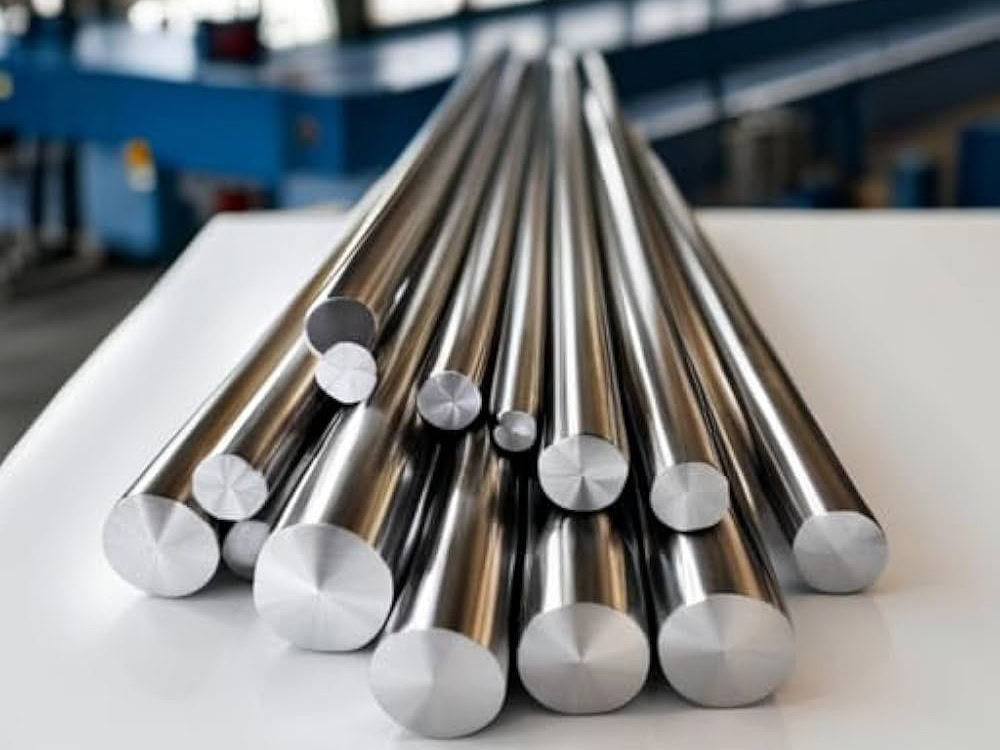
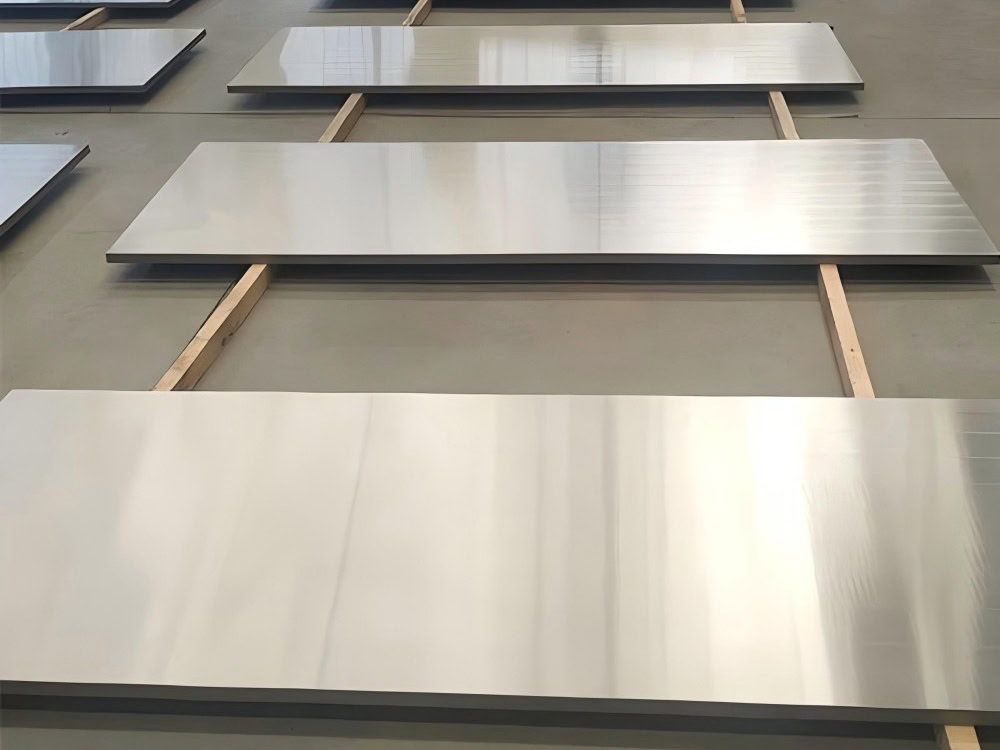
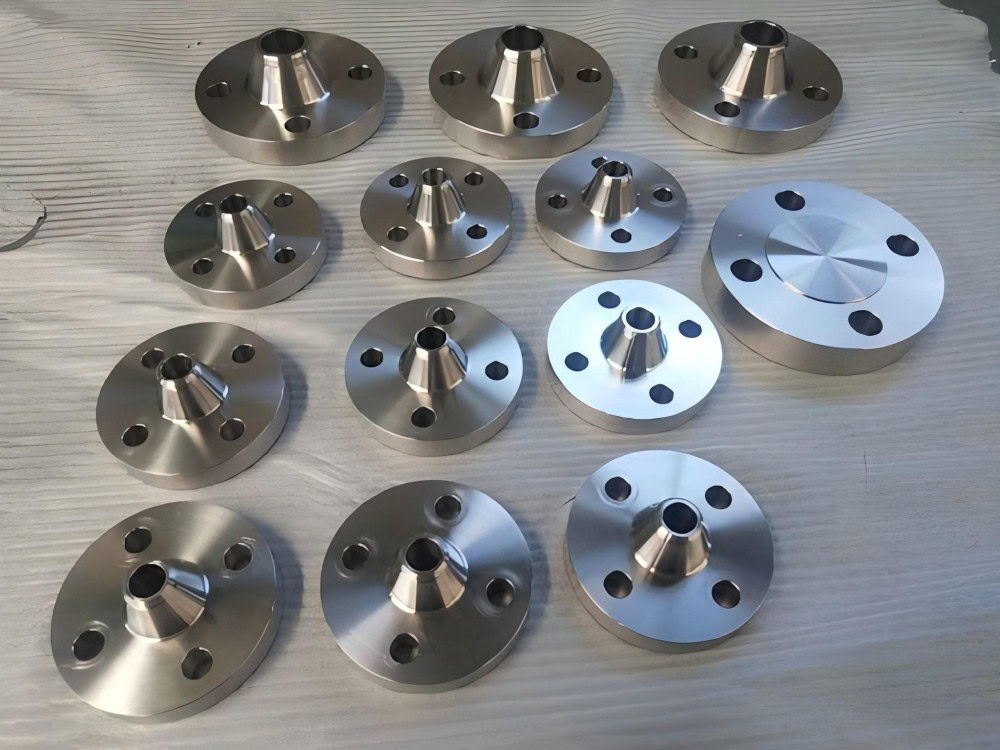
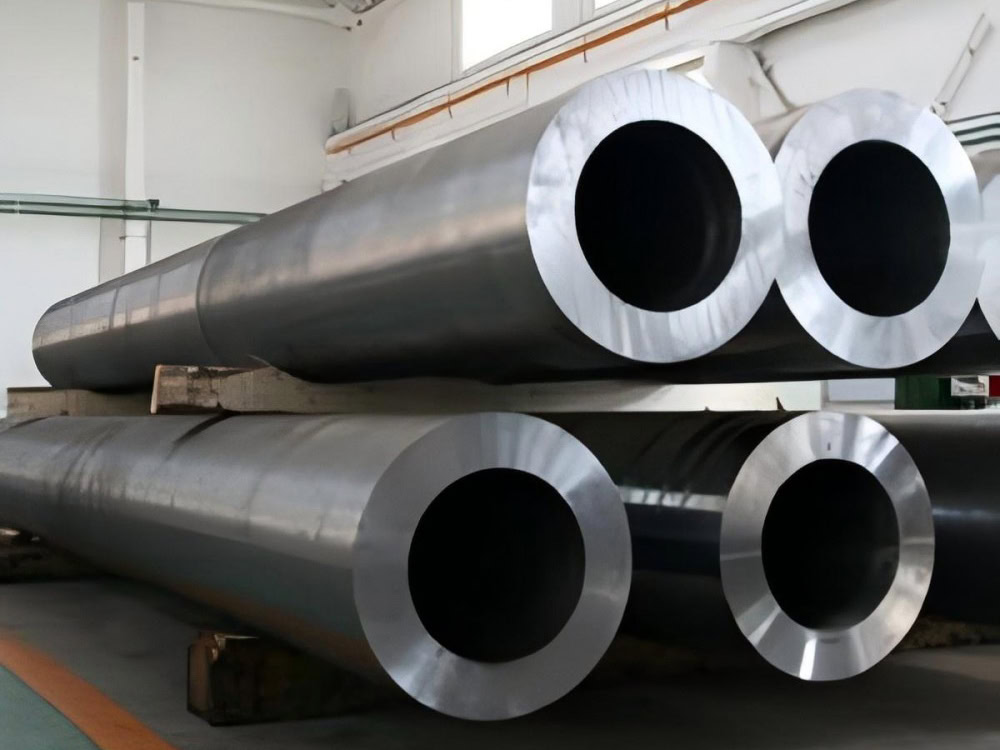
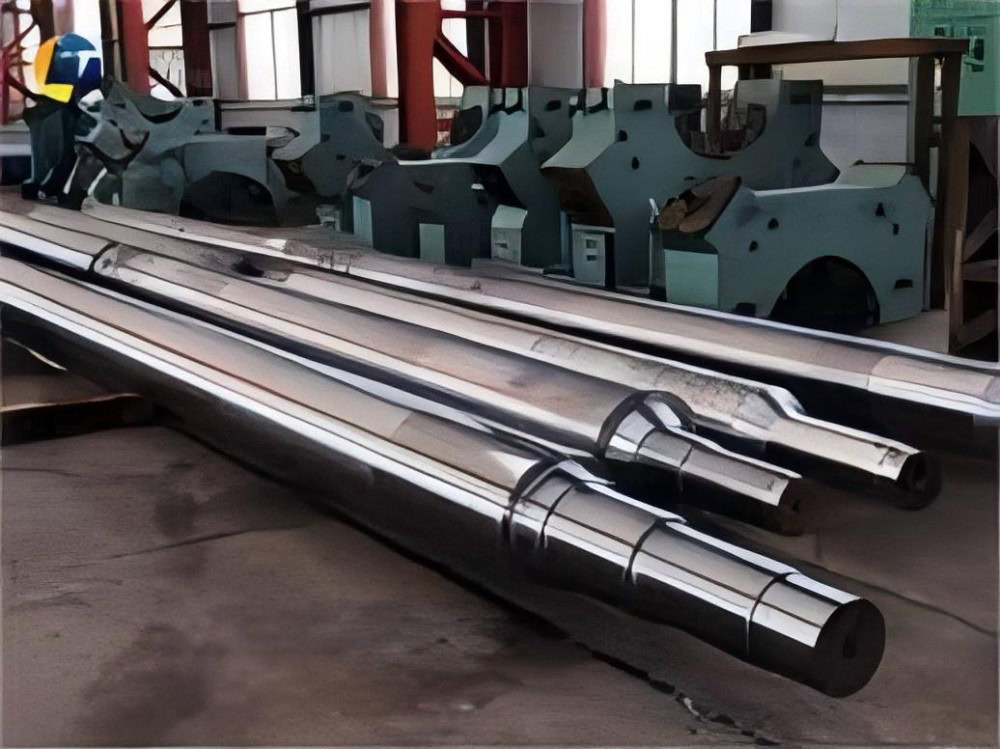
Precision Forging Titanium Services
Wstitanium has been a highly respected supplier of titanium forging products, mainly for aerospace and medical manufacturing from rolled rings, squares, rectangles, cylinders to die-forged titanium parts. Investing in advanced equipment such as rolling mills, forging machines, heat treatment furnaces, etc.
- ASTM B348
- Arbitrary Complex Geometries
- Tight Tolerances +/- 0.002”
- Reduce Steps In Assembly
- Functional End-Use Parts
Wstitanium Workshop
Our Powerful Facilities

Precision Forged Titanium Products Manufacturer
Forging creates predictable and uniform grain size and flow characteristics, which translate into superior metallurgical properties and mechanical quality, resulting in improved directional toughness of the final part. Forging also eliminates internal voids and air pockets in titanium parts, achieves predictable structural integrity, simplifies heat treatment and machining, and ensures optimal performance under load conditions. In this way, the high-strength characteristics of forgings can reduce section thickness and overall weight without compromising final integrity. If your needs are more complex titanium parts, we will be happy to accept the challenge. Wstitanium as a forging manufacturer and technically trained sales staff (many of whom have mechanical engineering degrees or workshop experience) is the solution that can provide you with on-site forging information.
What is Forging Titanium?
Titanium forging is a manufacturing process that applies external force to plastically deform solid titanium metal blanks to obtain specific shapes, sizes and properties. Forging refines the grains of titanium, makes the structure more dense and uniform, and significantly improves strength and toughness.For example, the common TC4 titanium alloy can reach a tensile strength of more than 900MPa after forging, and can withstand large impact loads. Titanium itself can form a stable and dense oxide film in most media, and forging further enhances this property. After forging, titanium can resist corrosion for a long time and has obvious advantages in marine engineering, chemical industry and other fields.
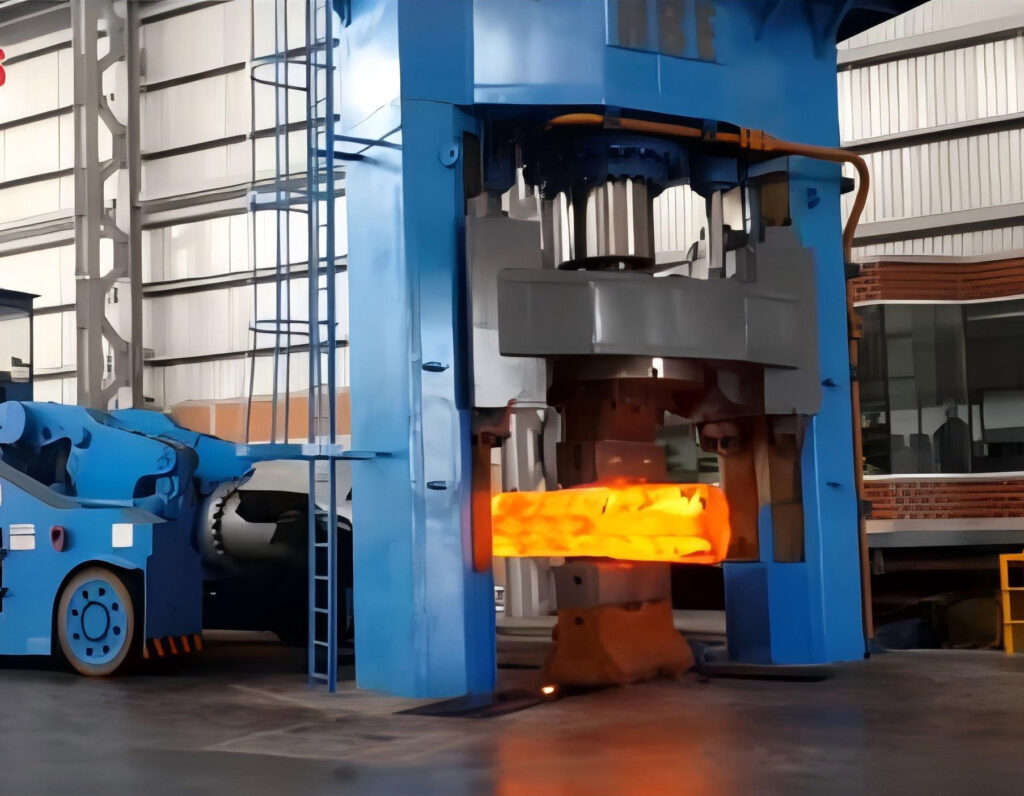
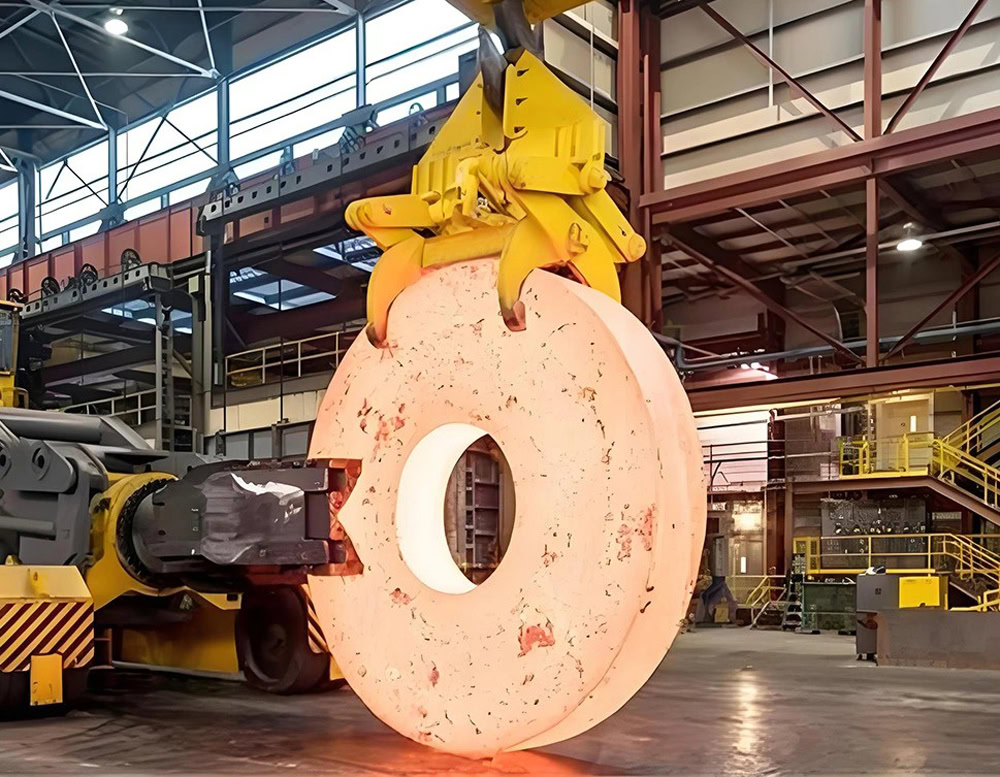


Advantages of Forging Titanium
- High Strength
The forging process refines the internal grains of titanium and makes them more tightly arranged, thereby significantly improving its strength. For example, the tensile strength of TC4 can reach more than 900MPa, and it can withstand large external forces without being prone to deformation or damage.
- Reduce Weight
In applications where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and automotive, titanium forging can significantly reduce weight without compromising strength. Titanium’s lightweight properties allow for the design of more efficient structures, thereby improving fuel efficiency and performance.
- More Resistant to Corrosion
As mentioned previously, forged titanium components can withstand harsh corrosive environments, reducing the need for protective coatings and maintenance. This feature is particularly valuable in industries such as oil and gas, where equipment is frequently exposed to corrosive substances.
- Flexible Design
Titanium forging allows greater design flexibility than other manufacturing processes. The ability to create complex shapes and geometries enables engineers to optimize designs for performance and functionality. This flexibility is critical in an industry where innovation and customization are critical.
- Cost Effective
Titanium is often considered an expensive material, but the long-term cost benefits of titanium forging cannot be ignored. The durability and longevity of forged titanium components can reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Good Toughness
while improving strength, forged titanium also maintains good toughness. This means that it can absorb and dissipate energy and will not break easily when subjected to impact or vibration, but can withstand greater dynamic loads to a certain extent.
Wstitanium Forging Titanium Capability
Wstitanium’s highly skilled forging team understands the complexity of titanium alloy processing and provides high-quality low-volume to high-volume manufacturing. It is your trusted titanium forging partner. The 4,000-ton press invested can customize titanium parts of various shapes and sizes, such as hubs, blanks, flanges, shafts, rings, discs, stepped shafts, crankshafts, cranks, etc. Forging services include free forging, die forging, rolling rings, radial forging, hot forging, cold forging, etc.
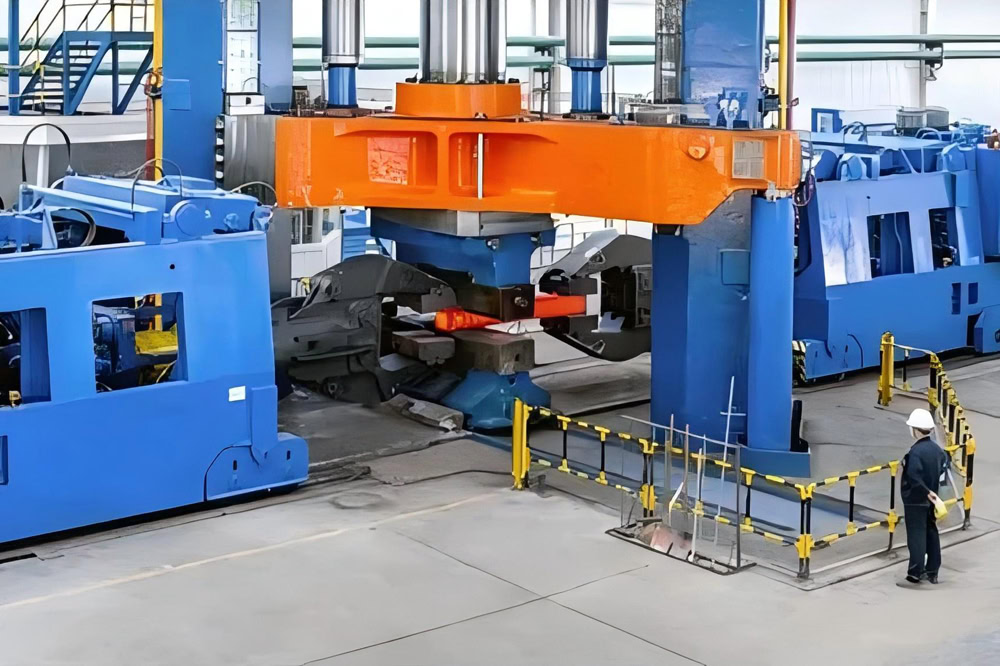

Free forging refers to a forging method that uses impact force or pressure to deform the titanium billet between the upper and lower anvils to obtain the desired shape and size. During the free forging process, the deformation of the titanium billet is not restricted.

Die forging is a manufacturing process in which a titanium billet is placed in a forging die cavity with a certain shape, and the billet is plastically deformed in the die cavity by applying pressure to obtain a part with the same shape as the die cavity. The die cavity determines the shape of the forging.
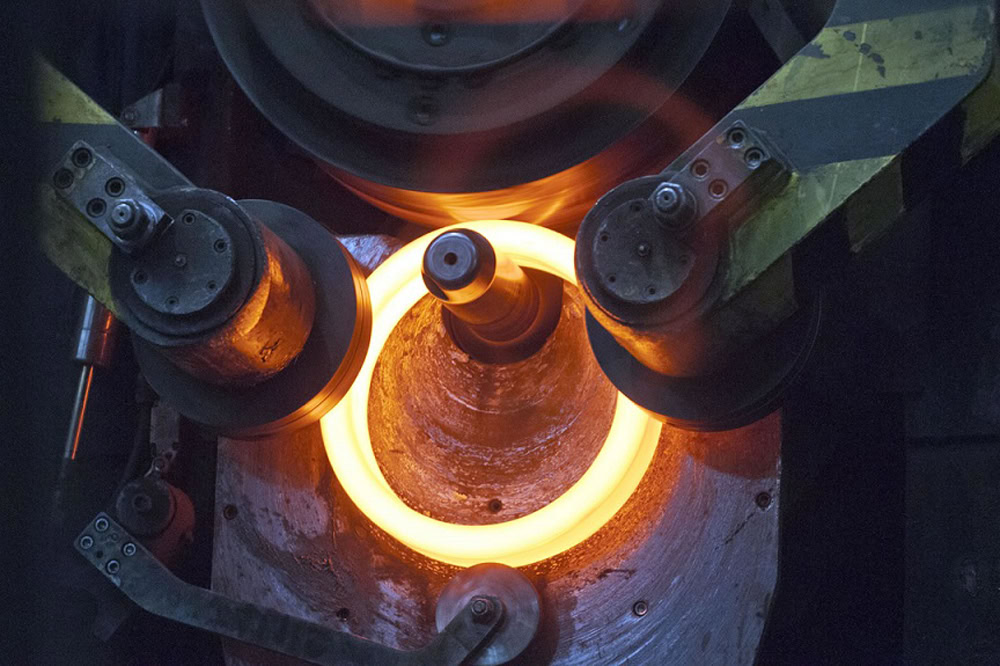

Rollers manufacture titanium rings in various diameters and weights. A round titanium part is punched to form the ring component, heated to the recrystallization temperature, then placed on an idler roll and moved toward a drive roll to expand to the desired diameter.
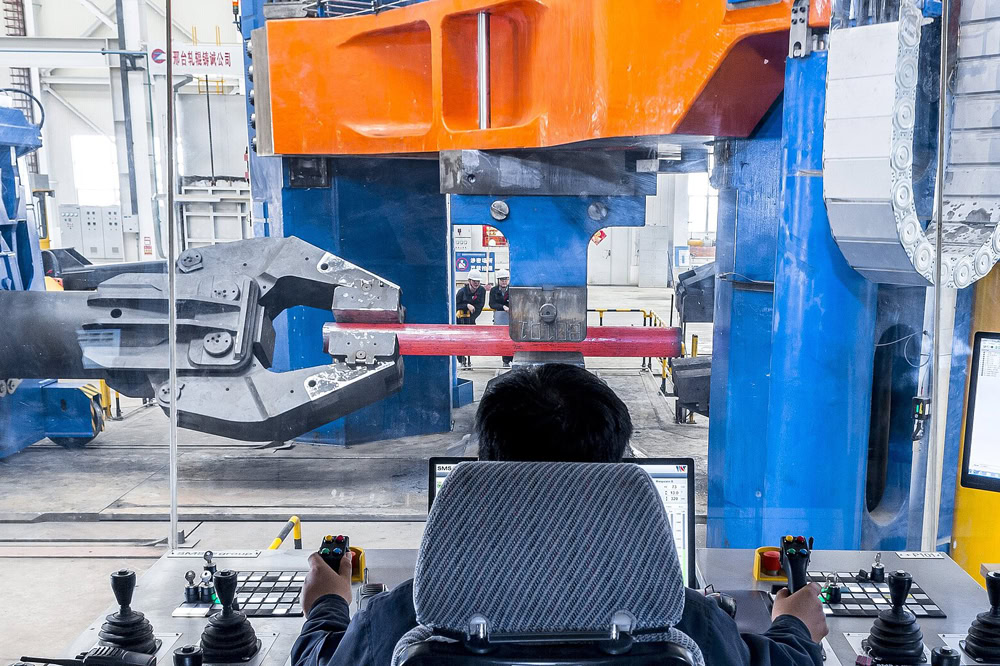

Radial Forging
Radial forging refers to the fact that the hammer heads of the forging equipment are distributed in a circle. During operation, multiple hammer heads strike the blank at a high frequency and simultaneously. It is a common process for manufacturing titanium rods, titanium tubes, and titanium shafts.
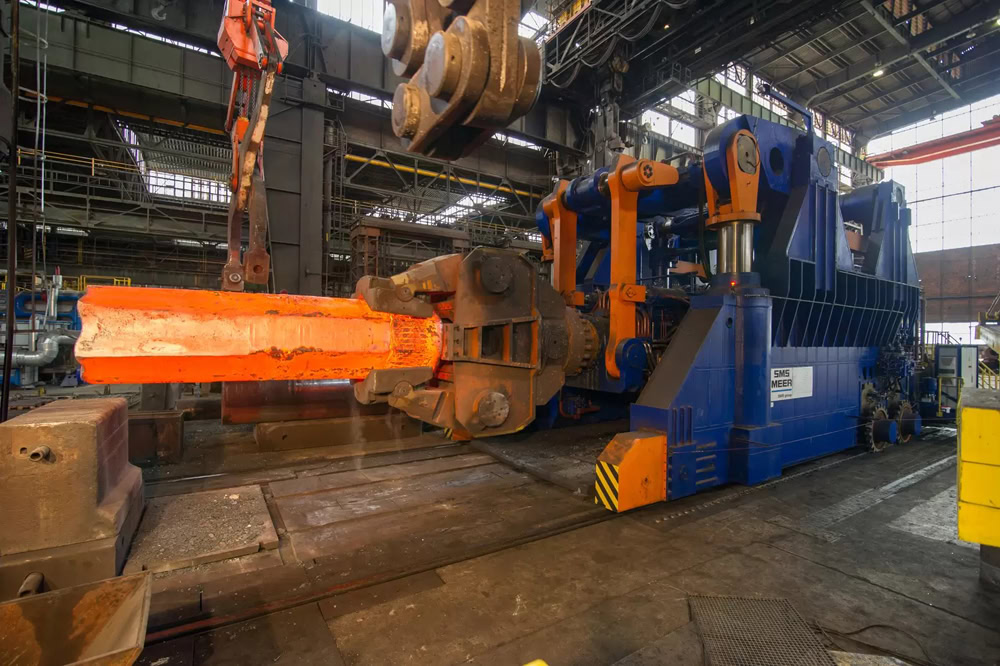

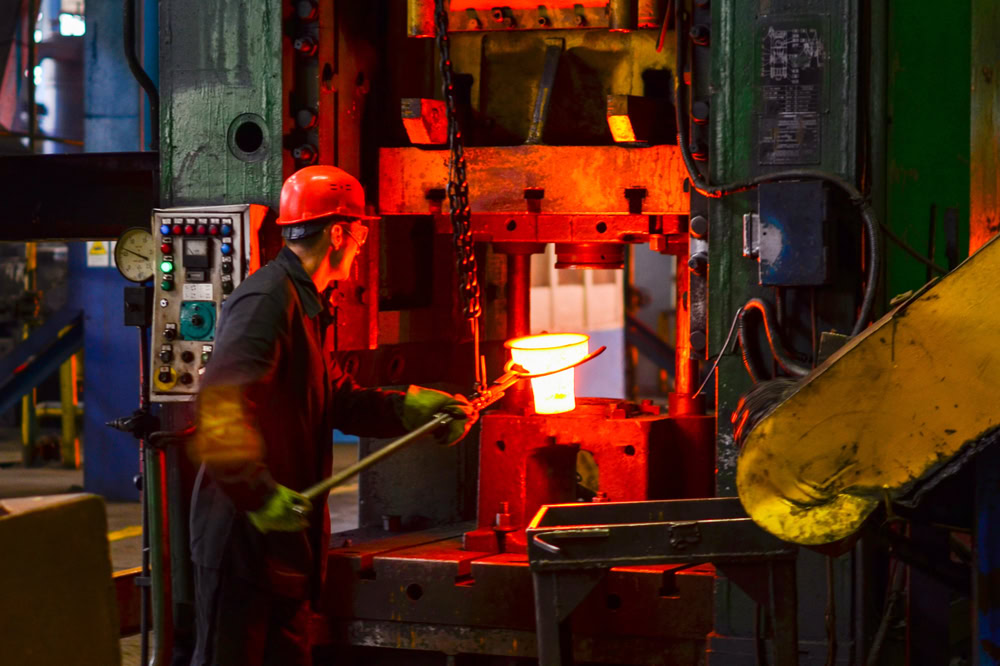
Hot Forging
Hot forging titanium refers to the process of heating titanium or titanium alloy and then forging it. It refines the grain structure of titanium. After heating, the plasticity of titanium increases significantly. The hot forging temperatures of different titanium alloys vary, usually between 800 – 1100°C.
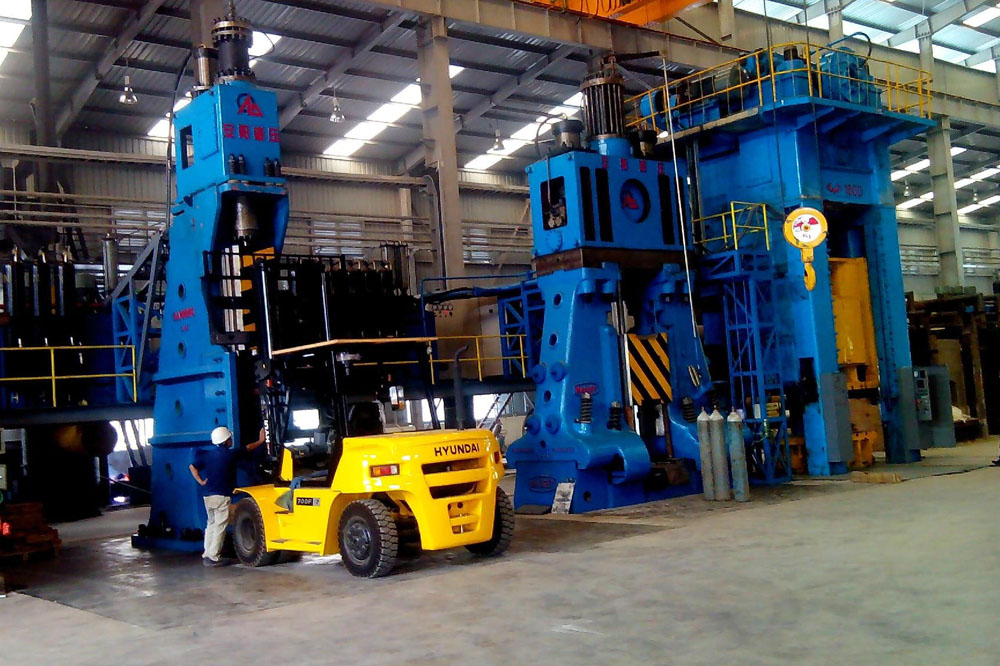

Cold Forging
Cold forging refers to the process of forging titanium or titanium alloys at room temperature. Cold forged titanium parts have better precision, surface quality, strength, hardness, and more precise control of size and shape. Cold forging requires greater pressure, which places high demands on forging facilities.
Forged titanium parts generally need to be heat treated to eliminate stress and optimize metallographic structure and performance. After that, the titanium parts are machined according to actual needs, such as turning, milling, drilling, etc., to achieve the required dimensional accuracy.
Stress Elimination
During the forging process, residual stress will be generated inside the titanium parts. This is because when titanium is plastically deformed by external pressure, its internal lattice structure is twisted and distorted, and the degree of deformation in different areas is inconsistent, which leads to the generation of stress. If these residual stresses are not eliminated, the parts will be deformed and cracked during subsequent processing or use. Through appropriate heat treatment processes, such as stress relief annealing, the atoms inside the parts can be rearranged, these residual stresses can be effectively eliminated, and the dimensional stability and reliability of the parts can be improved.
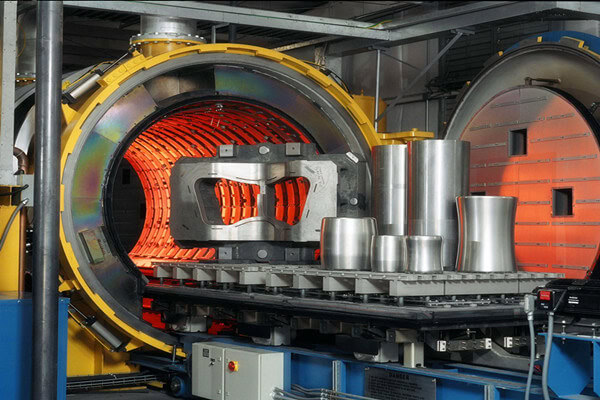

Improve The Organizational Structure
The organizational structure of titanium parts after forging may be uneven. Although the forging process can refine the grains, in some cases, the size and shape of the grains may not meet the ideal requirements, or there may be some forging defects, such as banded structure. Heat treatment can improve this situation. For example, through recrystallization annealing, the deformed grains can be re-nucleated and grown to obtain a more uniform and fine grain structure, thereby improving the mechanical properties of the parts. Appropriate heat treatment can also make the alloy elements more reasonably distributed in the matrix, forming a more favorable phase structure, and further optimizing the strength, toughness, hardness and other properties of the parts.
Adjusting Mechanical Properties
– According to the specific use requirements of the parts, it is necessary to adjust their mechanical properties through heat treatment. For example, some titanium parts require higher strength and hardness. Through a heat treatment process that combines solution treatment and aging treatment, the alloy elements can be fully dissolved into the titanium matrix, and then the strengthening phase can be precipitated during the aging process, significantly improving the strength and hardness of the parts. On the contrary, if the parts require better plasticity and toughness, appropriate annealing treatment can reduce the hardness of the material, improve its plasticity, and make the parts less likely to break when subjected to impact or complex deformation.
Forged Titanium Grades
Different grades of forged titanium materials show different performance characteristics due to the difference in their trace element ratios, and are suitable for different application fields. In practical applications, it is necessary to comprehensively consider and select appropriate titanium grades according to specific use requirements, such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, thermal properties and biocompatibility. At the same time, the forging process will also have an important influence on the performance of the material. Therefore, it is necessary to formulate reasonable forging process parameters according to different grades to give full play to the excellent performance of titanium materials and meet the needs of various engineering and industrial applications.
- TA1
- TA2
- TA3
- TA4
- TA7
- TA11
- TA11
- TA12
- TC4
- TC11
- α Titanium Alloy
- α + β Titanium Alloy
- TA15
- TA16
- TA18
- TA19
- TC1
- TA2
- TC6
- TC16
- TC17
- TC18
- TB2
- TB3
Popular Forged Titanium Products
Wstitanium has always regarded environmental protection as an important responsibility for corporate development and actively promotes the concept of green production. Advanced energy-saving and emission reduction technologies are used in the production process, and heating furnaces, forging machines, rolling mills and other equipment are transformed to save energy and reduce energy consumption. At the same time, a complete wastewater and waste gas treatment system has been established to effectively treat pollutants generated during the production process to ensure that emissions meet standards. By continuously optimizing production processes and equipment, while improving production efficiency, the impact on the environment is minimized.