
Titanium Wire With Competitive Price In China
In the field of titanium wire manufacturing, Wstitanium strictly controls the quality from raw material selection to final products, deeply understands the characteristics of titanium grades, and provides customized titanium wire solutions for different industries, from low-strength and high-ductility commercial pure titanium to high-performance titanium alloys.
- Gr.1
- Gr.2
- Gr.3
- Gr.4
- Gr.5
- Gr.7
- Gr.9
- Gr.10
- Gr.11
- Gr.12
- Gr.16
- Gr.17
- Gr.23
- Gr.27
- Gr.29
- AWS A5.16 & ASTM B863
- Wire Coil, Wire Spool, Straight Rod
- T 0.1-0.6*W 200-500mm*L Required
- Supply capacity: 3000 tons per month
- Customization available upon request
Trustworthy Titanium Wire Manufacturer & Supplier - Wstitanium
Wstitanium manufactures a variety of titanium wire types, whether it is pure titanium wire, titanium alloy wire, medical titanium wire, titanium-nickel alloy wire, etc., all of which play a key role in various fields with their unique properties. Advanced smelting technology, forging, rolling, wire drawing, heat treatment and surface treatment and other precision technologies give titanium wire excellent mechanical properties.
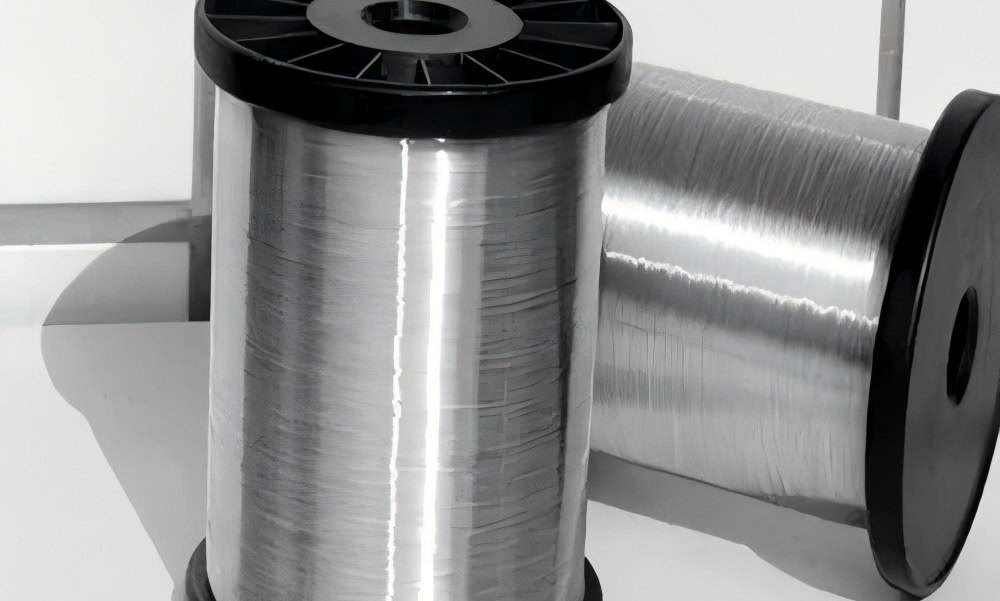

Pure Titanium Wire
Made of high purity (>99.9%) titanium. It has good corrosion resistance. Pure titanium wire is used to make electrodes, filter screens, catalyst carriers, etc.

Titanium Alloy Wire
Add other alloying elements (such as aluminum, vanadium, molybdenum, tin, etc.) to titanium. Different alloying elements give titanium alloy wire different properties.

Titanium Welding Wire
Specially designed for welding of titanium and titanium alloys, its chemical composition matches the welded material to ensure the quality and performance of the welded joint.

Medical Titanium Wire
Usually made of titanium alloy with good biocompatibility, such as Ti-6Al-4V ELI (GR23). It does not cause immune response or other adverse reactions. Such as orthodontic wire, etc.

Titanium Nickel Alloy Wire
Has unique shape memory effect and superelasticity. It withstands large strains without permanent deformation. Suitable for manufacturing satellite antennas, self-expanding stents, etc.

Ultrafine Titanium Wire
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

α Titanium Wire
α Titanium wire is mainly composed of single-phase α structure, including Grade 1-4 and Grade 7, 12, etc. Its characteristics are excellent corrosion resistance (especially resistance to seawater and chloride ion corrosion).

β Titanium Wire
β Titanium wire is mainly composed of single-phase β structure, such as Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al, Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al, etc. Its advantages are high strength (tensile strength can reach 1200-1400MPa) and high toughness.

α+β Titanium Wire
It is an α+β dual-phase structure, combining the advantages of both, such as Grade 5/Ti-6Al-4V, Grade 23/Ti-6Al-4V ELI, etc.). Its strength, plasticity, corrosion resistance, and high temperature performance are balanced.
Customized Manufacturing Titanium Wire
Wstitanium introduces a series of precision technologies such as vacuum consumable arc melting, forging, rolling, wire drawing, heat treatment and surface treatment, giving titanium wire excellent mechanical properties and outstanding surface quality.
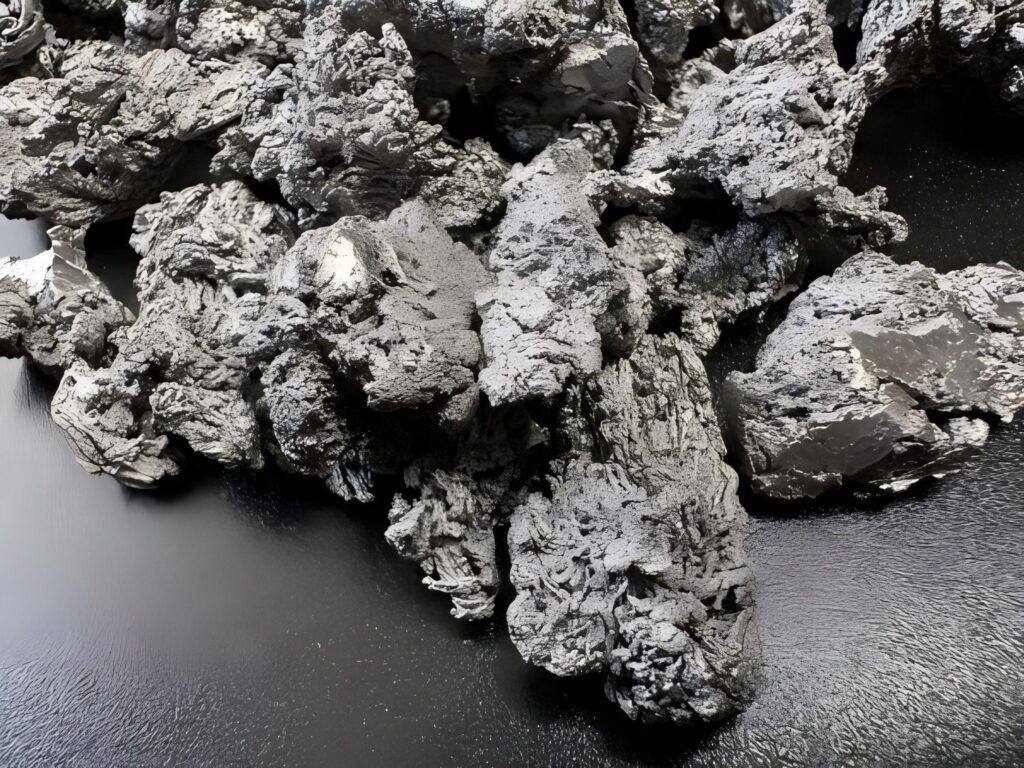
Sponge Titanium
The main raw material for manufacturing titanium wire is sponge titanium, and Wstitanium will strictly select high-quality sponge titanium. The purity, impurity content and other indicators of sponge titanium have an important impact on the performance of the final titanium wire. The source of sponge titanium is strictly examined, and the content of impurity elements such as iron, silicon and carbon is strictly controlled at an extremely low level. To manufacture titanium alloy wire, the amount of alloy elements added is accurately calculated according to the requirements of different alloy grades. For example, Ti-6Al-4V alloy wire will be mixed with sponge titanium with an intermediate alloy of aluminum and vanadium in a ratio of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium.

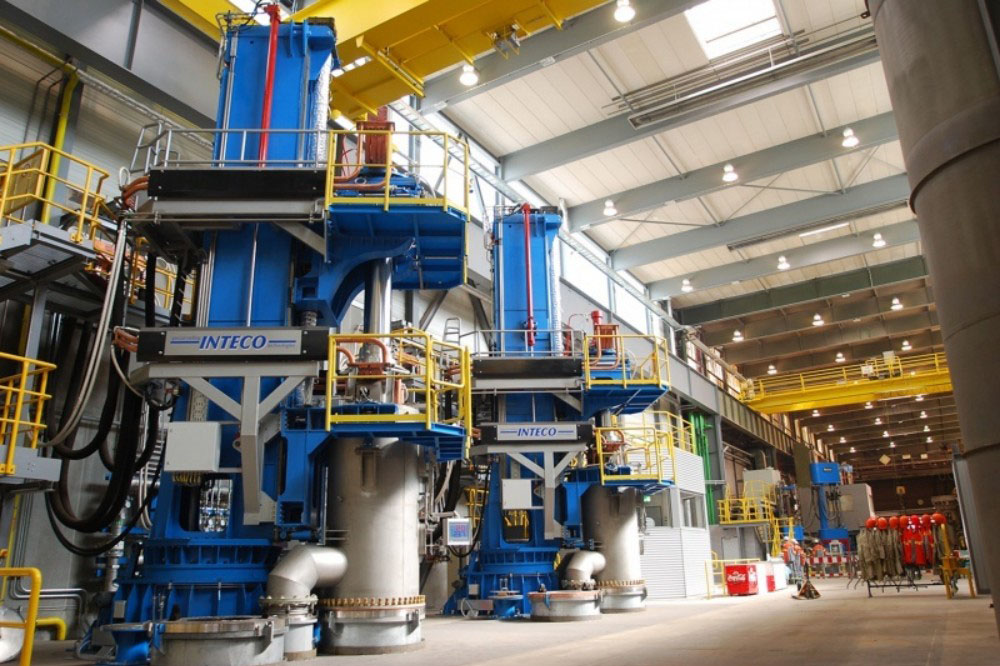
Vacuum consumable arc melting (VAR)
This is one of the commonly used melting techniques in titanium wire manufacturing. The prepared sponge titanium and alloy elements (if any) are made into electrodes and placed in a vacuum melting furnace. In a vacuum environment, the high temperature of the arc is used to melt the electrode, and the molten titanium droplets fall into a water-cooled copper crucible and solidify into an ingot. The vacuum environment can effectively prevent the metal from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen and other gases in the air during the smelting process, and reduce the introduction of impurities. In VAR smelting, the stability of the smelting process and the uniformity of the metal composition are ensured by precisely controlling parameters such as current and voltage. The titanium ingot obtained by VAR smelting has a denser internal structure and a more uniform composition, laying a good foundation for subsequent processing.

The titanium ingot obtained by smelting needs to be forged to improve its structure and processing performance. First, the titanium ingot is heated to a suitable forging temperature range. The forging temperature varies for different titanium alloy grades. For example, the forging temperature of Ti-6Al-4V alloy is generally between 900-1100°C. During heating, an advanced temperature control system is used to ensure that the titanium ingot is evenly heated. Then, forging is carried out on large-scale forging equipment. Through multiple upsetting and drawing, the internal structure of the titanium ingot is made denser and the grains are refined.
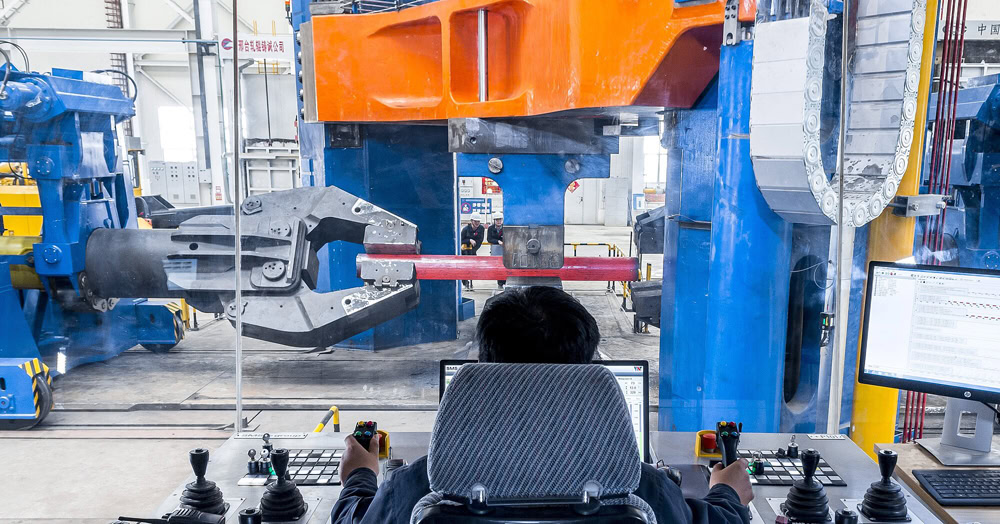

The billet after forging needs to be quality tested. Ultrasonic flaw detection and metallographic analysis are used to detect whether there are defects such as cracks and pores inside, and to check whether its structure meets the requirements.
Hot Rolling
The forged billet is heated to above the recrystallization temperature for hot rolling. Through the rolling of the rolling mill, the billet is further deformed, the diameter is reduced, and its internal structure and performance are improved. In hot rolling, parameters such as rolling speed, rolling temperature and reduction are controlled to obtain the required dimensional accuracy and structural performance. For example, for the production of titanium wire billets with larger diameters, it may be necessary to undergo multiple passes of hot rolling to gradually reduce its diameter. A layer of oxide scale will form on the surface of the billet after hot rolling.
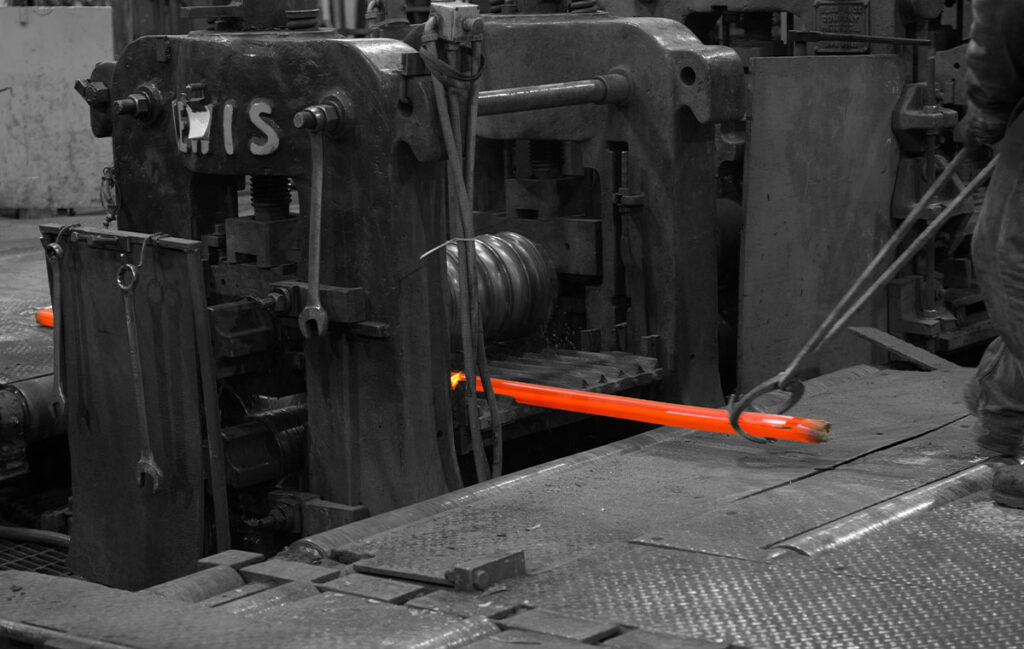
Cold rolling
In order to obtain higher dimensional accuracy, surface quality and finer grain structure, cold rolling is usually performed after hot rolling. Cold rolling is performed at room temperature, and the hot-rolled billet is rolled by a cold rolling mill to further reduce its diameter and improve its surface quality. During the cold rolling process, lubricants are required to reduce friction and prevent scratches on the surface of the rolled piece. At the same time, according to different product requirements, the number of cold rolling passes and reduction are controlled to achieve the required performance and dimensional accuracy. After cold rolling, the titanium wire billet has a smooth surface, high dimensional accuracy, and further optimized mechanical properties.
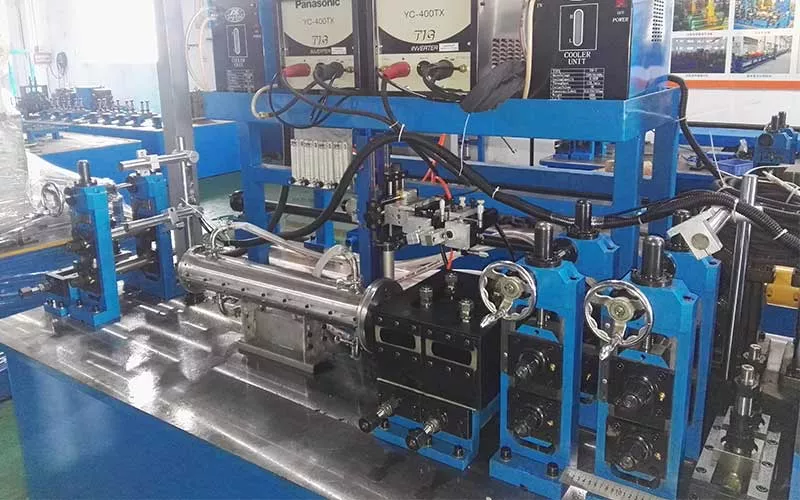

Wire drawing
Wire drawing is the key technology to process titanium wire blanks into titanium wires of required diameter. According to the required diameter and precision requirements of the titanium wire, select the appropriate wire drawing die, which is usually made of cemented carbide or diamond. Before wire drawing, the titanium wire blank is surface treated and coated with a special lubricant to reduce friction during wire drawing, reduce die wear, and ensure the surface quality of the titanium wire. Commonly used lubricants include lime, borax, etc., which can form a lubricating film at high temperatures to effectively protect the surface of the titanium wire.

The wire drawing process generally uses multiple passes of drawing to gradually reduce the diameter of the titanium wire. The drawing reduction rate of each pass needs to be reasonably controlled according to the material, specifications and performance requirements of the titanium wire to avoid breaking or deterioration of the titanium wire due to excessive drawing reduction rate. Real-time monitoring of parameters such as drawing force and speed to ensure the stability of the wire drawing process. After multiple passes of wire drawing, the diameter of the titanium wire gradually reaches the required dimensional accuracy, and its strength and hardness will also be improved.
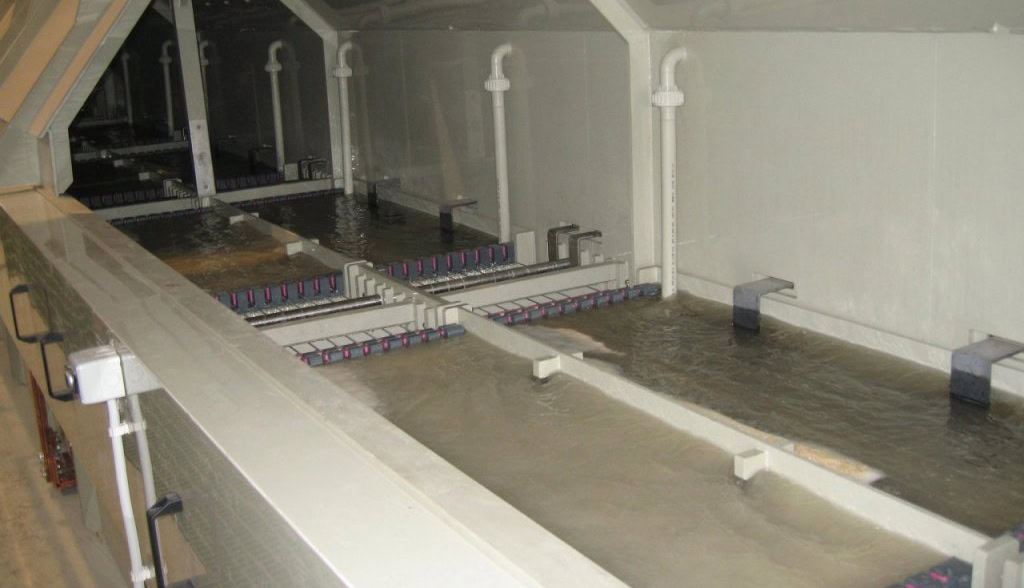
Pickling
Pickling is a common technique for removing oxide scale and impurities from the surface of titanium wire. The titanium wire is immersed in an acidic solution, such as a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, to dissolve the oxide scale and impurities on the surface through chemical reactions. During the pickling process, the concentration, temperature and immersion time of the acid solution are strictly controlled to avoid excessive corrosion of the titanium wire matrix. The surface of the titanium wire after pickling is smooth and can meet the application scenarios with high requirements for surface quality.

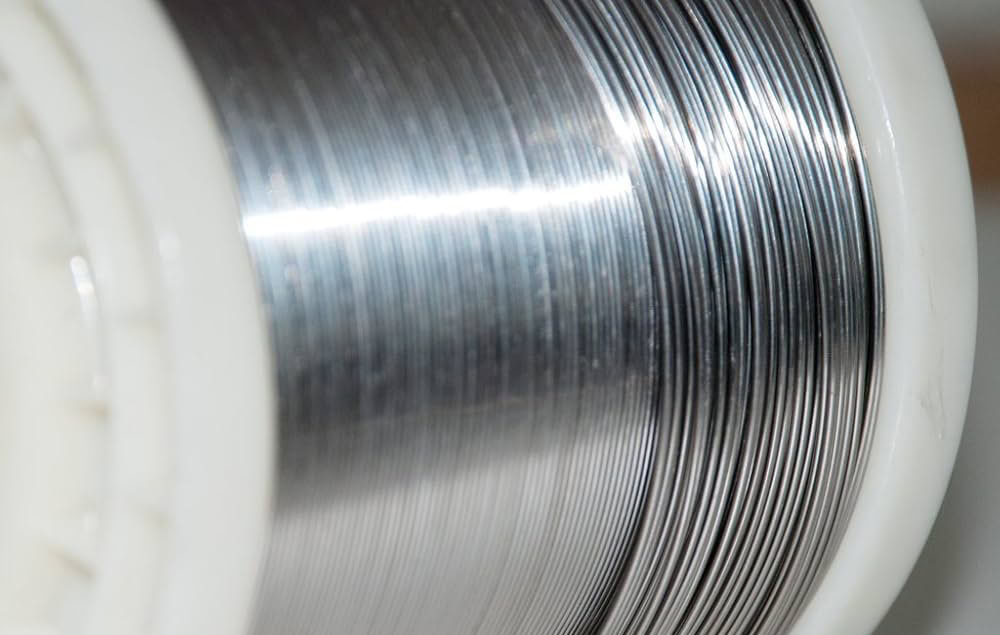
Polishing
For some titanium wires with extremely high surface roughness requirements, such as titanium wires used in the manufacture of precision instruments, optics and other fields, polishing is also required. Polishing can be done by mechanical polishing, chemical polishing or electrolytic polishing, etc., by removing the microscopic protrusions on the surface of the titanium wire to make the surface extremely smooth. For example, the surface roughness of the titanium wire used in optical equipment can reach Ra0.01μm or less after polishing, meeting the strict requirements of the optical system for surface quality.

Titanium wire is widely used in many industries such as aerospace, medical, chemical, marine engineering, electronics, sporting goods and architectural decoration. With its outstanding advantages such as high strength, low density, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, it solves the material problems faced by various industries.