Titanium Fasteners For Robots
Certified: CE & SGS & ROHS
Shape: Requested
Diameter: Customized
Drawings: STEP, IGS , X_T, PDF
Shipping: DHL, Fedex, or UPS & Ocean Freight

20+ YEARS EXPERIENCE SENIOR BUSINESS MANAGER
Ask Michin For What You Want?
Robotic is rapidly penetrating high-end applications, such as precision electronics, medical surgery, and aerospace. As core components of robotic structural connections, the performance of fasteners directly determines the robot’s operating accuracy, load capacity, and service life. Titanium, with its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, superior fatigue performance, and good biocompatibility, is an ideal material for robotic fasteners.

| Size | M3-M120. or non-standard according to your requirements. |
| Materials | Gr1 Gr2 Gr3 Gr4 Gr5 Gr6 Gr7 Gr9 Gr11 Gr12 Gr23 |
| Type | Screw/bolts(cap head/socket head/hex head/round head/headless/taper head/shoulder head.etc) |
| Thread | UNC, UNF, UNEF, M, BSW, BSF, TR, ACME, NPT TP |
| Surface Treatment | Anodizing, sandblasting,black oxide, polishing. powder coating, brushing,electroplating, passivation |
| Drawingformat | IGS,STP,STEP,X-T,DXF,DWG,PrO/E,PDF,PNG,JPG |
| Application | Motorcycle,Bicycle,cars |
| Certifications | ISO9001,CE,BV |
| Service | 1,Free samples will be sent to you after confirming the order. |
| 2,Material test report,Hardness test report,Quality Inspection Report as your require. | |
| 3,video and photos with details freely during. | |
| 4,Drawing formation: PDF, CAD/DWG/DXF, IGS/STP etc.If you don’t have a professional drawing, you can contact us and we will customize it for you according to your requirements. | |
| Euipment | CNC Turning, CNC Milling, CNC 5-axis Turning-milling Compound, CNC Gear Hobbing Machine, CNC Gear Shaping Machine, Manual Milling Machine, Grinding Machine, and Laser Engraving Machine. |
| Quality | Two-dimensional Imager, CCD Image Detection Equipment, Rockwell Hardness Tester, Vickers Hardness Tester, Electron Microscope,Salt Spray Tester,etc. |
| Packing | PE bag,EPE, standardcardboard boxes or plastic trays, sponge trays,cardboard trays,etc |
| Precision | TIR ≤.002″ (0.02mm-5mm) |
| MOQ | In stock:50pcs Custom-made:100pcs |
| Color | Silver, black, red, yellow, green, blue, color, customized according to your requirements |
| Delivery time | In stock : Sample 3days,Bulk goods 7-15days. |
| Custom : Sample 7-10 working days, Bulk goods 15-20 working days. |
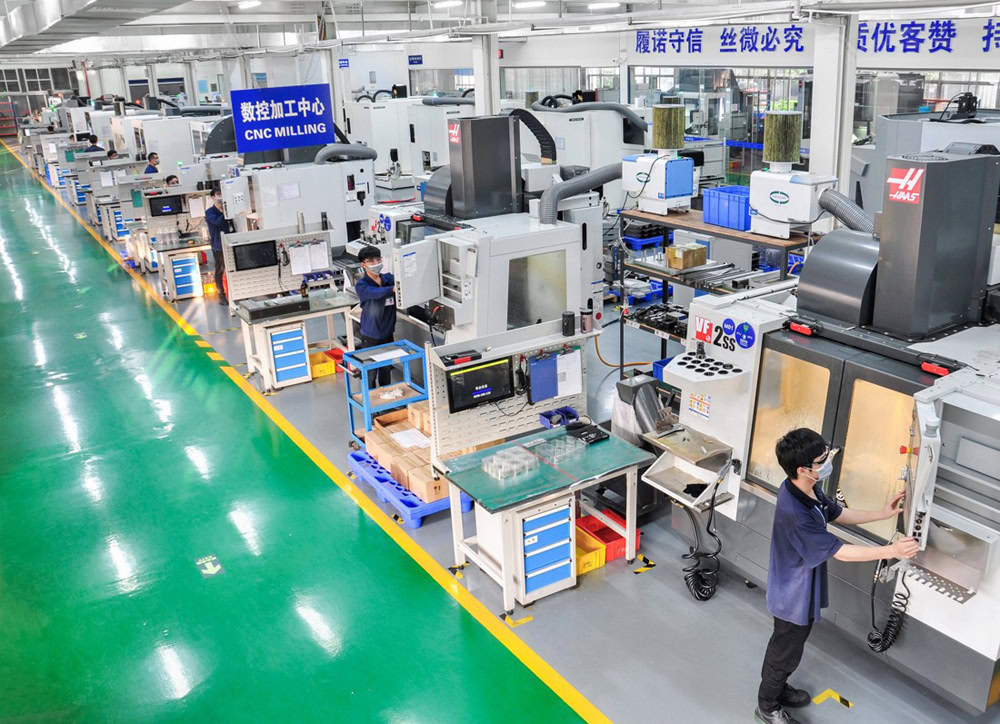

Manufacturing Titanium Fasteners for Robots
Manufacturing titanium fasteners for robots is a complex system engineering process that integrates materials science, precision machining, heat treatment, and surface treatment.
CNC Precision Machining
Robot fasteners (such as bolts, nuts, and screws) require extremely high dimensional accuracy and geometric tolerances. For example, a 0.01mm misalignment in the bolts at the joints of an industrial robot can cause the joint to stall and affect the robot’s repeatability (typically required to be within ±0.02mm). Wstitanium utilizes high-rigidity CNC machining centers and customized process parameters to achieve precision machining of titanium fasteners. Wstitanium has invested in a DMG MORI DMC 635 V vertical machining center from Germany and a FANUC ROBODRILL α-DiB series drilling and tapping center from Japan. These equipment boasts positioning accuracy of ±0.003mm and repeatability of ±0.0015mm. Wstitanium’s titanium fasteners maintain dimensional tolerances of IT6-IT7 (for example, the pitch diameter tolerance of an M10×1.5 bolt is ±0.015mm), while geometric and positional tolerances (such as coaxiality and perpendicularity) are controlled within 0.01-0.02mm, fully meeting the stringent requirements of key robotic components such as joints, reducers, and motors.
Heat Treatment
Titanium’s mechanical properties are extremely sensitive to heat treatment processes. Wstitanium offers customized heat treatment solutions tailored to the specific application scenarios of robotic fasteners (e.g., high-load joints, lightweight arms, and corrosive environments) to optimize their strength, hardness, toughness, and fatigue performance.
– β-annealing: The titanium alloy is heated to 20-50°C above the β-transformation point (approximately 995°C for Ti-6Al-4V), held at this temperature for a period of time, and then air-cooled or furnace-cooled. This technique produces a coarse β-grain structure, significantly improving the fracture toughness of titanium fasteners (KIC can reach over 60 MPa·m¹/²), making them suitable for robot joint bolts subjected to impact loads.
– Duplex annealing: The alloy is first held below the β-transformation point (approximately 920°C), air-cooled to room temperature, and then aged at 500-600°C. This technique balances the strength and ductility of the titanium alloy, achieving a tensile strength of 900-950 MPa and an elongation of 15%-18% for Ti-6Al-4V fasteners, making them suitable for most structural connections in industrial robots.
– Solution Treatment and Aging: The titanium alloy is heated to the α+β phase region (approximately 940°C), held there, then water quenched and aged at 480-540°C. This technology can increase the tensile strength of titanium fasteners to over 1100 MPa and the hardness to HRC38-42, making them suitable for high-load, high-precision robotic reducer connection bolts.
Surface Treatment
Robotic fasteners must withstand certain preloads during assembly, and some applications (such as food processing robots and ocean exploration robots) require extremely high corrosion resistance. Wstitanium uses a variety of surface treatment technologies to further enhance the surface properties of titanium fasteners.
– Pickling and Passivation: Wstitanium uses a nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid mixture to pickle the fasteners to remove scale and surface contaminants generated during processing. The fasteners are then passivated in nitric acid to form a uniform, dense TiO₂ oxide film (approximately 5-10 nm thick). This oxide film exhibits exceptional chemical stability, ensuring titanium fasteners remain corrosion-free for over 1,000 hours in a neutral salt spray test, making it suitable for most industrial environments.
– Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO): Also known as micro-arc oxidation, this process involves applying a high-voltage pulsed current to the titanium alloy surface, causing a plasma chemical reaction in an electrolyte to form a 10-50μm thick ceramic oxide film. This film exhibits strong adhesion to the substrate (adhesion ≥ 50MPa), a hardness of HV500-800, and excellent wear and corrosion resistance (salt spray test life exceeding 5,000 hours). It is suitable for robotic fasteners in high-wear and high-corrosion environments (such as marine robots and food processing robots).
– Nitriding: Under high temperatures (700-800°C) and a high-nitrogen atmosphere, nitrogen atoms penetrate the titanium alloy surface, forming a TiN compound layer (approximately 5-15μm thick). The TiN layer boasts a hardness of HV1000-1200 and a low coefficient of friction (0.15-0.25), significantly improving the wear resistance and anti-seizure properties of fasteners, preventing galling during assembly. It is suitable for bolts in robot joints that require frequent disassembly.
– PVD coating (Physical Vapor Deposition): Using magnetron sputtering or arc ion plating technology, a hard coating (2-5μm thick) such as TiN or TiAlN is deposited on the surface of titanium fasteners. This coating exhibits extremely high hardness (above HV2000) and a very low coefficient of friction. It also offers excellent high-temperature resistance (up to 600°C), making it suitable for fasteners connecting high-speed, high-temperature robotic motors.
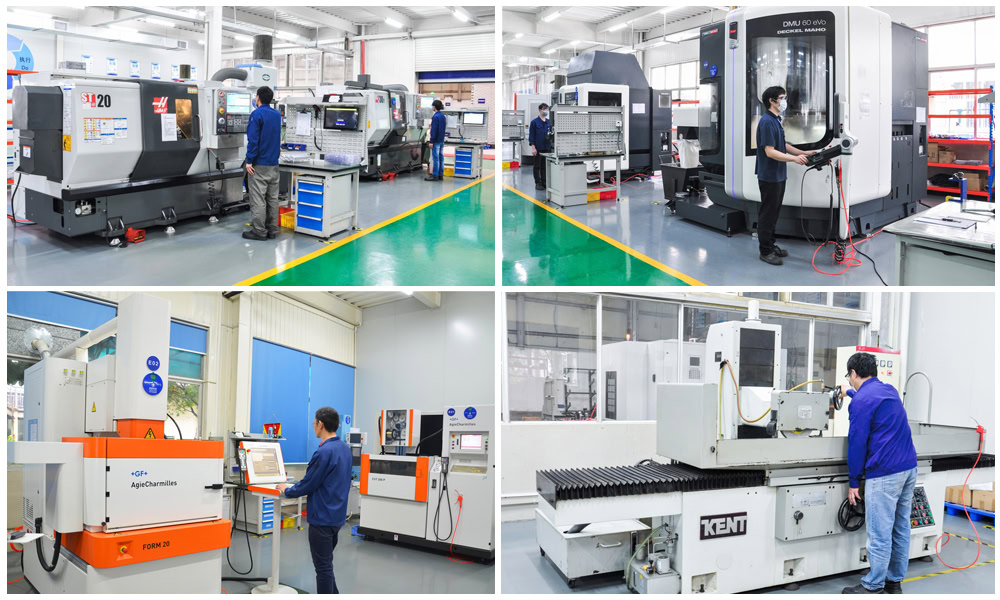

Wstitanium utilizes advanced CNC machining technology and a rigorous quality control system to ensure the exceptional precision and stability of its titanium fasteners:
– Dimensional Accuracy: Key fastener dimensions (such as thread pitch diameter, bolt diameter, and length) are held to tolerances of IT6-IT7, significantly exceeding national standards (typically IT8-IT9).
– Geometric Tolerances: Bolt coaxiality and perpendicularity are controlled within 0.01-0.02mm, ensuring minimal axial deviation of the joint after assembly.
– Stability: Titanium alloy has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (8.6×10⁻⁶/°C), only 60% of that of steel. In environments with significant temperature fluctuations (such as automotive welding robots), fasteners experience minimal dimensional change, maintaining a stable preload and preventing joint loosening that could affect precision.
Related products
-
Titanium Fasteners
Motorcycle Titanium Bolts Pin
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Hexagon Head Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Bolts Supplier
-
Titanium Fasteners
Anodized Titanium Nut
-
Titanium Fasteners
Gr5 Titanium Wheel Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Gr5 Manifold Titanium Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Titanium Springs
-
Titanium Fasteners
Burnt Titanium Wheel Bolt