Ruthenium-Iridium Titanium Anodes Manufacturers & Suppliers In China
Wstitanium has made remarkable achievements in the field of ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anodes. The anodes have low overpotential, high catalytic activity and good conductivity, and are widely used in chlor-alkali industry, wastewater treatment, hydrometallurgy and other fields.
- High Iridium Content
- Medium Iridium Content
- Low Iridium Content
- Plate, Mesh, Tube, Customized
- For Electroplating
- For Sewage Treatment
- For Electrolysis of Water
- For Chlor-alkali Industry
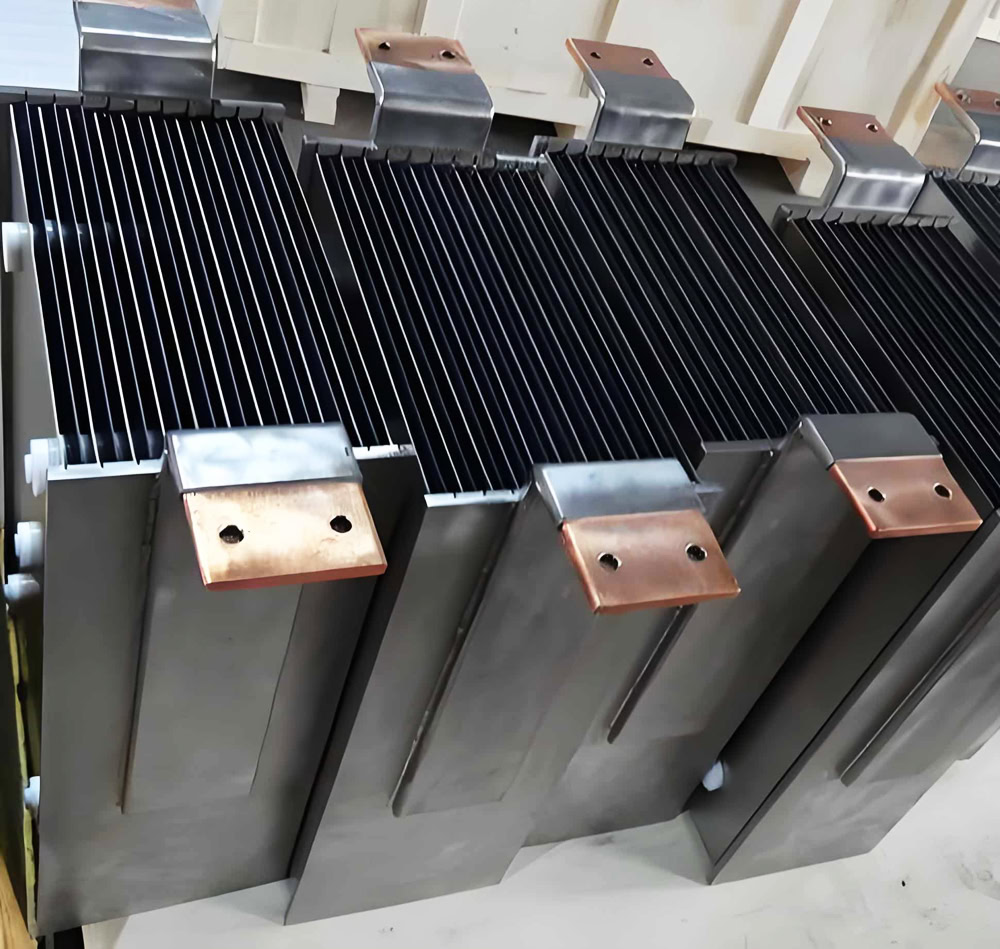

Ruthenium-Iridium Titanium Anodes Factory - Wstitanium
Ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anodes are mainly composed of ruthenium (Ru), iridium (Ir) and titanium (Ti), and take advantage of the catalytic efficiency of ruthenium and the excellent antioxidant capacity of iridium. The coating is usually 8 grams of ruthenium and 2 grams of iridium per square meter, with a thickness of about 8 microns. It has good electrocatalytic activity and corrosion resistance, and exhibits excellent performance in many electrolytic environments. It can effectively reduce the overpotential of oxygen and chlorine evolution reactions, and is widely used in chlor-alkali industry, electrolytic chlorine production, disinfection and other fields.
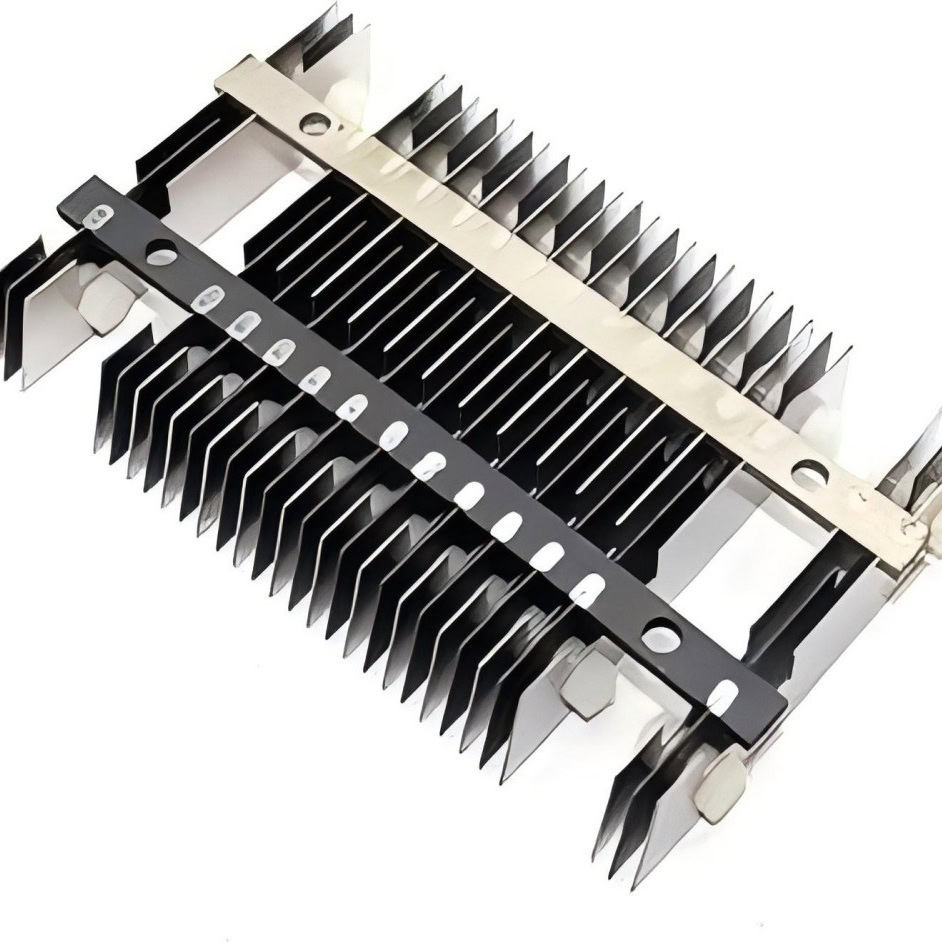

Chlorine Anode
It is used in environments with high chloride ion content in the electrolyte, such as hydrochloric acid environment, electrolysis of seawater, electrolysis of salt water, etc., and mainly precipitates chlorine.
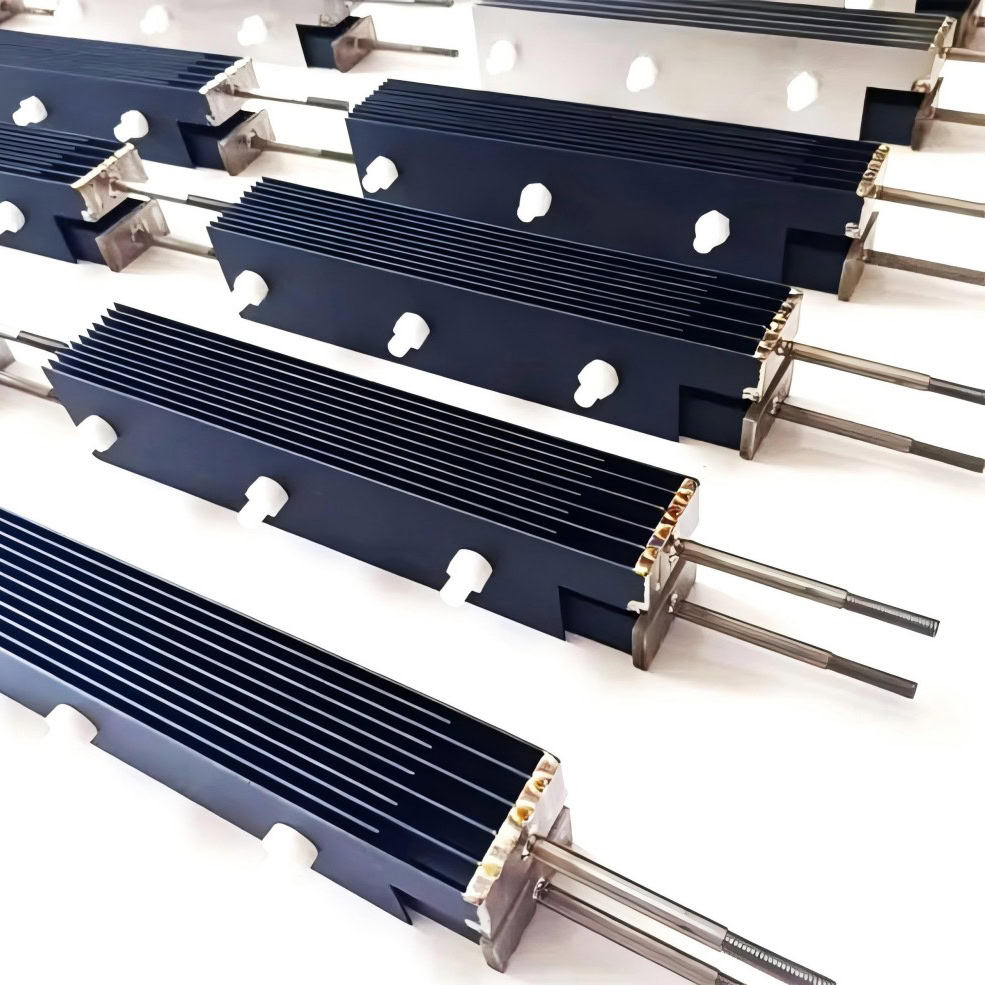

Oxygen Anode
It is used in the environment where the electrolyte is sulfuric acid. In the electrolysis process, oxygen is mainly released. It has good electrocatalytic activity and stability in the oxygen evolution reaction.

It is flat and has a large surface area, which can provide more reaction sites. It is suitable for some occasions that require large-area electrodes for reaction, such as anodes in large electrolytic cells.
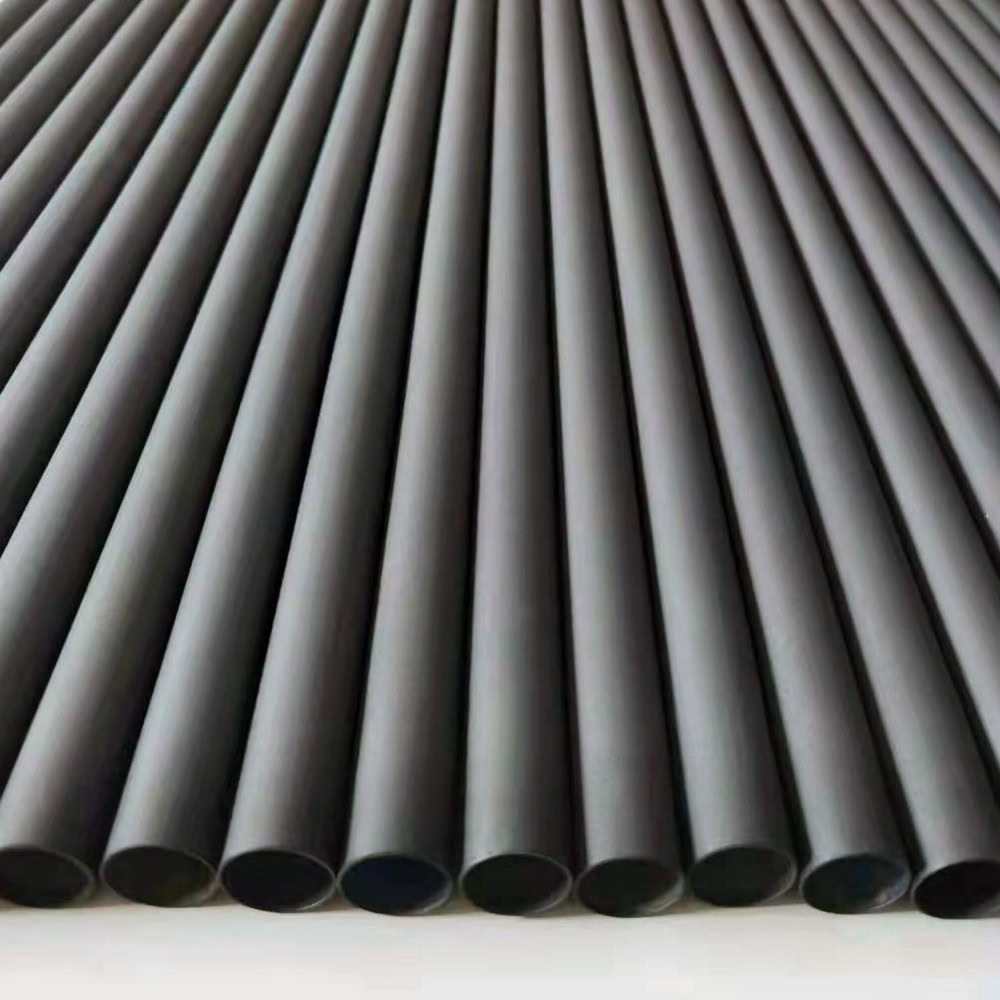

It is a tubular structure with unique geometric shape and spatial characteristics. It is used in some specific electrolysis equipment, such as tubular electrolysis reactors.
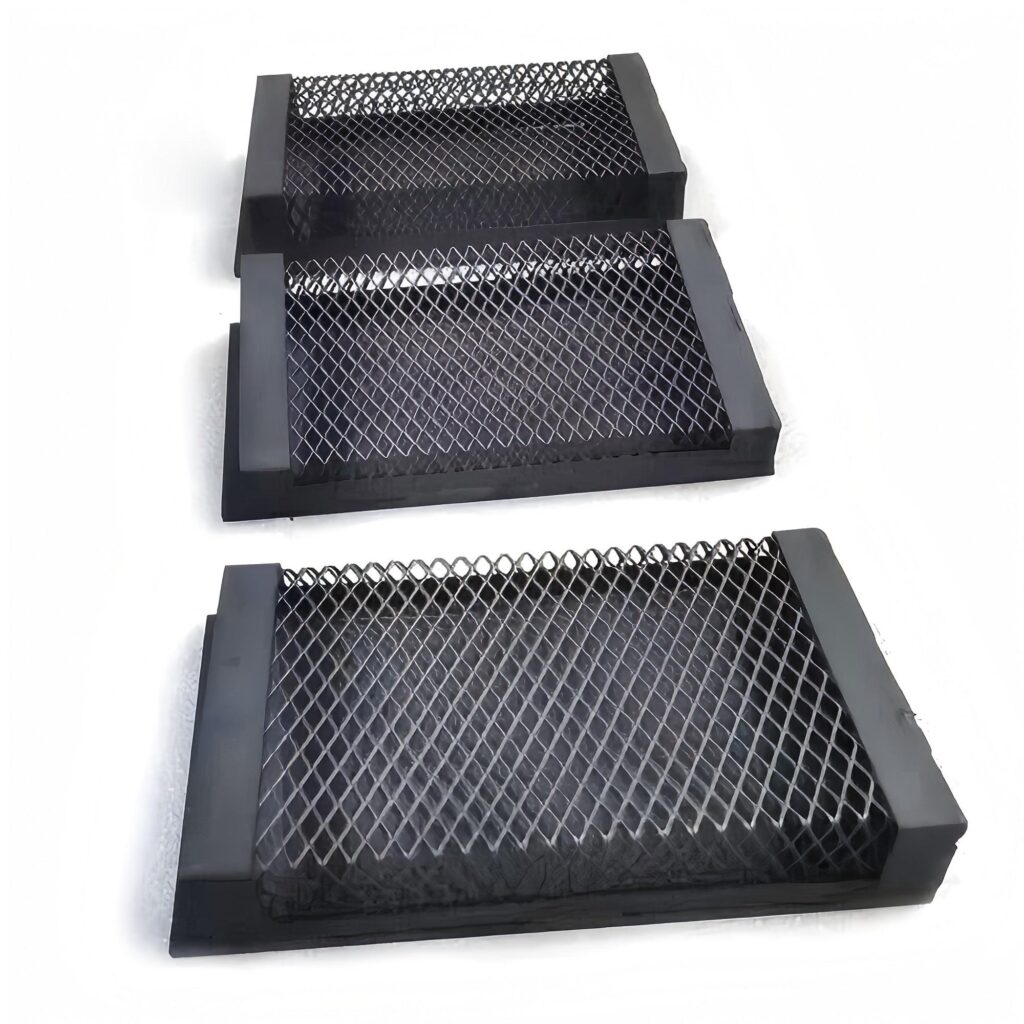

It has a mesh structure. The size and shape of the mesh can be designed according to different application requirements. The mesh structure can make the electrolyte flow better.
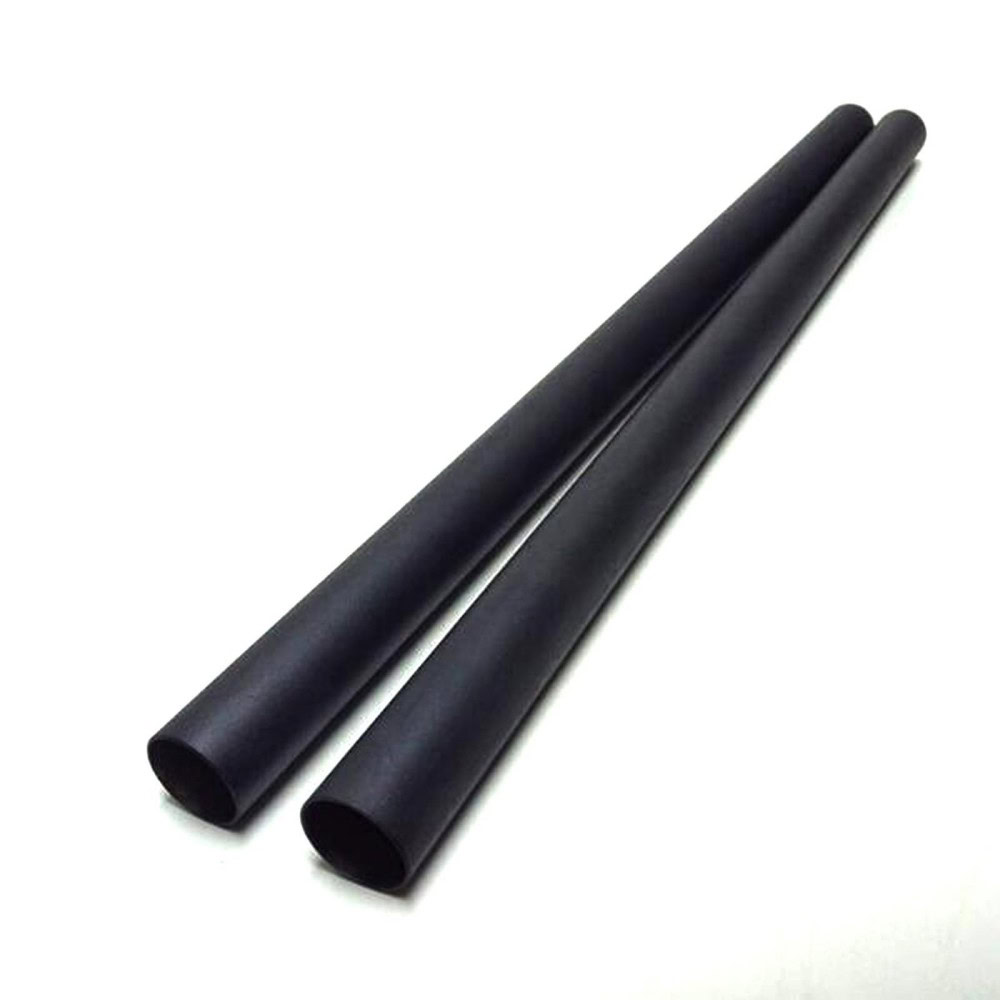

It is rod-shaped with a certain length and diameter. It is suitable for some occasions that need to go deep into the electrolyte for reaction, such as in small electrolysis experimental devices.
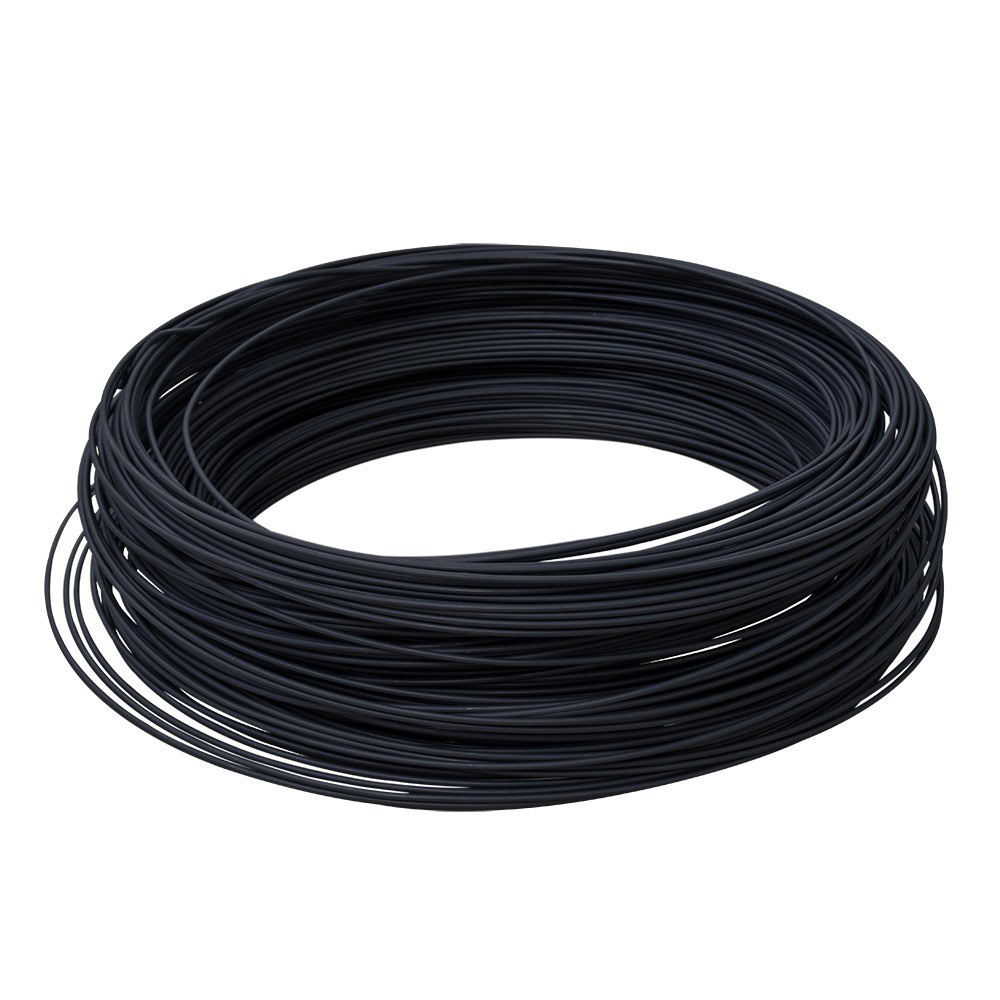

Wire
It is wire-shaped, with a small diameter and a large specific surface area, and has advantages in some special applications that require high electrode size and specific surface area.

For Organic Synthesis
It is used in reactions such as electro-oxidation and electro-reduction of some organic compounds. By adjusting the coating parameters, effective catalysis of organic synthesis reactions can be achieved.

For Electroplating
As an anode, it provides oxidation reaction of metal ions, ensures the smooth progress of the electroplating process, and helps to improve the quality and efficiency of electroplating.
Custom Manufacturing Ruthenium Iridium Titanium Anode Services
Wstitanium has a team of experts, engineers and technicians in the field of electrochemistry. The team members have rich theoretical knowledge and practical experience, and are able to continuously explore and innovate to develop more advanced ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anode technology. They have the ability to provide diversified product specifications according to different needs. Whether it is the shape and size of the anode, or the thickness of the coating, the composition ratio, etc..Customizing ruthenium-iridium-coated titanium anodes requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, from basic material properties to specific application scenario requirements and manufacturing process control.
Specifications of Ruthenium Iridium Coated Electrode
| Material | Gr1 Titanium as substrate, MMO as coating | Current Density | <5,000A/㎡ |
| Coating Types | RuO2 +IRO2 +X | Work time | 80-120 H |
| Dimension & Shape | Plate, mesh, rod, or customized | Noble Metal Content | 8-13g/㎡ |
| Voltage | <24V | Coating Thickness | 8~15μm |
Application Determination
Different application scenarios have very different performance requirements for ruthenium-iridium-coated titanium anodes. For example, in the chlor-alkali industry, the anode needs to work for a long time in a high-concentration sodium chloride solution, requiring the anode to have good resistance to chloride ion corrosion and high chlorine evolution activity. In the field of sewage treatment, the anode may need to treat a variety of complex organic and inorganic pollutants, requiring the anode to have a wide range of electrocatalytic activity and a certain pollution resistance. In the electroplating industry, the main function of the anode is to provide metal ions, requiring the anode to have stable electrochemical properties and an appropriate dissolution rate.

Performance Requirements
Determining the performance according to the application is a key step in customization. Performance indicators include but are not limited to current density, electrode potential, oxygen evolution overpotential, corrosion resistance, service life, etc. For example, for applications that require high current density, the anode needs to have good conductivity and heat dissipation performance to avoid overheating and performance degradation. For applications with strict requirements on electrode potential, the composition and thickness of the ruthenium-iridium coating need to be precisely controlled to ensure that the potential of the anode meets the requirements. When determining performance indicators, it is also necessary to consider the actual operating conditions, such as the influence of factors such as temperature, pressure, and electrolyte concentration on anode performance.
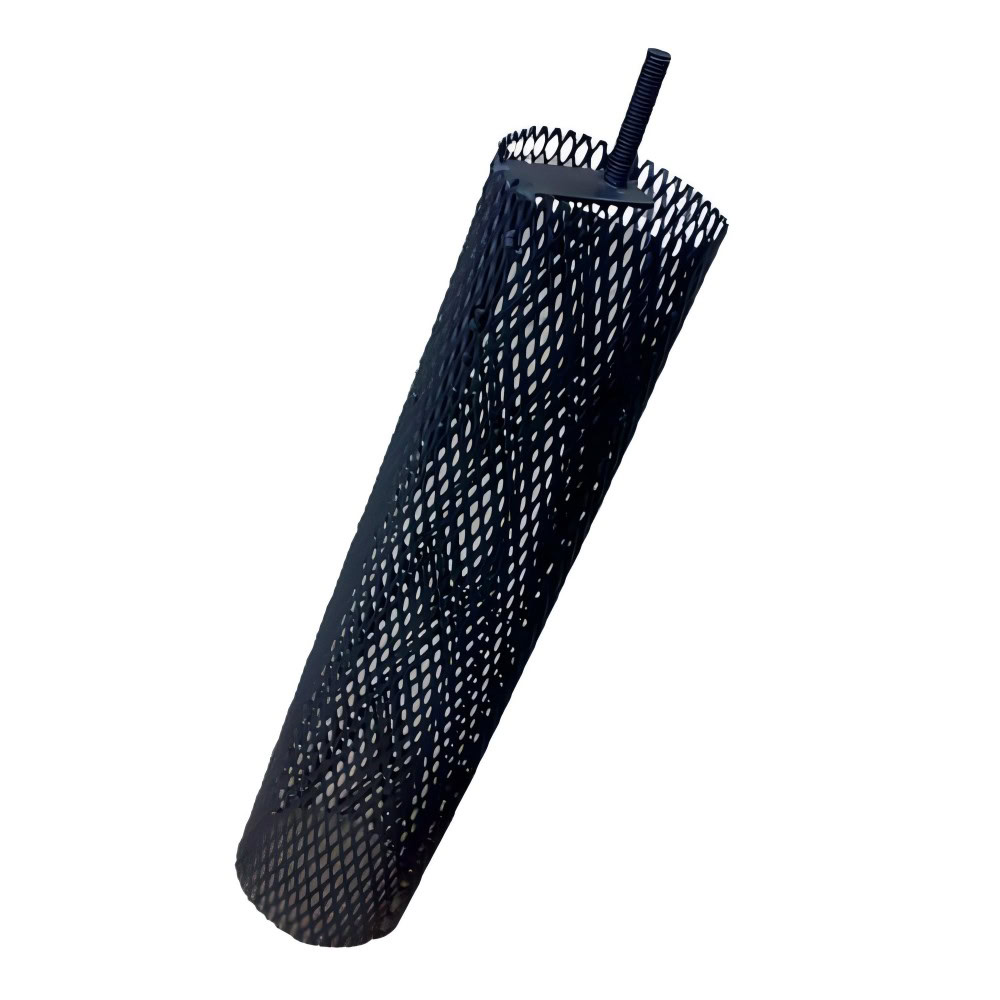
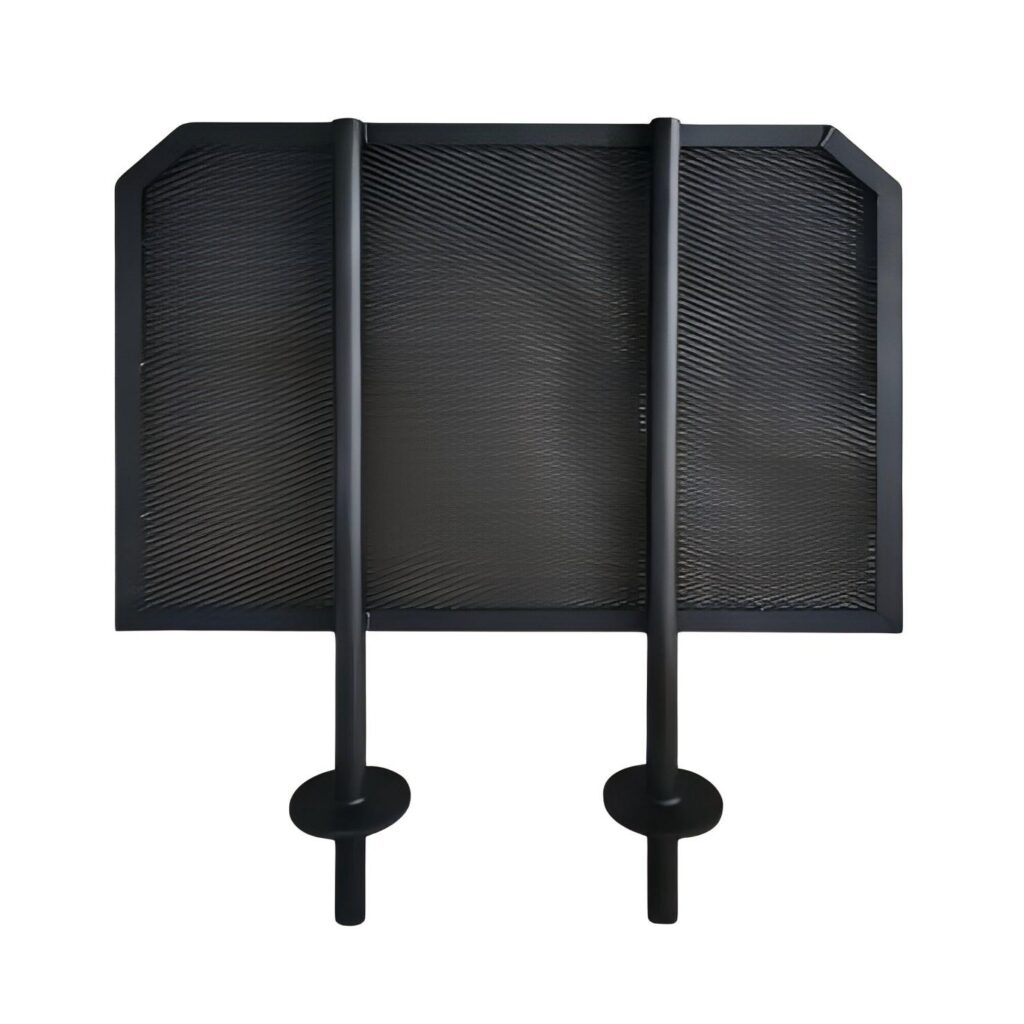
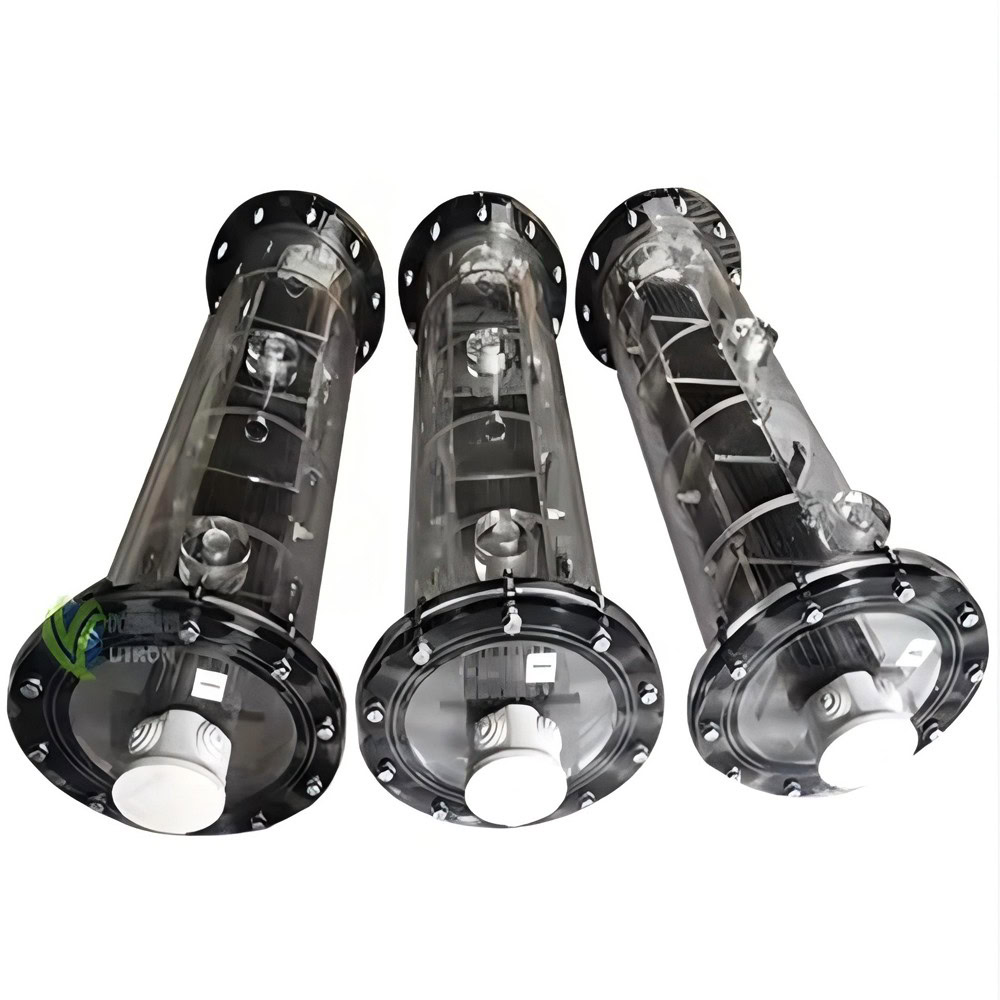




Size and Shape
The size and shape of the ruthenium-iridium-coated titanium anode also need to be customized according to the specific application. The size of the anode may affect its installation and spatial layout in the equipment. The shape may affect the current distribution and electrochemical efficiency. For example, in some large electrolytic cells, large-area flat anodes may need to be customized; in some special reactors, anodes with special shapes may need to be customized, such as strips, plates (conventional, expanded, corrugated or perforated formats), foils, squares, wires, rods, discs, bars and tubes.
- Rods: Customizable from 10mm to 50mm in diamete.
- Wires: A diameter range of 0.5mm to 10mm.
- Tubes: Available from 10mm to 200mm.
- Plates: Offered in thicknesses from 0.5mm to 5mm.
- Meshes: The thickness options from 0.5mm to 2.0mm.
Titanium Substrate
The purity and quality of the titanium substrate have an important influence on the performance of the ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anode. Generally speaking, industrial pure titanium (>99.5%) or titanium alloy with higher purity should be selected as the substrate. Industrial pure titanium has good corrosion resistance and processing performance, and is suitable for most conventional application scenarios. Titanium alloys can improve their strength and corrosion resistance by adding other elements (such as aluminum, vanadium, etc.), which is suitable for some special applications with high requirements for substrate performance. When selecting a titanium substrate, its surface quality should also be considered to ensure that the surface is flat and defect-free to ensure that the coating can adhere evenly.

Ruthenium-iridium Coating
The materials of ruthenium-iridium coating are mainly compounds of ruthenium and iridium, such as ruthenium oxide (RuO₂) and iridium oxide (IrO₂). When determining the composition of ruthenium-iridium coating, it is necessary to optimize it according to the specific application requirements. Generally speaking, the ratio of ruthenium to iridium affects the electrocatalytic activity and corrosion resistance of the coating. A higher iridium content can improve the corrosion resistance of the coating, but may reduce its electrocatalytic activity; while a higher ruthenium content can improve the electrocatalytic activity, but may reduce corrosion resistance.

Auxiliary Materials
In the process of customizing ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anodes, some auxiliary materials such as binders and catalyst additives may also be needed. Binders are used to enhance the bonding force between the coating and the substrate to ensure that the coating does not fall off during use; catalyst additives can further improve the electrocatalytic activity of the coating and improve the performance of the anode. When selecting auxiliary materials, it is necessary to consider their compatibility with the titanium substrate and ruthenium-iridium coating, as well as their impact on the performance of the anode.
Ruthenium-iridium Coated Titanium Anode Manufacturing
Before applying the ruthenium-iridium coating, the titanium substrate must be pretreated. The purpose of pretreatment is to remove oil, scale, impurities, etc. on the surface of the titanium substrate, improve the cleanliness and roughness of the surface, and enhance the bonding force between the coating and the substrate. Common pretreatment methods include mechanical grinding, chemical cleaning, electrochemical polishing, etc. Mechanical grinding can remove larger particles and scale on the surface; chemical cleaning can remove oil and some impurities that are difficult to remove mechanically; electrochemical polishing can further improve the flatness and finish of the surface.

Select Titanium Substrate
Select high-purity titanium materials, such as industrial pure titanium Gr1, Gr2 or titanium alloys, to ensure that they have good corrosion resistance and conductivity.

Forming
According to the design requirements, the titanium materials are processed into the required shape and size through cutting, drilling, bending and other technologies.
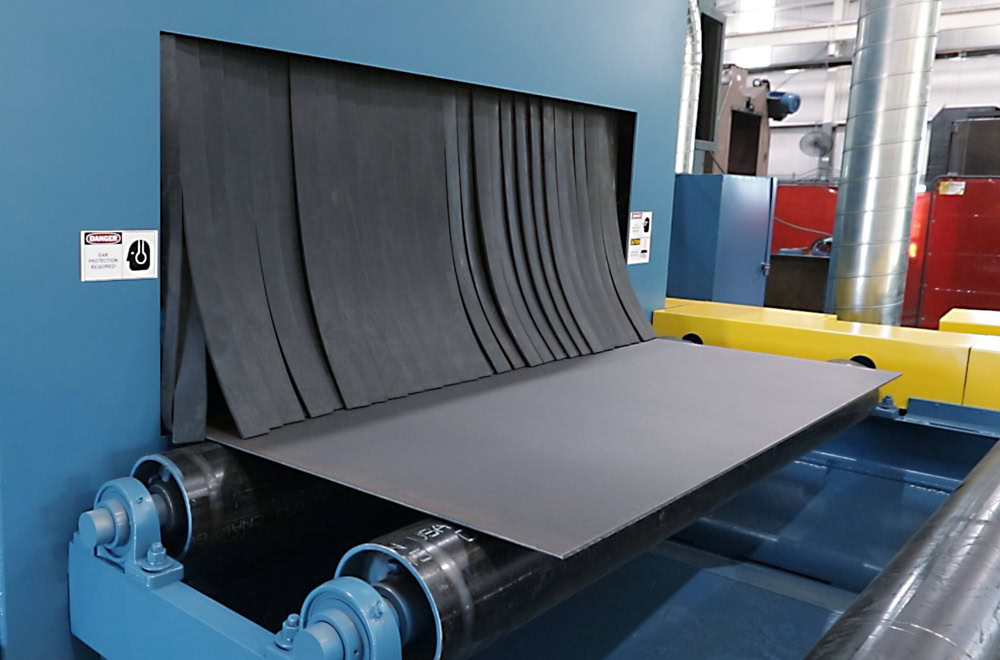

Sand Blasting
Use compressed air to spray sand particles onto the surface of the titanium substrate for impact grinding. The surface forms uniform pitting, improves the roughness, and increases the adhesion of the coating.
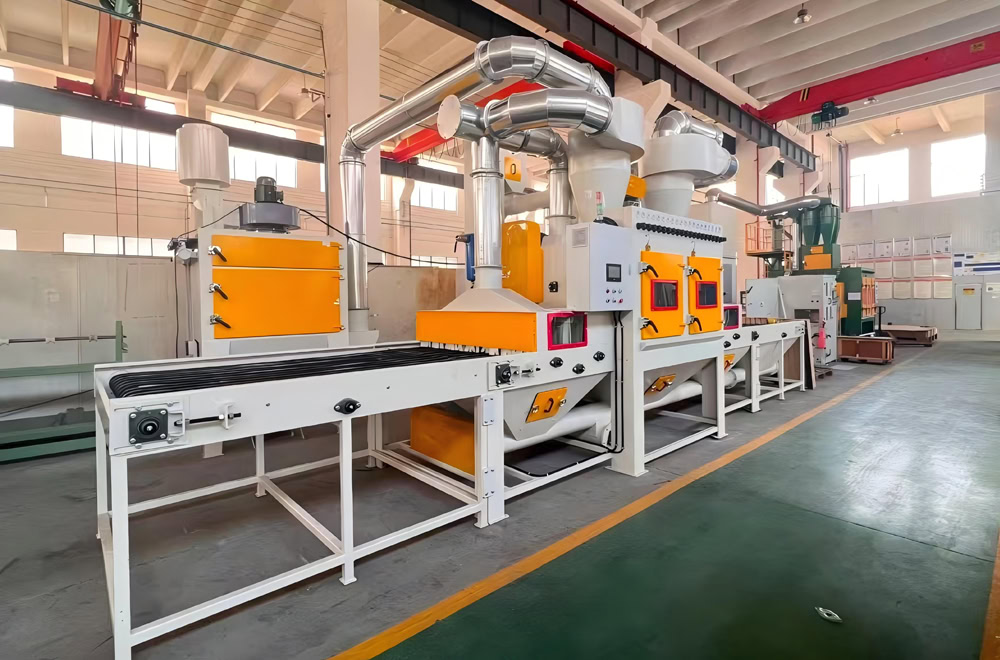

Leveling / Annealing
Heat and shape the titanium material in a furnace at about 500°C, keep it warm for about 2 hours, eliminate the stress inside the material, and improve the material’s organizational structure.
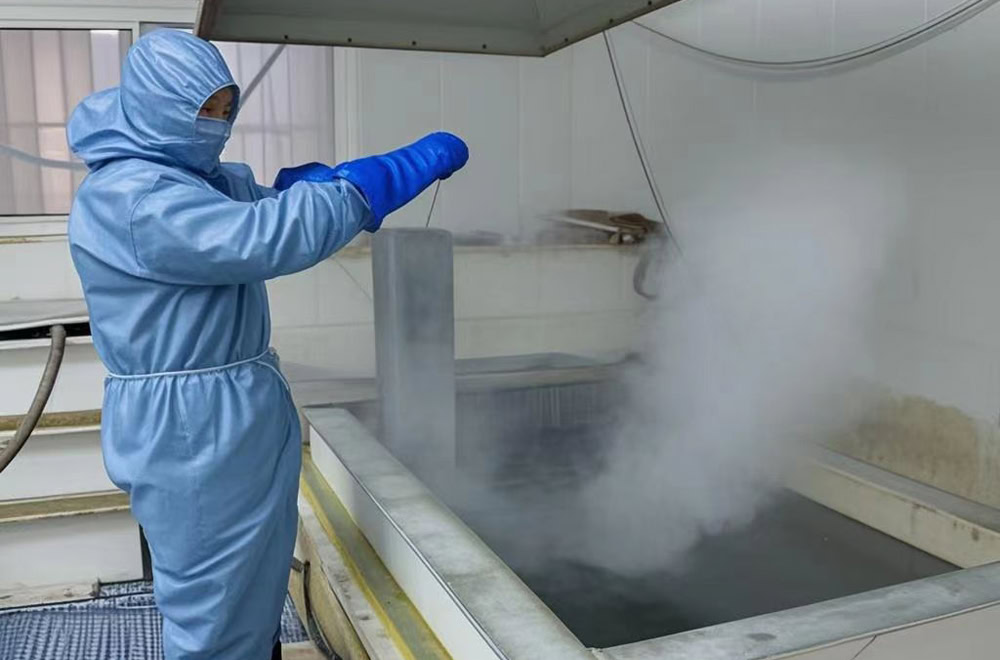

Pickling
Put the titanium substrate into a mixed acid solution composed of sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid for pickling to remove the oxide layer, rust and other impurities on the surface.
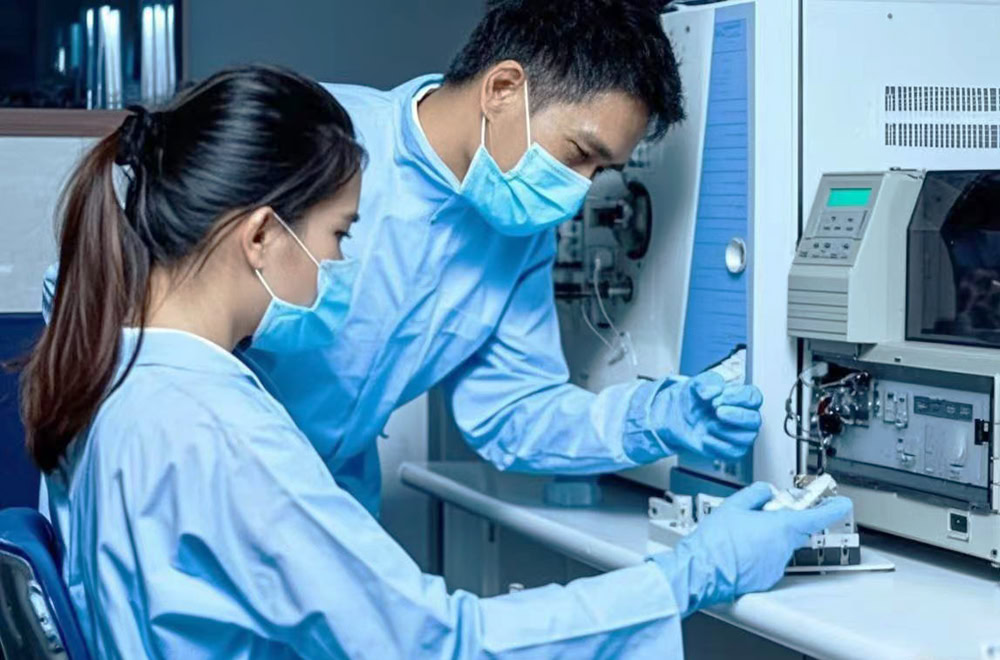

Liquid Preparation
Soluble salts or compounds of ruthenium and iridium are used as the main raw materials, such as ruthenium trichloride (RuCl₃) and iridium trichloride (IrCl₃). Dissolve in the solvent in a certain proportion.
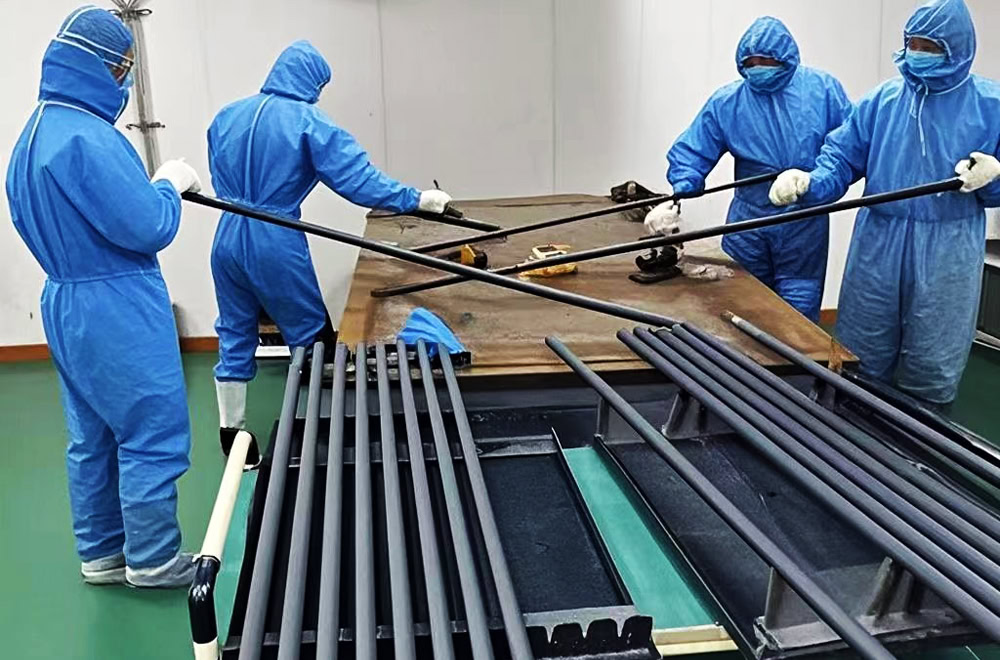

Coating
Use a brush or spray gun to evenly apply or spray the prepared coating solution on the surface of the pretreated titanium substrate. The thickness and uniformity of the coating should be controlled during operation.
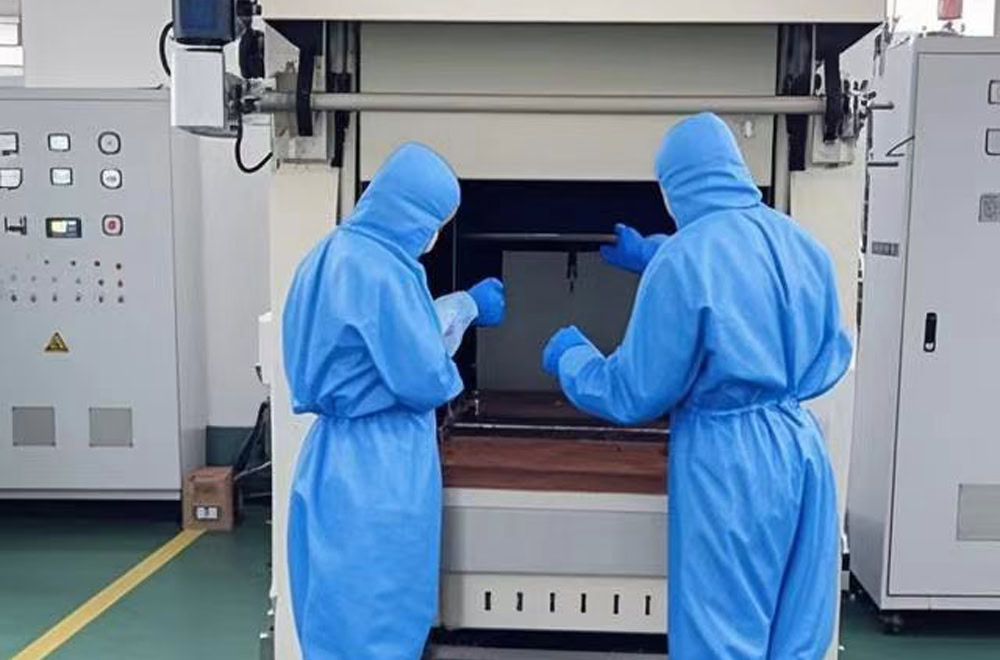

Drying
The coated titanium substrate needs to be placed in a high-temperature furnace for sintering. The sintering temperature is generally between 450-550℃, and the sintering time is 10-20 minutes.
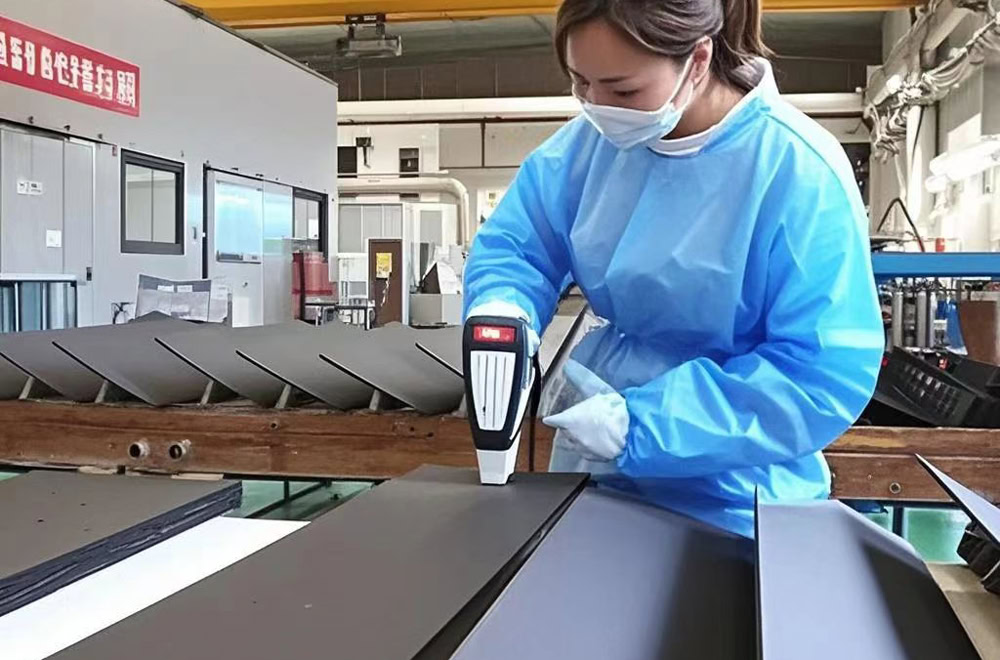

Quality Inspection
The composition and crystal structure of the coating are detected by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy spectrum analysis (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), etc.
Quality Inspection
Wstitanium conducts strict inspections on raw materials to ensure that the raw materials used, such as titanium substrates, organic salts of ruthenium and iridium, meet quality standards. Each batch of raw materials needs to undergo chemical analysis, physical performance testing and other inspection items.
Real-time monitoring of titanium substrate pretreatment, coating preparation, coating, coating heat treatment and other processes to ensure stability and quality consistency. At the same time, regular maintenance and calibration of equipment are carried out to ensure normal operation.
Perform an appearance inspection on the ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anode to check whether the coating surface is uniform and smooth, and whether there are defects such as cracks and peeling. A series of performance tests are carried out, including electrochemical performance tests (such as overpotential tests, current efficiency tests, etc.), corrosion resistance tests (such as corrosion tests in different electrolyte solutions, etc.), coating thickness tests, etc.
| Test Items | Test Conditions | Qualification |
|---|---|---|
| Combining Power | 3M adhesive tape | No black marks on the tape |
| Bend 180° on Φ12mm round shaft | No peeling at the bend | |
| Uniformity test | X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer | ≤15% |
| Coating thickness | X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer | 2-10μm |
| Chlorination potential | 2000A/m2, Saturation NaCl,25±2℃ | ≤1.08V |
| Analytical chlorine polarization rate | 200/2000A/m2, Saturation NaCl,25±2℃ | ≤35mV |
| Enhanced Lifespan | 40000A/m2,1mol/L H2SO4,40±2℃ | ≥45h(Ir+Ru 8g) |
| Intensive weightlessness | 20000A/m2,8mol/L NaOH,95±2℃,electrolysis 4h | ≤10mg |
Ruthenium Iridium Coated Titanium Anode Application
As an excellent electrode material, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anode is widely used in many fields such as chlor-alkali industry, sewage treatment, electroplating industry, hydrometallurgy, seawater desalination, etc. Its good electrocatalytic activity, high corrosion resistance, low cell voltage and long service life make it an indispensable and important part in the field of electrochemistry.
Chlor-alkali Industry
The chlor-alkali industry is one of the earliest and most important application areas of ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes. In the chlor-alkali production process, chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide are prepared by electrolysis of saturated sodium chloride solution. As an anode material, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anode can effectively catalyze the oxidation reaction of chloride ions to generate chlorine, improve the production efficiency and quality of chlorine, and reduce power consumption and production costs.

Sewage Treatment
In the field of sewage treatment, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can be used to treat sewage by electrochemical oxidation. Through the oxidation of the anode, pollutants such as organic matter and ammonia nitrogen in the sewage can be oxidized and decomposed to achieve the purpose of purifying water quality. For example, when treating industrial wastewater containing difficult-to-degrade organic matter, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can effectively improve the biodegradability of wastewater and create conditions for subsequent biological treatment.

Electroplating
In the electroplating process, the performance of the anode has an important influence on the quality of the coating and the efficiency of the electroplating. Ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes have good conductivity and corrosion resistance, can provide a stable current density, and ensure the uniformity and quality of the coating. At the same time, its lower cell voltage also reduces the power consumption during the electroplating process.

Hydrometallurgy
In the field of hydrometallurgy, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can be used for electrolytic extraction and refining of metals. For example, in the electrolytic refining process of copper, zinc and other metals, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can effectively catalyze the anode reaction and improve the purity and production efficiency of the metals.

Seawater desalination
In the electrochemical desalination process of seawater desalination, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can be used as anode materials to remove salt from seawater by electrolyzing seawater. Its good corrosion resistance and electrocatalytic properties enable it to work stably in a high-salt, highly corrosive environment such as seawater, providing an effective technical means for seawater desalination.

Ruthenium-iridium-coated titanium anode VS iridium-tantalum-coated titanium anode
Ruthenium-iridium-coated titanium anode has low overpotential, high catalytic activity and good conductivity, and is widely used in the chlor-alkali industry and some conventional electrochemical processes. Iridium-tantalum-coated titanium anode is suitable for application scenarios that handle highly corrosive media due to its excellent corrosion resistance, especially its excellent performance in special corrosive environments. When choosing to use these two anodes, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as application requirements, working environment, and cost-effectiveness. For applications that pursue high efficiency and energy saving and have a relatively mild corrosive environment, ruthenium-iridium-coated titanium anode may be a better choice. For applications in special corrosive environments, iridium-tantalum-coated titanium anodes can provide more reliable performance and longer service life.
| Comparison Items | Ruthenium-Iridium Coated Titanium Anode | Iridium-Tantalum Coated Titanium Anode |
| Coating Composition | Mainly composed of ruthenium and iridium oxides, such as RuO₂, IrO₂, etc. | Mainly composed of iridium and tantalum oxides, such as IrO₂, Ta₂O₅, etc. |
| Applicable Environment | Mostly used in environments with high chloride ion content, such as hydrochloric acid environment, seawater electrolysis, brine electrolysis, etc. | Generally used in sulfuric acid environment. |
| Oxygen Evolution Overpotential | Relatively high. In some systems, the oxygen evolution overpotential may be about 0.1V – 0.2V higher than that of the iridium-tantalum coated titanium anode. | Relatively low, generally around 1.4V – 1.6V. |
| Initial Anode Potential | Generally around 1.48V. | Generally around 1.51V. |
| Working Current Density | Can reach a relatively high level. For example, in the diaphragm method of chlor-alkali production, it can reach 17A/dm². | Can bear a very high current density, and in practical applications, it is close to or higher than that of the ruthenium-iridium coated titanium anode. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Shows good corrosion resistance in strongly corrosive environments containing chlorine. | Has excellent corrosion resistance in strongly oxidizing acid environments such as sulfuric acid. |
| Service Life | Under suitable working conditions, it can reach more than 5 – 7 years. | Under normal operating conditions, it has a relatively long service life. For example, in the application of aluminum foil formation, it can reach more than 9 – 18 months. |
| Application Fields | Chlor-alkali industry, chlorine dioxide production, chlorate industry, hypochlorite industry, swimming pool disinfection, seawater chlorination, etc. | Non-ferrous metal electrolytic production, electrolytic silver catalyst production, wool textile factory dyeing and finishing wastewater treatment, copper foil electrolytic production, aluminum foil formation, etc. |
| Cost | The price of ruthenium is relatively lower than that of iridium in raw materials, and the overall cost may be slightly lower than that of the iridium-tantalum coated titanium anode. The prices of common products on the market can be as low as tens of yuan per set, and there are also higher-end customized products with higher prices. | The price of iridium is relatively high in raw materials, and it accounts for a relatively large proportion in the coating. With the factor of tantalum added, the overall cost is relatively high. According to the data in 2023, the unit price of iridium is about 4 times that of ruthenium. |
With the continuous advancement of science and technology and the increasing demand for high-performance electrode materials, the research and application of ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes will continue to deepen and expand. By optimizing coating formulas and preparation processes, expanding application areas, and reducing costs, ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes will play a more important role in the future electrochemical field and make greater contributions to industrial manufacturing and environmental protection.