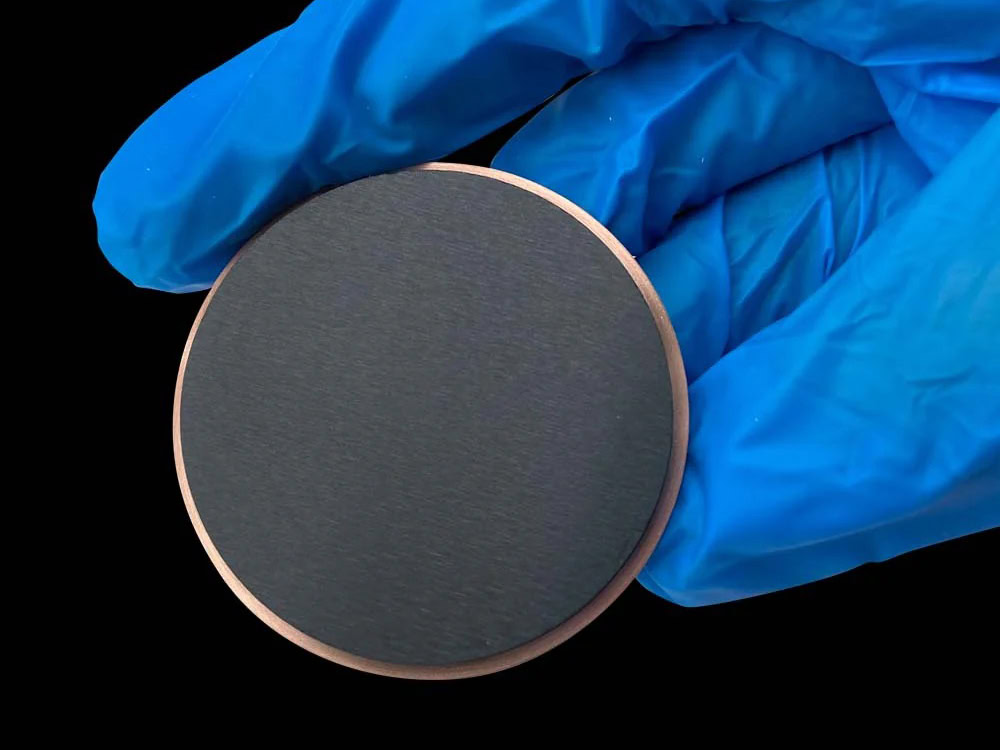
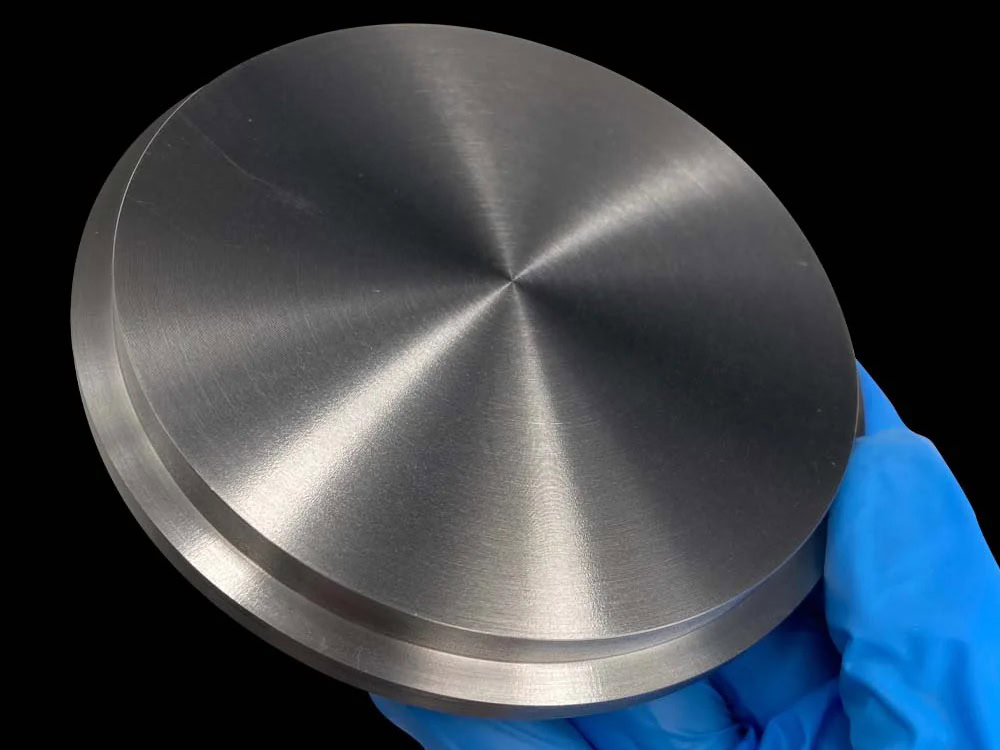
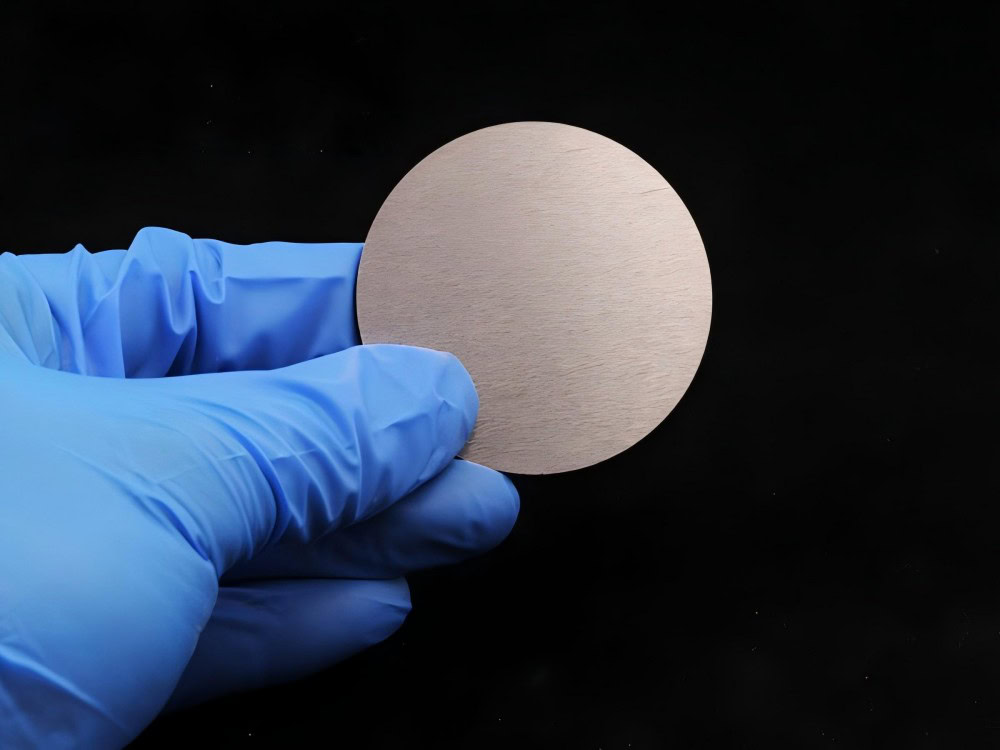
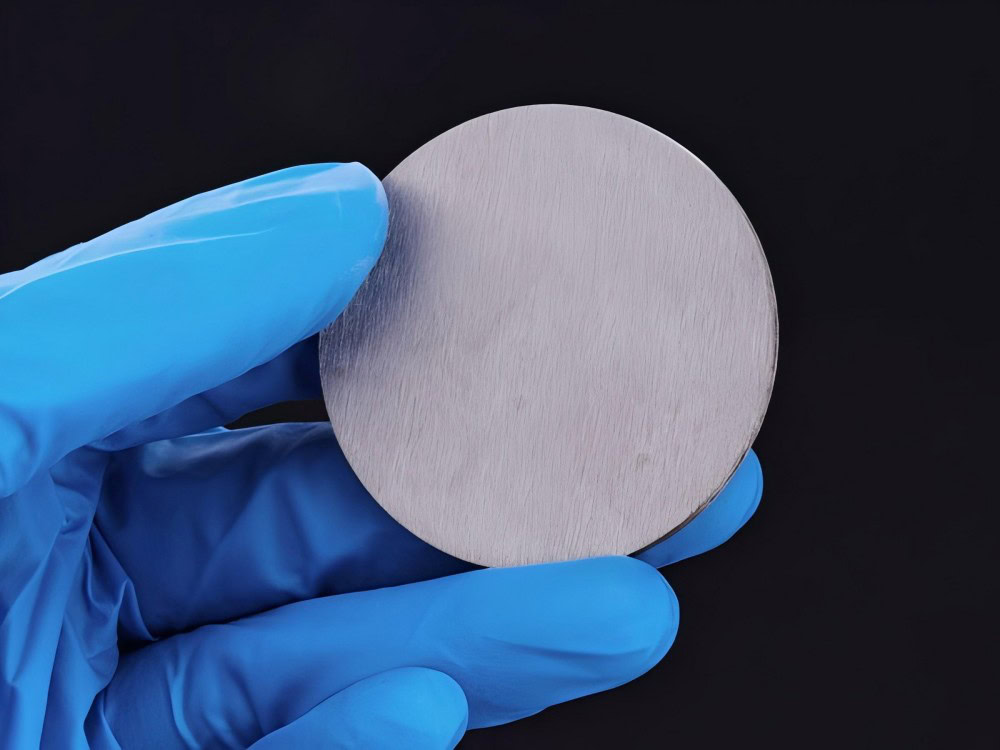
Sputtering Target Powder Metallurgy Services
Powder metallurgy plays a vital role in the manufacturing of sputtering targets and can meet the high-precision and high-quality processing requirements of sputtering targets in different industries.
- Tolerance: +/-0.005mm
- ISO 9001: 2016 Certified
- Dimension: 2mm-400mm
- Ceramic Sputtering Target
- Pure Metal Sputtering Target
Wstitanium Workshop
Our Powerful Facilities

Powder Metallurgy Sputtering Target Manufacturer
Sputtering targets are a key material widely used in many high-tech fields such as semiconductors, flat panel displays, and solar cells. Their quality and performance directly affect the quality and performance of the final product. Powder metallurgy technology plays an increasingly important role in the manufacture of sputtering targets with its unique advantages. Wstitanium has set an excellent industry benchmark in the field of sputtering target manufacturing with its deep technical accumulation and continuous innovation in the field of powder metallurgy. We focus on providing high-quality, customized sputtering target solutions to customers around the world.
What is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a process technology that uses powder (a mixture of metal or ceramic and non-metal powder) as raw material, through molding and sintering, to manufacture various types of sputtering targets of metal, ceramic and composite materials. Its basic principle is to use the mechanical bite and atomic diffusion between powder particles to combine powder particles at a temperature below the melting point to form a sputtering target with a certain shape, size and performance.
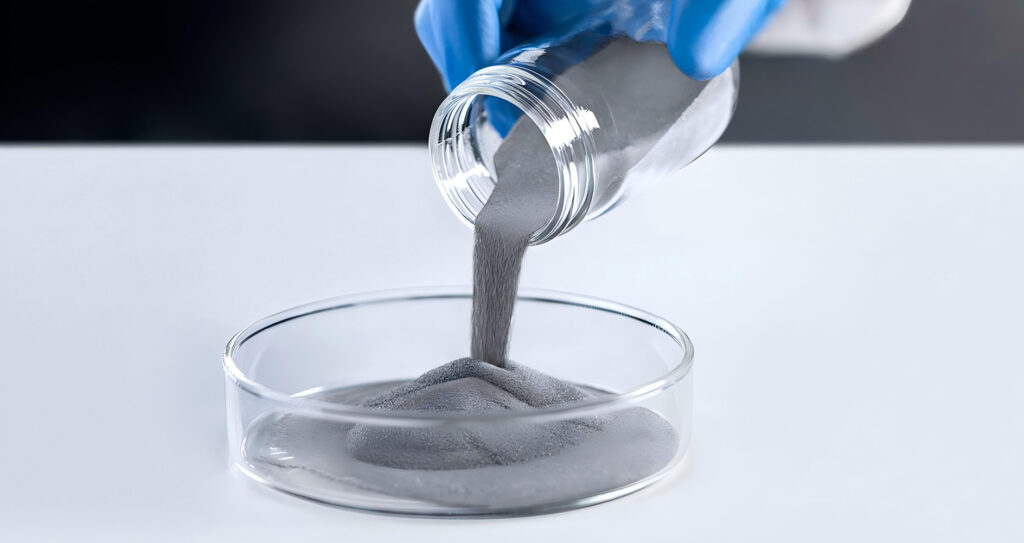

- 1. Powder Production
Any metal or ceramic that can be made into powder can be used as raw material. Commonly used powder preparation techniques include mechanical crushing, atomization, reduction, etc. Different preparation methods will affect the particle size, shape, purity and activity of the powder.
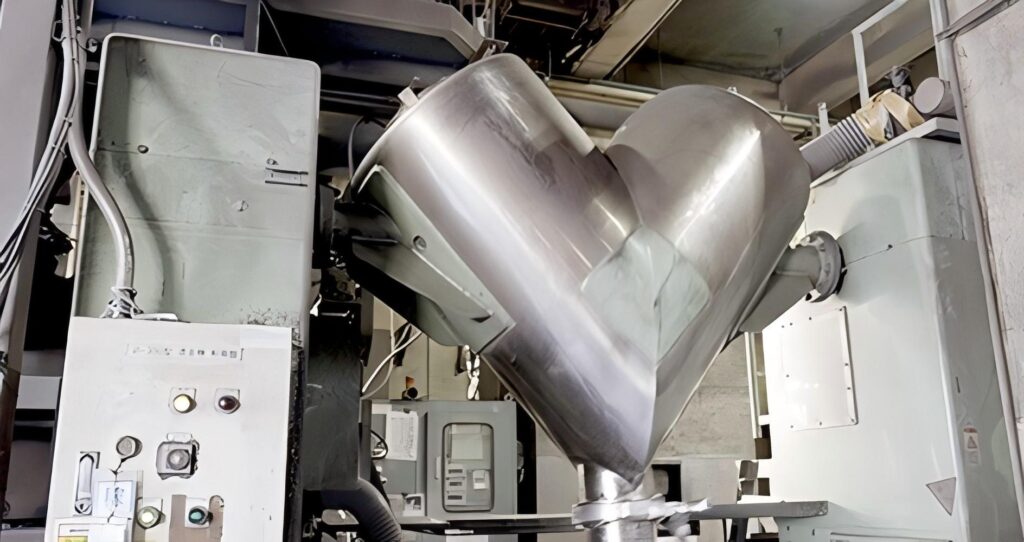

- 2.Powder Mixing
Powders of different components are mixed evenly in a certain proportion to ensure the uniformity of the sputtering target composition. The mixing process can be carried out by mechanical stirring, ball milling, etc.
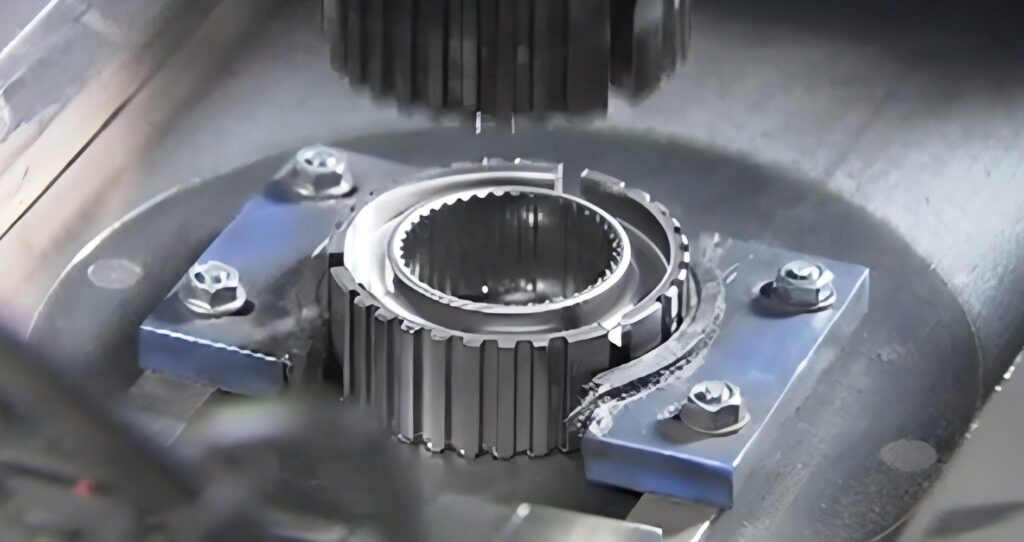

- 3. Compaction Forming
Apply pressure to the mixed powder to form a blank of the desired shape. Common forming includes compression molding, isostatic pressing, injection molding, etc. The choice of forming process depends on the shape, size and precision requirements of the target.
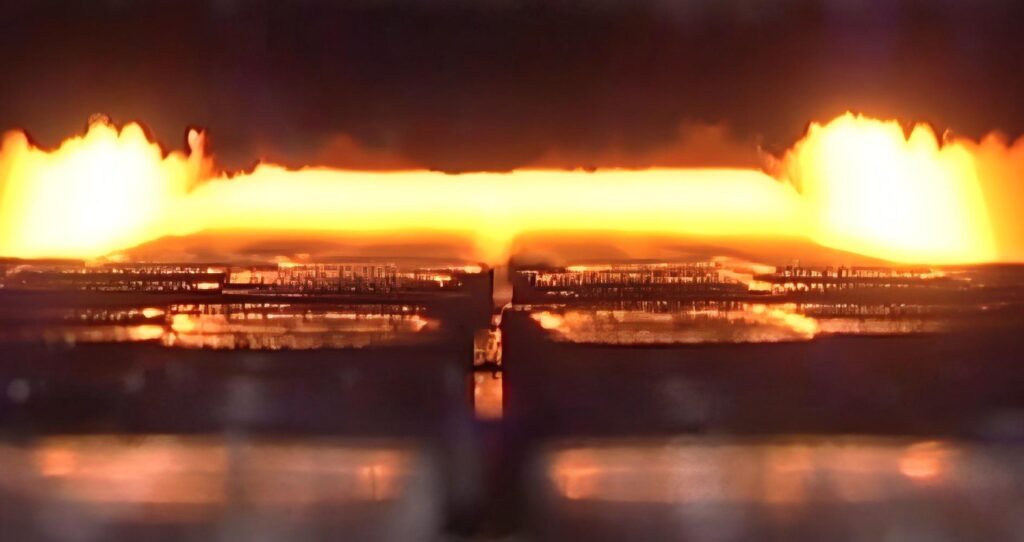

- 4. Sintering
Heat the blank to a certain temperature under protective gas to cause atomic diffusion and metallurgical bonding between particles to increase its density and strength. Sintering has a decisive influence on the final performance of the target.
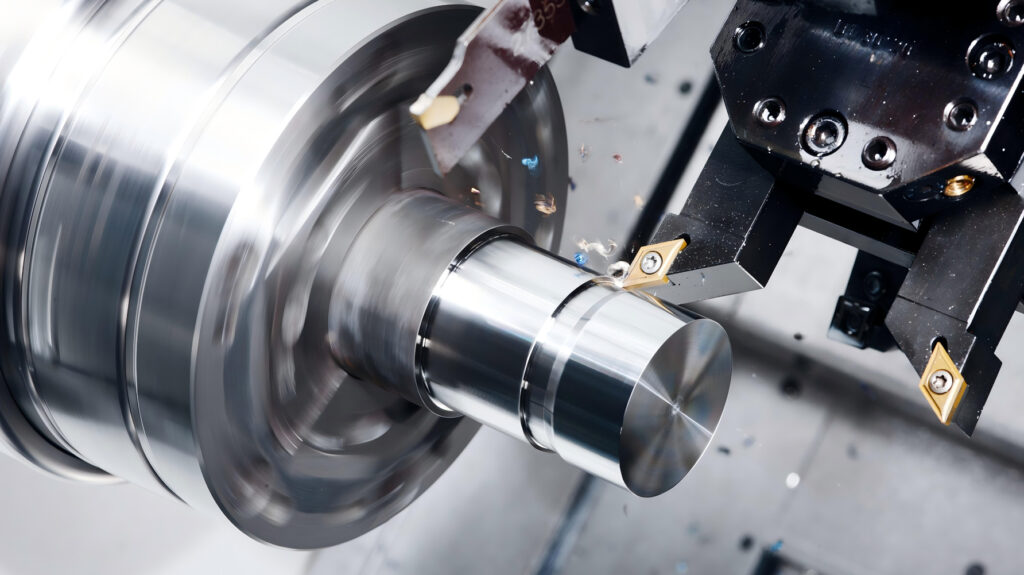

- 5. Finishing
According to the requirements specified in the drawing, the sintered sputtering target is further processed, such as CNC machining, grinding, drilling, heat treatment, surface treatment, etc., to obtain the final performance and dimensional accuracy.
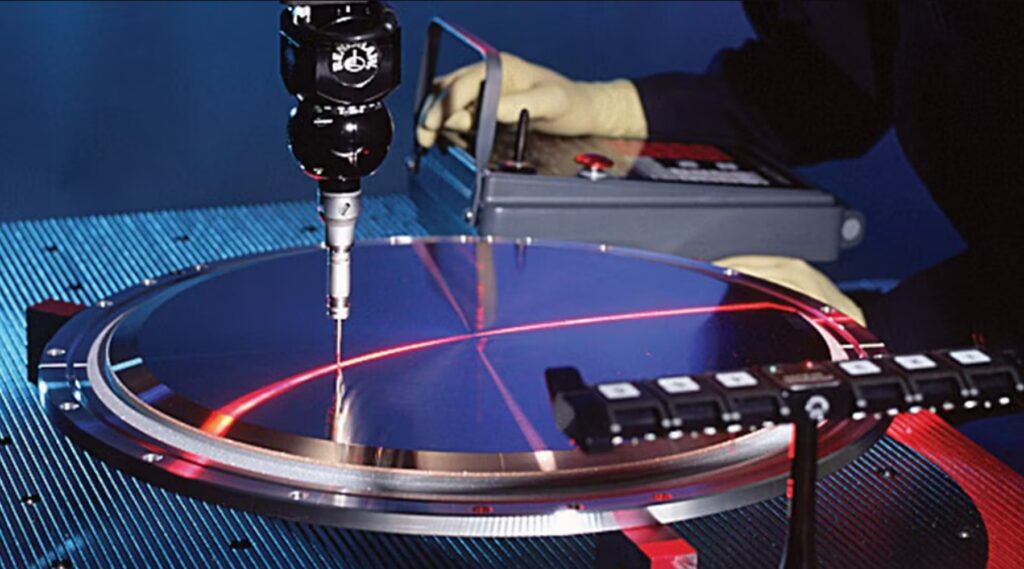

- 6. Quality Inspection
With the help of spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and other technologies, the chemical composition of the target is accurately tested to ensure that the purity and composition of the target meet the requirements.
Wstitanium Compression Forming Capabilities
Compaction Forming is a key process to give the sputtering target its initial shape. Through specific molds and pressure application, raw material powders such as metals and ceramics can be processed into the desired shape, such as flat, square, cylindrical, irregular, etc. Flat targets used in the manufacture of flat-panel displays need to be precisely shaped into large-area, high-precision flat shapes with the help of compression molding. If the shape deviation in the compression link is difficult to correct in the subsequent process, it will directly affect the adaptability of the target in the sputtering equipment and the uniformity of the coating. WSTITANIUN has three technologies for Compaction Forming sputtering targets.
- Min Size: 1×2×2 mm
- Max Size:200×200×80 mm
- Min Wall Thickness: 0.4 mm
- Max Wall Thickness: 80 mm
- Min Net Weight: 0.1 g
- Max Net Weight: 750 g
- Precision Design Reference: 0.1 % part size
- Min Tolerance: ± 0.02 mm
- Cost Effective MOQ: 100 pcs
- Max Efficiency: 30K Pcs Per Day
Compression Molding
Compression molding is one of the common molding processes used by WSTITANIUN to manufacture sputtering targets. We have invested in advanced compression molding equipment that can accurately control parameters such as pressing pressure, speed and holding time. During the compression molding process, the pre-treated powder is placed in a mold of a specific shape, and pressure is applied to the mold through a press to compact the powder in the mold. For some targets with simple shapes and small sizes, compression molding can efficiently produce high-quality blanks. In order to improve the density and uniformity of the blank, the company also uses technologies such as two-way compression and multiple compression, and adds an appropriate amount of lubricant to the powder to reduce the friction between the powder and the mold and ensure more uniform pressure transmission.
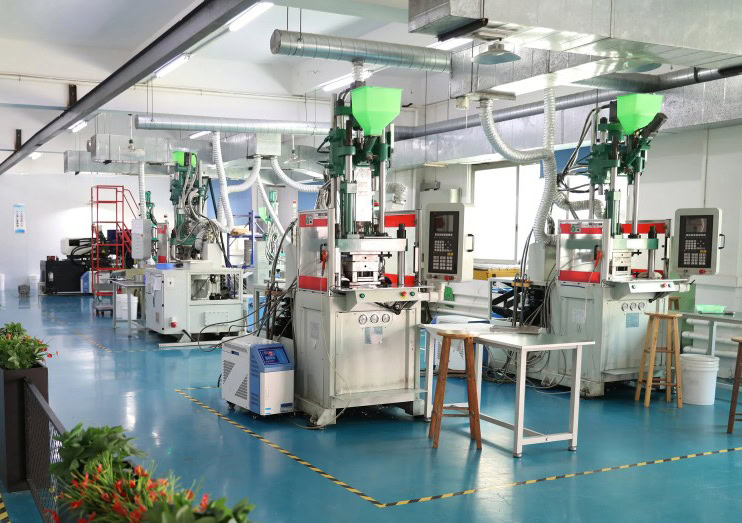

For sputtering targets with complex shapes, injection molding is an ideal molding process. First, metal or ceramic powder is fully mixed with an appropriate amount of binder to make an injection material with good fluidity. The quality and stability of the injection material are ensured by optimizing the binder formula and mixing process. Then, the injection material is heated to an appropriate temperature in the injection machine to give it good fluidity, and the injection material is injected into the mold cavity at high speed through the screw or plunger of the injection machine. During the injection process, the injection pressure, speed, temperature and other parameters are precisely controlled to ensure that the injection material evenly fills the mold cavity to form a high-precision blank. The blank after injection molding is subjected to subsequent treatments such as degreasing and sintering to obtain the final target product.
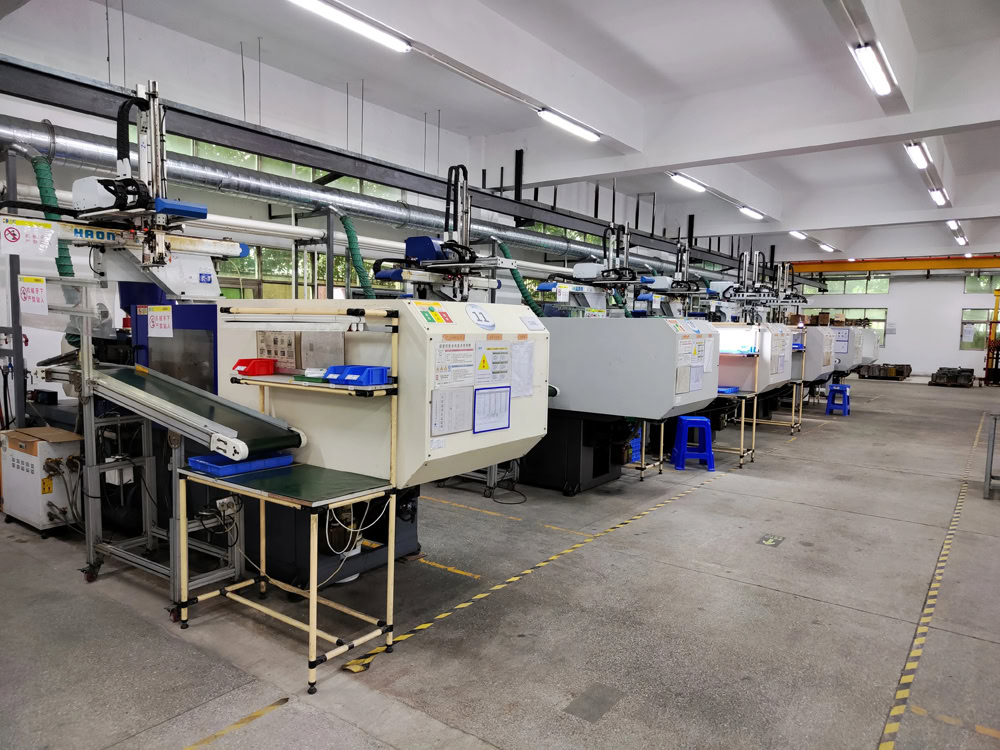

Isostatic Pressing
Isostatic pressing is a key process for WSTITANIUN to manufacture large and complex sputtering targets. Cold isostatic pressing is to load the powder into an elastic mold, seal it and put it into a high-pressure container, and evenly apply pressure through a liquid medium (such as water, oil, etc.) so that the powder is compacted and formed by the same pressure in all directions. Hot isostatic pressing is to put the powder or green body into a sealed package and put it into the hot isostatic pressing equipment under high temperature and high pressure environment, so that the powder is not only compacted, but also sintered to a certain extent, which significantly improves the density and strength of the green body. During the isostatic pressing process, it is necessary to strictly control parameters such as pressure, temperature, and holding time to ensure the stability and consistency of the molding quality.
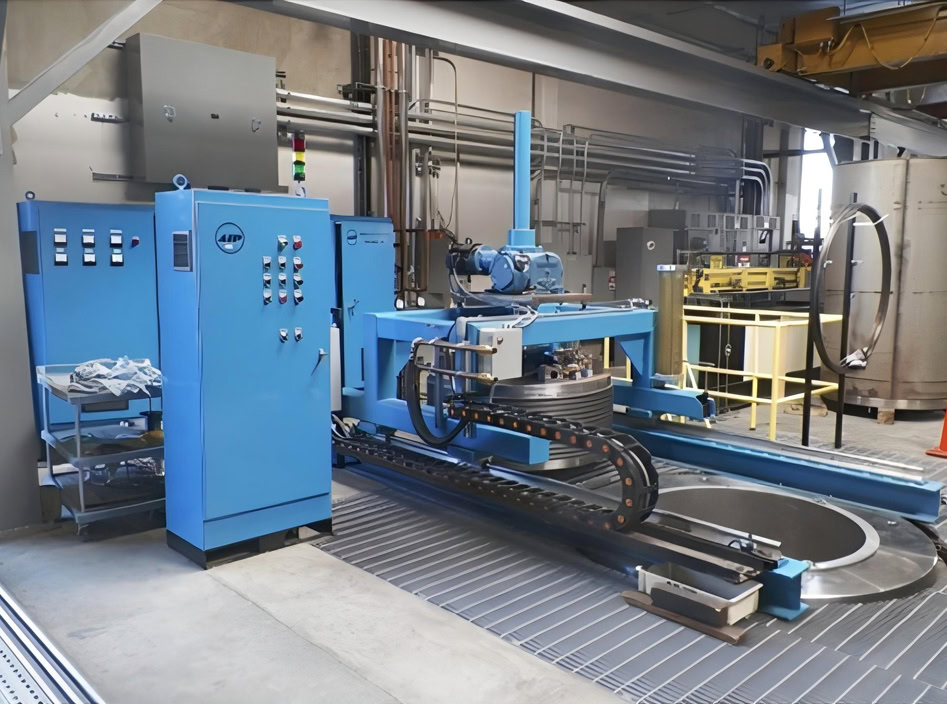

– Cold isostatic pressing equipment: WSTITANIUN has a number of cold isostatic pressing equipment of different specifications, with a pressure range of usually between 50MPa and 300MPa, which can provide uniform and stable pressure to compact the powder. These equipment adopt advanced high-pressure container design and sealing technology to ensure safety and reliability under high-pressure environment. The equipment is equipped with a high-precision pressure control system, which can accurately adjust the pressure size and holding time, and the pressure control accuracy can reach ±0.5MPa. At the same time, the cold isostatic pressing equipment has an automatic loading and unloading system to improve production efficiency and reduce the errors that may be caused by manual operation.
– Hot isostatic pressing equipment: Hot isostatic pressing equipment is one of the key equipment for WSTITANIUN to manufacture high-performance sputtering targets. The equipment can process powders or blanks under high temperature (up to 2000℃) and high pressure (up to 200MPa) environment to further improve the density, strength and comprehensive performance of the target. The hot isostatic pressing equipment adopts advanced heating systems, such as graphite resistance heating, molybdenum wire heating, etc., which can achieve rapid heating and precise temperature control, and the temperature control accuracy can reach ±5℃. The pressure system adopts advanced hydraulic drive technology and can stably provide the required pressure.
Powder Metallurgy Materials
Physical vapor deposition has strict requirements on the purity, density, microstructure and shape accuracy of sputtering targets. Different types of targets are used in different fields due to their unique physical and chemical properties. Common target materials include pure metal targets (3N, 3N5, 4N, 4N5, 5N, 6N, etc.), ceramic targets, alloy targets and rare earth targets. WSTITANIUN’s material scientists have a deep theoretical foundation in materials science and can provide you with customized sputtering target solutions. According to the requirements of different application fields for the performance of sputtering targets, the material composition is precisely designed.
Pure Metal Sputtering Target
- Gold (Au)
- Silver (Ag)
- Nickel (Ni)
- Copper (Cu)
- Titanium (Ti)
- Tungsten (W)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Chromium (Cr)
- Ruthenium (Ru)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Indium (In)
- Platinum (Pt)
- Hafnium (Hf)
- Vanadium (V)
- Niobium (Nb)
- Rhodium (Rh)
- Tantalum (Ta)
- Zirconium (Zr)
- Palladium (Pd)
- Manganese (Mn)
Ceramic Sputtering Targets
- Zinc oxide (ZnO)
- Yttrium oxide (Y₂O₃)
- Titanium nitride (TiN)
- Indium tin oxide (ITO)
- Titanium dioxide (TiO₂)
- Aluminum nitride (AlN)
- Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃)
- Zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
- Barium titanate (BaTiO₃)
- Zinc sulfide (ZnS)
- Boron nitride (BN)
- Silicon carbide (SiC)
- Zinc selenide (ZnSe)
- Cerium oxide (CeO₂)
- Scandium oxide (Sc₂O₃)
- Lanthanum oxide (La₂O₃,
- Lithium tantalate (LiTaO₃)
- Cadmium telluride (CdTe)
- Lead zirconate titanate (PZT)
Rare Earth Alloy Sputtering Target
- Cerium oxide (CeO₂)
- Terbium oxide (Tb₄O₇)
- Holmium oxide (Ho₂O₃)
- Europium oxide (Eu₂O₃)
- Samarium oxide (Sm₂O₃)
- Lanthanum oxide (La₂O₃)
- Gadolinium oxide (Gd₂O₃)
- Dysprosium oxide (D y₂O₃)
- Neodymium oxide (Nd₂O₃)
- Praseodymium oxide (Pr₆O₁₁)
- Yttrium (Y)
- NdFeB Alloy
- Scandium (Sc)
- Erbium oxide (Er₂O₃)
- Thulium oxide (Tm₂O₃)
- Lutetium oxide (Lu₂O₃)
- Ytterbium oxide (Yb₂O₃)
- Lanthanum-cerium alloy
- Terbium-doped yttrium aluminate
- Europium-doped yttrium oxide (Y₂O₃:Eu)
Alloy Sputtering Target
- Nickel-iron alloy (NiFe)
- Silver-copper alloy (AgCu)
- Nickel-vanadium alloy (NiV)
- Aluminum-nickel alloy (AlNi)
- Nickel-aluminum alloy (NiAl)
- Tungsten-titanium alloy (WTi)
- Chromium-nickel alloy (CrNi)
- Cobalt-chromium alloy (CoCr)
- Tantalum-niobium alloy (TaNb)
- Zirconium-titanium alloy (ZrTi)
- Iron-cobalt alloy (FeCo)
- Titanium-zinc alloy (TiZn)
- Zinc-aluminum alloy (ZnAl)
- Titanium-nickel alloy (TiNi)
- Titanium-silicon alloy (TiSi)
- Aluminum-silicon alloy (AlSi)
- Nickel-chromium alloy (NiCr)
- Chromium-silicon alloy (CrSi)
- Titanium-aluminum alloy (TiAl)
- Titanium-zirconium alloy (TiZr)
Sputtering Target Gallery