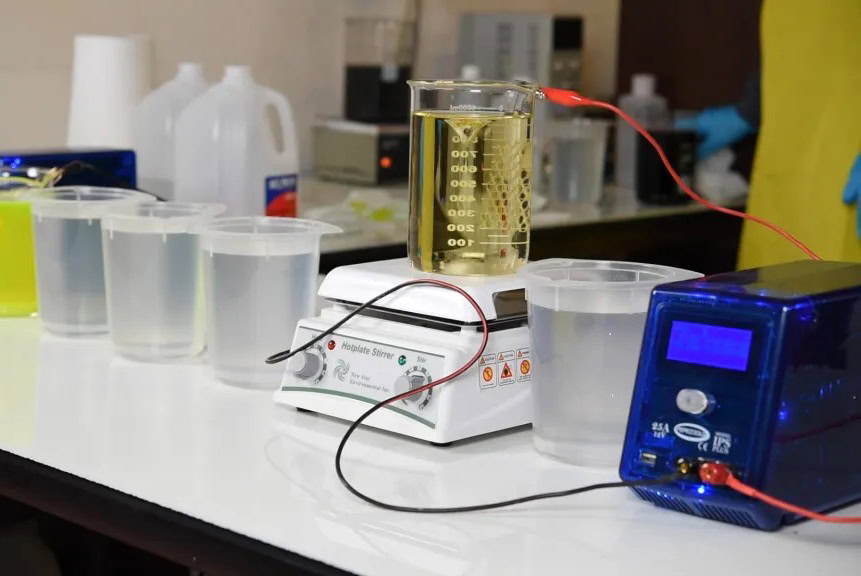

Under acidic conditions, platinum ions mainly exist in the form of PtCl₆²⁻, which is conducive to the electroplating reaction. Under alkaline conditions, platinum ions may form hydroxide precipitation, affecting the electroplating effect. Therefore, it is usually necessary to control the pH value of the electrolyte at 1-3.
Thermal Decomposition
The thermal decomposition method is to dissolve a compound containing platinum (such as chloroplatinic acid, platinum salt, etc.) in an appropriate solvent to prepare a coating liquid, and then evenly coat the coating liquid on the surface of the titanium substrate by spraying, dipping, etc. to form a thin film. After that, the titanium substrate coated with the platinum compound is thermally decomposed at a high temperature to decompose the platinum compound and form a platinum coating on the surface of the titanium substrate.
- H₂PtCl₆ → Pt + 2HCl↑ + 2Cl₂↑

The thermal decomposition temperature is between 400-800℃, and the specific temperature needs to be adjusted according to the platinum compound used and the material of the titanium substrate. The thermal decomposition time is between 30-120 minutes, and the optimal thermal decomposition time needs to be determined through experiments.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
During the ion plating process, a certain amount of working gas (such as argon) needs to be introduced to generate plasma. By precisely controlling parameters such as ion source power, bias voltage, gas flow rate, etc., the structure and composition of the coating can be adjusted to prepare platinum coatings with different properties. Dense, uniform coatings with specific crystal structures improve the corrosion resistance, conductivity and catalytic activity of the coating.
PVD technology is carried out in a vacuum environment and does not use chemical solutions. Therefore, it does not produce pollutants such as wastewater and waste gas like electroplating. It is environmentally friendly and meets the requirements of green development of modern industry.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a process in which a gaseous precursor (a compound containing platinum) undergoes a chemical reaction under high temperature, low pressure or plasma conditions to decompose platinum atoms and deposit them on the surface of a titanium substrate to form a platinum coating. For example, an organic metal compound of platinum (such as platinocene) is used as a precursor. At high temperature, platinocene decomposes to produce platinum atoms and other volatile products, which are deposited on the surface of the titanium substrate and gradually grow to form a platinum coating.
- (C₅H₅)₂Pt → Pt + 2C₅H₅↑
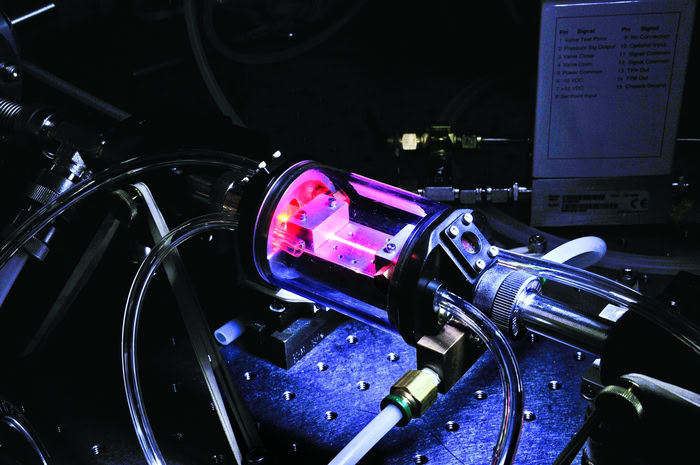
Temperature is an important factor affecting the CVD reaction, generally between 500℃ and 1000℃ to ensure that the precursor can be fully decomposed. The reaction pressure also has a significant effect on the CVD process, usually between 10⁻¹ and 10³Pa.
Quality Inspection and Performance Evaluation
The surface of the platinum-titanium anode should be uniform and smooth under an optical microscope, without obvious scratches, bubbles, peeling and other defects. The coating thickness should meet the design requirements, and the deviation should be controlled within ±3%. The bonding strength between the platinum coating and the titanium substrate is evaluated by scratch test, bending test or thermal shock test. In the scratch test, the coating should not peel or peel off under a certain load. At the specified bending angle, the coating should not crack or fall off. In the thermal shock test, the coating should remain intact after multiple hot and cold cycles. Finally, the platinum-titanium anode is subjected to polarization curve test, cyclic voltammetry test, AC impedance test, etc. to evaluate its electrochemical activity, stability and electrocatalytic performance in different electrolyte solutions.
| Test Items | Test Condition | Qualification |
| Combining power | 3M adhesive tape | No black marks on the tape |
| Bend 180° on Φ12mm round shaft | No peeling at the bend | |
| Uniformity test | X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer | ≤15% |
| Coating thickness | X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer | 0.1-15μm |
| Chlorination potential | 2000A/m2, Saturation NaCl,25±2℃ | ≤1.15V |
| Analytical chlorine polarization rate | 200/2000A/m2, Saturation NaCl,25±2℃ | ≤40mV |
| Enhanced lifespan | 40000A/m2,1mol/L H2SO4,40±2℃ | ≥150h(1μm) |
| Intensive weightlessness | 20000A/m2,8mol/L NaOH,95±2℃, electrolysis 4h | ≤10mg |
Platinum Titanium Anode Application
As an excellent electrode material, platinum-titanium anode has the advantages of excellent electrocatalytic activity, good chemical stability, high conductivity and long service life. It is widely used in chlor-alkali industry, sewage treatment, electroplating, metal extraction and other fields.
Chlor-alkali Industry
The platinum-titanium anode is used as an anode material in the chlor-alkali industry. Its main function is to catalyze the oxidation reaction of chloride ions, causing them to lose electrons on the anode surface to generate chlorine. The production environment of the chlor-alkali industry is characterized by strong corrosion and high current density. With its excellent corrosion resistance, the platinum-titanium anode can work stably for a long time in a high-concentration salt water and a strong oxidizing chlorine environment, greatly reducing the loss and replacement frequency of the anode. Its good catalytic activity significantly improves the efficiency of chlorine generation, and it can operate at a higher current density, thereby increasing the production capacity of the entire chlor-alkali production system.

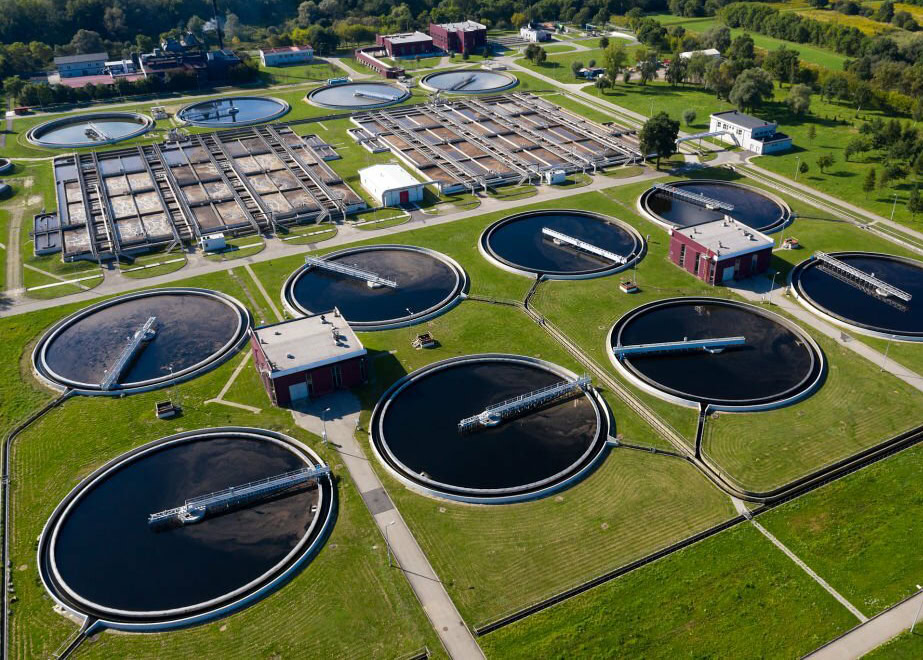
Sewage Treatment
In the field of sewage treatment, platinum-titanium anodes can decompose organic pollutants in sewage into harmless substances such as carbon dioxide and water, or oxidize and precipitate heavy metal ions by applying current, thereby purifying sewage. Platinum-titanium anodes are suitable for various types of sewage, such as industrial wastewater and domestic sewage. When treating industrial wastewater containing difficult-to-degrade organic pollutants (such as pesticide residues, antibiotics, etc.), their strong catalytic ability can accelerate the decomposition of these stubborn pollutants. In domestic sewage treatment, it can effectively remove nutrients such as ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage to prevent eutrophication of water bodies.

Seawater Desalination
Common methods for seawater desalination include electrodialysis and reverse electrodialysis. In the electrodialysis process, the platinum-titanium anode acts as an anode, which can attract anions to move toward it, and a corresponding electrochemical reaction occurs on the anode surface, promoting ion separation and water purification. In reverse electrodialysis, it also plays a key electrode role, helping to achieve the effective separation of salt and water in seawater. Its good conductivity and catalytic properties ensure that electrochemical reactions can be carried out efficiently during the desalination process, maintaining stable ion transmission and separation efficiency.

Electroplating
Platinum-titanium anodes are widely used in various electroplating processes such as copper plating, nickel plating, and gold plating. As an anode, it can provide a stable current, so that the metal ions in the plating solution are evenly deposited on the surface of the cathode (the workpiece to be plated), thereby obtaining a high-quality, uniform and dense metal coating. The high conductivity and stability of the platinum-titanium anode ensure the stable distribution of current density during the electroplating process, which helps to control the thickness and quality of the coating, reduce the defects and impurities of the coating, and meet the strict requirements of electronic components for coating performance.

Circuit Board Printing
In the manufacturing process of some electronic components, such as the etching of printed circuit boards, platinum-titanium anodes also play an important role. During the etching process, the platinum-titanium anode participates in the electrochemical reaction as an electrode, which can accurately control the etching rate and depth, and ensure the accuracy and quality of the circuit graphics on the printed circuit board.
New energy
In fuel cell technology, platinum-titanium anodes are mainly used in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) and the like. On the anode side, hydrogen undergoes an oxidation reaction under the catalytic action of the platinum-titanium anode, releasing electrons and protons. The high catalytic activity of platinum can significantly reduce the activation energy of the hydrogen oxidation reaction, increase the reaction rate, and thus improve the power generation efficiency of the fuel cell.
In addition, the platinum-titanium anode acts as an anode in the process of water electrolysis, catalyzing the oxidation reaction of water to produce oxygen. Its high catalytic activity can accelerate the decomposition reaction of water and increase the generation rate of hydrogen.

Protection principle and anode application: Cathodic protection is an effective method to prevent metal corrosion. It applies cathodic current to the protected metal to reduce its potential to a certain value, thereby inhibiting the corrosion of the metal. Platinum-titanium anodes are used as auxiliary anodes in cathodic protection systems to provide the required cathodic current for the protected metal. For example, in marine engineering, for metal structures such as offshore platforms and ships, a cathodic protection system composed of platinum-titanium anodes can be installed to effectively prevent seawater from corroding the metal structures.

With the continuous development of industrial technology and the increasing requirements for environmental protection, the application prospects of platinum titanium anodes will be broader, and at the same time, continuous technological innovation and improvement are required to improve their performance and reduce costs. Wstitanium uses more than ten years of expertise in the titanium anode industry to provide materials, surface treatments and customized specifications that match the unique needs of your project.