Titanium Fasteners Manufacturer and Supplier
Certified: CE & SGS & ROHS
Shape: Requested
Diameter: Customized
Drawings: STEP, IGS , X_T, PDF
Shipping: DHL, Fedex, or UPS & Ocean Freight

20+ YEARS EXPERIENCE SENIOR BUSINESS MANAGER
Ask Michin For What You Want?
In modern industry, fasteners are critical components that connect various parts. Their quality and performance play a crucial role in the stability, reliability, and safety of the entire system. With the continuous advancement of industrial manufacturing, the requirements for fasteners are becoming increasingly stringent. They must not only possess high strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance, but also meet the diverse needs of different industries and applications. Titanium fasteners, with their superior comprehensive performance, stand out among fasteners made from numerous materials and are becoming the preferred fastener component in high-end fields such as aerospace, medical devices, marine engineering, and petrochemicals.
Titanium Fastener Manufacturer & Supplier – Wstitanium
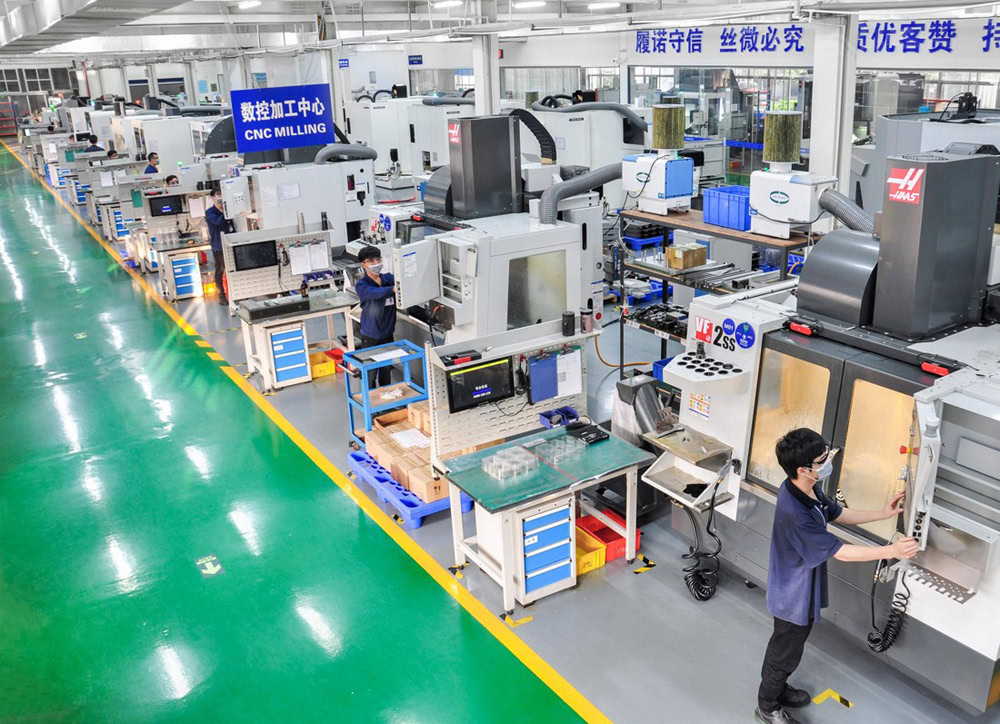
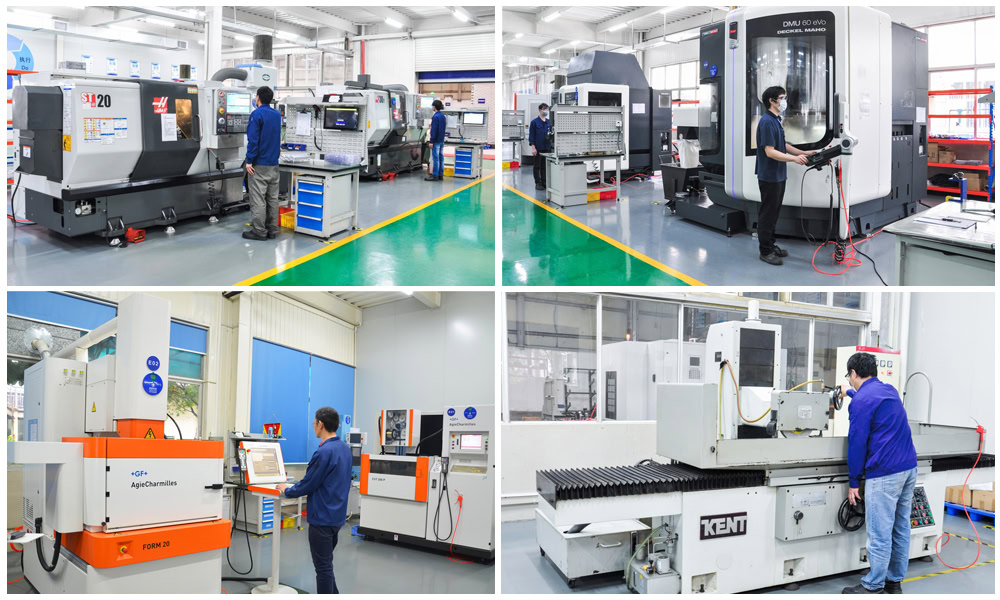
Advanced Equipment: Wstitanium has invested in a wide range of advanced equipment, including 5-axis CNC machining centers, lathes, and milling machines, to ensure efficient and precise manufacturing of various titanium fasteners. Wstitanium is capable of producing even more complex, high-precision titanium fasteners, such as specialized studs and special-shaped screws.


Strict Raw Material Inspection: Wstitanium rigorously inspects every batch of titanium ingots, bars, and wire. Advanced testing equipment, such as PMI handheld spectrometers, accurately analyzes the chemical composition of the raw materials to ensure compliance with the corresponding titanium grade standards. For example, indicators such as titanium content and alloying element ratios are within specified ranges. Physical properties, including hardness, tensile strength, and yield strength, are also tested. Only raw materials that meet these requirements are allowed into the manufacturing process, ensuring product quality from the source.
Comprehensive in-manufacturing monitoring: Wstitanium implements comprehensive quality control measures during the manufacture of titanium fasteners. Advanced automated testing equipment, such as online thread gauges, performs real-time inspections of key dimensions such as thread accuracy, pitch, and diameter on each fastener.
Strict Quality Inspection: After titanium fastener manufacturing, Wstitanium conducts comprehensive and rigorous finished product inspections on each batch. Hardness tests are used to verify compliance with applicable standards. Universal testing machines are used to conduct mechanical tests, such as tensile and shear tests, to verify performance under actual loads. For titanium fasteners requiring corrosion protection, salt spray tests and other corrosion resistance tests are also performed.
Titanium Fasteners Specifications
Material : Gr1,Gr2,Gr5,Gr7,Gr12
Standard:DIN912 DIN913 DIN934 DIN965 DIN916 DIN931 DIN933 DIN7991 DIN7984 DIN6921…
Available Industry Standard Thicknesses for Titanium: .016, .020, .032, .063, .080

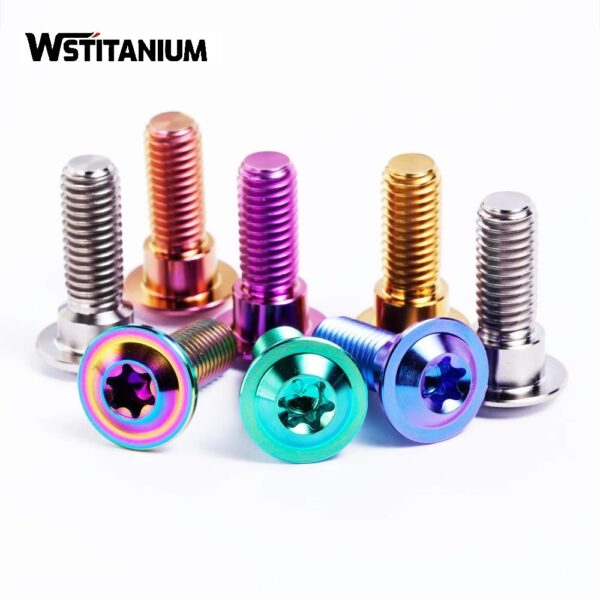
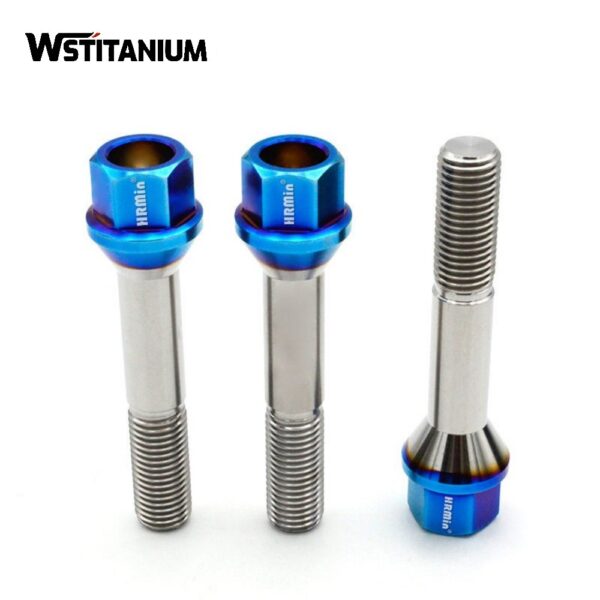
Titanium Bolts
Titanium bolts consist of a head and a shank. Head shapes vary, with common options including hexagonal, hexagonal, round, and countersunk heads to accommodate different installation spaces and tooling requirements. The shank features external threads, whose precision adheres to strict international and industry standards, such as ISO metric and UNC/UNF American standards, to ensure a precise fit in the nut or threaded hole. Some titanium bolts also feature special features on the head or shank end, such as bolts with holes (for inserting cotter pins to prevent loosening) and fine-thread bolts (suitable for thin-walled components or those requiring frequent disassembly).
Specification: Diameters typically range from M3 (US #4) to M64 (US 2.5 inches), with lengths ranging from 5mm to 300mm. Strength grades correspond to titanium grades, e.g., TA2 bolts have a tensile strength of approximately 340-440 MPa, while TC4 bolts have a tensile strength of 900-1100 MPa.
Performance Advantages: Due to the inherent properties of titanium, titanium bolts are approximately 40% lighter than steel bolts of the same specification, significantly reducing the weight of structures in weight-conscious applications such as aerospace and automotive. Their corrosion resistance far exceeds that of ordinary stainless steel bolts. When used in seawater and chemical media, they maintain stable performance without the need for additional plating or coating. Titanium bolts also exhibit excellent fatigue strength and are resistant to breakage under cyclic loading, making them suitable for equipment subjected to long-term vibration, such as engines and fans.
Applications: In the aerospace sector, they are used for connecting aircraft fuselage frames and wings; in marine engineering, they are used for securing jackets on offshore drilling platforms and ship decks; and in the petrochemical industry, they are used for flange connections on reactors and heat exchangers.
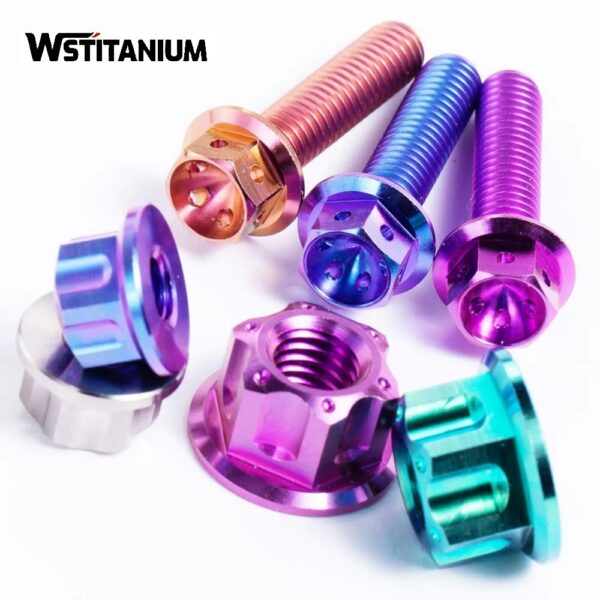
Titanium Nuts
Titanium nuts have internal threads and are used with titanium bolts. They can be categorized by structure, including hexagonal nuts, square nuts, round nuts, and lock nuts. Hexagonal nuts are the most commonly used type, with standard width and thickness across flats, making them easy to tighten with a wrench. Lock nuts (such as nylon lock nuts and all-metal lock nuts) feature special features (nylon rings and thread deformation) to prevent loosening, making them suitable for use in vibrating environments. Some titanium nuts also feature chamfers and stoppers to improve assembly precision and sealing.
Performance Advantages: When used with titanium nuts and bolts, they prevent galvanic corrosion caused by dissimilar metal contact, significantly extending the service life of the joint, especially in humid or corrosive environments. Titanium’s low elastic modulus allows the nut to compensate for tension after tightening, reducing preload loss caused by temperature fluctuations or vibration. Furthermore, titanium nuts exhibit excellent high-temperature stability, maintaining thread strength and fit accuracy at temperatures below 300°C.
Specification: Thread sizes match those of titanium bolts, ranging from M3 to M64, with precision grades ranging from 6H to 5H, with 5H offering higher precision and suitable for high-precision equipment.
Applications: Used in medical devices for securing artificial joint components; in new energy sectors (such as photovoltaics and wind power) for connecting equipment brackets; and in the high-end automotive industry for fastening engine cylinder heads and chassis components.
Titanium Screws
Titanium screws are similar to titanium bolts, but are typically smaller and lighter. They come in a variety of head styles, including pan head, Phillips pan head, countersunk Phillips head, hexagon socket head, and slotted head, to accommodate various assembly spaces and tightening tools. They can be categorized by their intended use as standard connecting screws, set screws, and self-tapping screws. Standard connecting screws are used to secure two or more components. Set screws (without heads or with small heads) are screwed into threaded holes in connected components, with the tip resting against the other component to achieve positioning. Self-tapping screws have sharp threads and can be used to tap directly into pre-fabricated holes or plastic materials, eliminating the need for a matching nut.
Performance Advantages: Titanium screws’ lightweight nature makes them particularly advantageous in electronic equipment and precision instruments, reducing overall weight and preventing additional stress on delicate components. Their excellent biocompatibility (particularly in pure titanium grades TA2 and TC4 ELI) makes them ideal for medical devices, preventing rejection after implantation. Titanium screws also boast a high surface finish and can be anodized to achieve various colors (such as natural, blue, and gold), balancing functionality and aesthetics.
Specifications: Diameters range from M1 (US #0) to M20, and lengths range from 2mm to 100mm. Self-tapping screws typically have an ST thread type (self-tapping).
Applications: They are used to secure motherboards and housings in electronic devices (such as mobile phones and laptops); to connect human tissue or device components in medical devices (such as dental implants and fracture fixation plates); and to precisely secure lenses and lens barrels in optical instruments (such as cameras and telescopes).
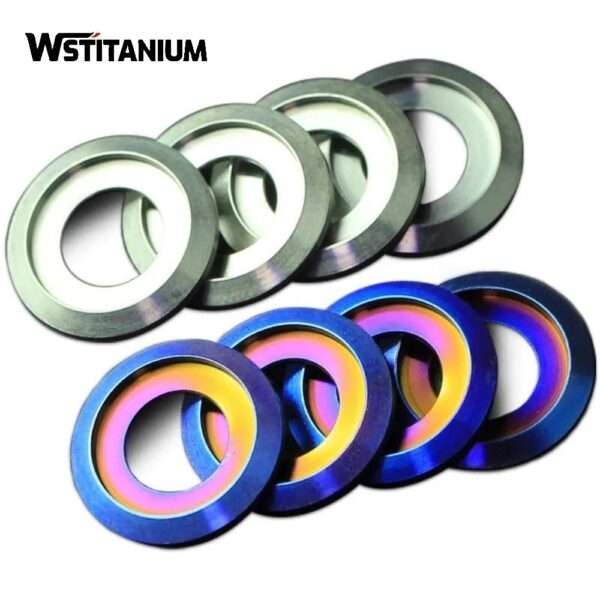
Titanium Washers
Titanium washers are annular components placed between the bolt/screw head and the connected part. They can be categorized by shape as flat washers, spring washers, wave washers, and thrust washers. Flat washers primarily increase contact area and distribute pressure, preventing deformation of the connected part’s surface due to excessive tightening force. Spring washers generate preload through their elastic deformation, preventing bolt loosening. Wave washers, with their multi-wave structure, provide cushioning and compensation, making them suitable for applications with vibration or clearance. Thrust washers, with their positioning bosses or friction surfaces, are used to withstand axial loads and limit component rotation.
Performance Advantages: The corrosion resistance of titanium washers allows them to form an “all-titanium connection system” with titanium bolts and nuts, completely eliminating the risk of corrosion at the joint. This is particularly effective in harsh environments such as marine and chemical industries. Compared to steel washers, titanium washers are lighter and do not experience galvanic corrosion with titanium connected parts. Furthermore, their excellent ductility allows them to deform slightly during tightening, filling minor surface irregularities in the connected parts and improving sealing performance.
Specification: The inner diameter matches the bolt/screw diameter (M3-M64), the outer diameter is 2-8mm larger than the inner diameter, and the thickness is 0.5mm-5mm. Some special washers (such as wave washers) can be over 10mm thick.
Applications: In the shipbuilding industry, they are used to seal hatches and pipe flanges; in chemical equipment, they are used to connect reactor and valve flanges; in the aerospace industry, they are used to connect engine components to the fuselage to prevent surface damage.
Titanium Studs
Titanium studs are cylindrical fasteners with external threads on both ends. They can be categorized by structure as equal-length studs, unequal-length studs, or single-ended studs (one end threaded and the other with a polished or stepped shaft). Equal-length studs have the same thread length at both ends and are commonly used to connect two components (they screw into threaded holes in the two components). Unequal-length studs have long threads on one end (for screwing into a fixed component) and short threads on the other end (for connecting a movable component with a nut). Single-ended studs are suitable for applications where a nut cannot be installed on one end (such as deep cavities). Some titanium studs also feature a polished section or relief groove in the middle for easier processing and assembly.
Performance Advantages: Titanium studs’ high strength allows them to withstand heavy axial loads, especially in high-temperature conditions (for example, TC4 studs can withstand long-term use at 350°C) while maintaining stable load-bearing capacity. Their low thermal conductivity reduces heat transfer within the joint, making them suitable for connecting high-temperature equipment (such as boilers and heat exchangers) to prevent damage to components at the lower end. Titanium studs also offer excellent fatigue resistance and are less susceptible to fracture under long-term cyclic loads, extending equipment life.
Specification: Thread sizes M4-M64, lengths 20mm-500mm, with thread accuracy of 6g at both ends. The polished rod diameter can be the same as or slightly smaller than the major thread diameter.
Applications: In the petrochemical industry, they are used to connect skirts of large storage tanks and towers; in power equipment (such as steam turbines and generators), they are used to secure stators and rotors; in the aerospace industry, they are used to splice aircraft engine cases.
Titanium Threaded Rod
Titanium threaded rod (also known as titanium lead screw or titanium threaded rod) is a long, headless fastener with full-length external threads. It can be cut to any length as needed. Thread types include coarse, fine, trapezoidal, and buttress threads. Regular threads are used for general connections, while trapezoidal and buttress threads are suitable for applications that transmit power or withstand heavy axial loads (such as in transmission mechanisms and adjustment devices). Some titanium threaded rods also feature surface treatments (such as knurling or chrome plating) to enhance friction or corrosion resistance.
Performance Advantages: Titanium threaded rod’s full-length thread design offers high flexibility, allowing it to be cut to length based on assembly requirements, reducing inventory variety and costs. Titanium’s high specific strength allows it to meet strength requirements for long-span connections or load-bearing applications (such as large brackets and lifting platforms) without significantly increasing the diameter, while also reducing structural weight. Furthermore, titanium threaded rod offers excellent weather resistance, ensuring long-term, stable operation without frequent maintenance when used outdoors or in exposed environments such as marine environments.
Specification Range: Diameters M3-M50, Lengths 1m-6m (longer sizes available on request), Thread Accuracy 6g/6h, Trapezoidal Thread Specifications Mostly Tr20×4, Tr30×6, etc.
Applications: Used in the construction industry for supporting and adjusting glass curtain walls and steel structures; in marine engineering for securing guardrails and steps on offshore platforms; and in mechanical manufacturing for machine tool guide rails and transmissions for lifting mechanisms.
Titanium Rivets
Titanium rivets are fasteners that achieve connection through deformation (such as upsetting or bending). They can be categorized by structure as solid rivets, semi-tubular rivets, hollow rivets, and blind rivets. Solid rivets consist of a head and a shank. The shank is holeless, and the head is formed by hammering or upsetting the end of the shank using a press. Semi-tubular rivets have a shallow hole at the end of the shank, making it easier to upset during deformation and suitable for joining thin sheets. Hollow rivets have a full-bore shank and are lightweight, making them suitable for lightweight and low-load applications. Blind rivets (such as pull rivets) have a built-in core rod that expands and deforms the rivet using a pull gun, eliminating the need for double-sided operation and making them suitable for single-sided assembly.
Performance Advantages: Titanium rivets offer high and permanent connection strength. Once riveted, they resist loosening due to vibration or temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for applications requiring extremely reliable connections, such as aerospace. Their corrosion resistance prevents rust in harsh environments, preventing joint failure due to corrosion. Furthermore, titanium rivets exhibit excellent deformation resistance and are resistant to cracking during the riveting process. They can accommodate components of varying thicknesses and materials (such as titanium alloy and aluminum alloy plates).
Specifications range from 1.5mm to 12mm in diameter and 3mm to 50mm in length. Head types include round, countersunk, and oval heads. Blind rivets are primarily open or closed.
Applications: In the aerospace industry, they are used for riveting aircraft skins and wing leading edges; in shipbuilding, they are used for joining hulls and decks; in the automotive industry, they are used for securing body frames and interior components; and in the medical industry, they are used for assembling surgical instruments and diagnostic equipment.
Related products
-
Titanium Fasteners
Anodized Titanium Screws
-
Titanium Fasteners
Motorcycle Titanium Bolts Pin
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Fasteners For Bicycles
-
Titanium Fasteners
Anodized Titanium Nut
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Titanium Washers
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Wheel Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Gr5 Titanium Wheel Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Titanium Springs