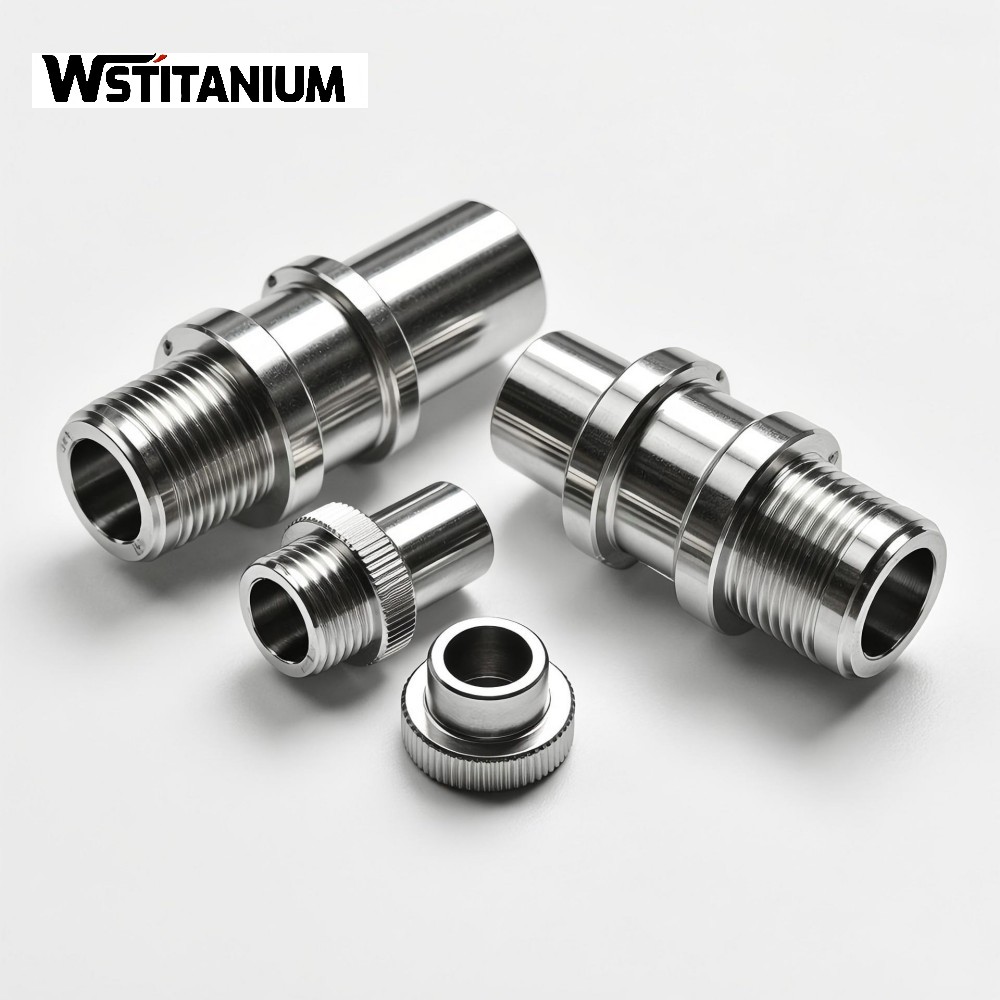
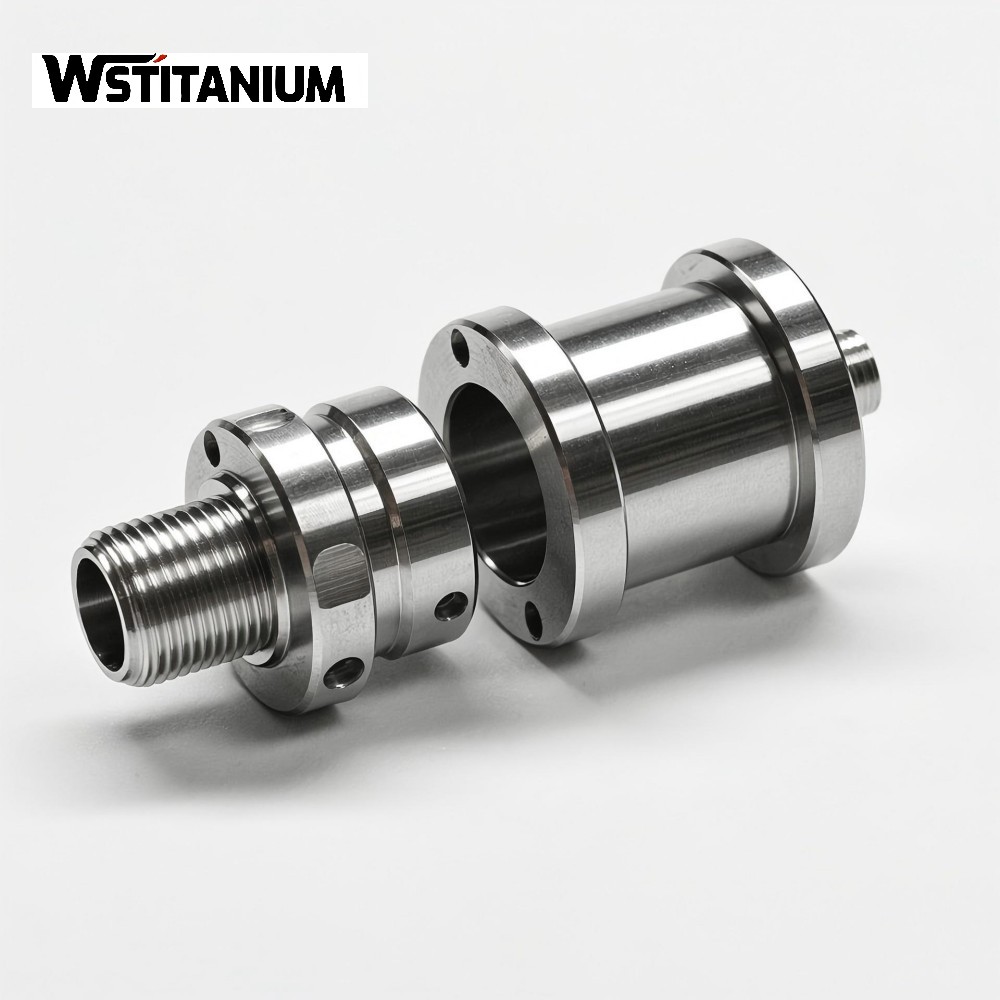
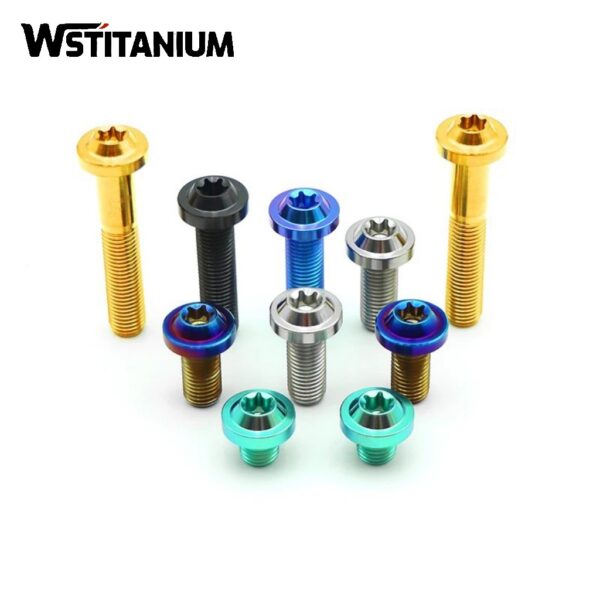
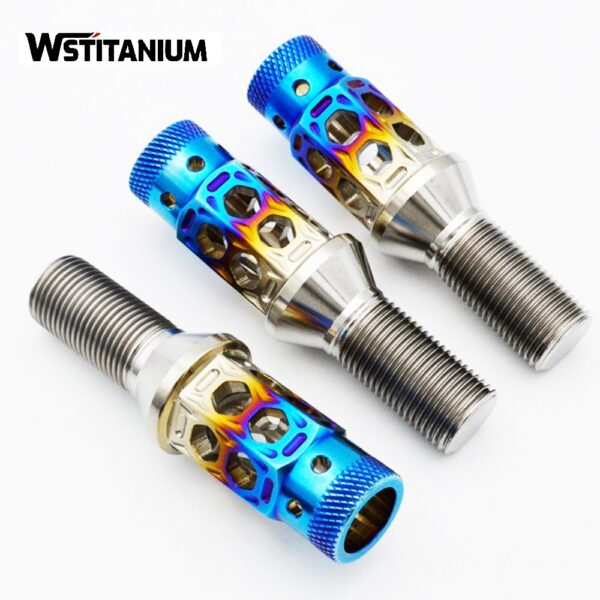
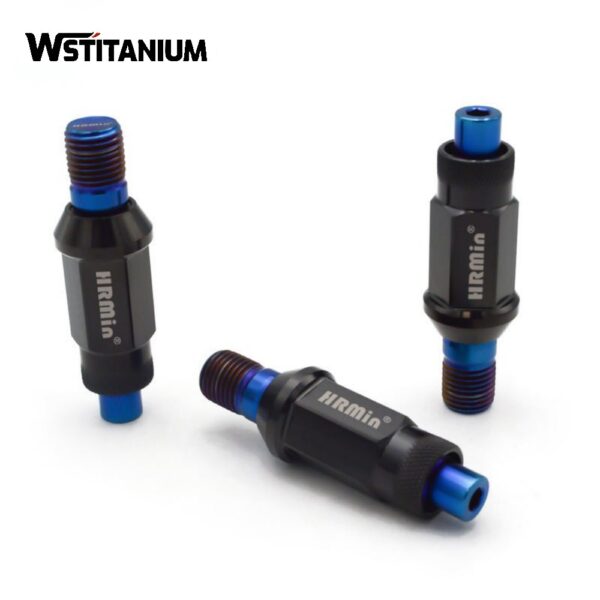
CNC Machining Aerospace Fasteners
Certified: CE & SGS & ROHS
Shape: Requested
Diameter: Customized
Drawings: STEP, IGS , X_T, PDF
Shipping: DHL, Fedex, or UPS & Ocean Freight

20+ YEARS EXPERIENCE SENIOR BUSINESS MANAGER
Ask Michin For What You Want?
In the aerospace industry, fasteners serve as core components that connect structural parts, transmit loads, and ensure system integrity. Their performance is directly related to the safety, reliability, and service life of aircraft. Titanium and titanium alloys are the preferred materials for aerospace fasteners due to their low density (approximately 60% that of steel), high strength (tensile strength exceeding 1000 MPa), excellent corrosion resistance (stable in air, seawater, and various media), and superior high-temperature mechanical properties (maintaining high strength at 300-600°C).
As modern aerospace technology evolves towards high loads, long life, and lightweighting, traditional machining methods are unable to meet the high precision (dimensional tolerances of up to ±0.005mm), complex structures (such as special-shaped heads and multiple threaded sections), and demanding surface quality (roughness Ra ≤ 0.8μm) required for titanium fasteners. CNC (computer numerical control) machining technology, with its advantages of high automation, stable precision, excellent repeatability, and adaptability to complex processes, has become a core technology path for the manufacture of titanium fasteners in aerospace.
| Size | M3-M36. or non-standard according to your requirements. |
| Materials | Gr1 Gr2 Gr3 Gr4 Gr5 Gr6 Gr7 Gr9 Gr11 Gr12 Gr23 |
| Type | Screw/bolts(cap head/socket head/hex head/round head/headless/taper head/shoulder head.etc) |
| Thread | UNC, UNF, UNEF, M, BSW, BSF, TR, ACME, NPT TP |
| Surface Treatment | Anodizing, sandblasting,black oxide, polishing. powder coating, brushing,electroplating, passivation |
| Drawingformat | IGS,STP,STEP,X-T,DXF,DWG,PrO/E,PDF,PNG,JPG |
| Application | Motorcycle,Bicycle,cars |
| Certifications | ISO9001,CE,BV |
| Service | 1,Free samples will be sent to you after confirming the order. |
| 2,Material test report,Hardness test report,Quality Inspection Report as your require. | |
| 3,video and photos with details freely during. | |
| 4,Drawing formation: PDF, CAD/DWG/DXF, IGS/STP etc.If you don’t have a professional drawing, you can contact us and we will customize it for you according to your requirements. | |
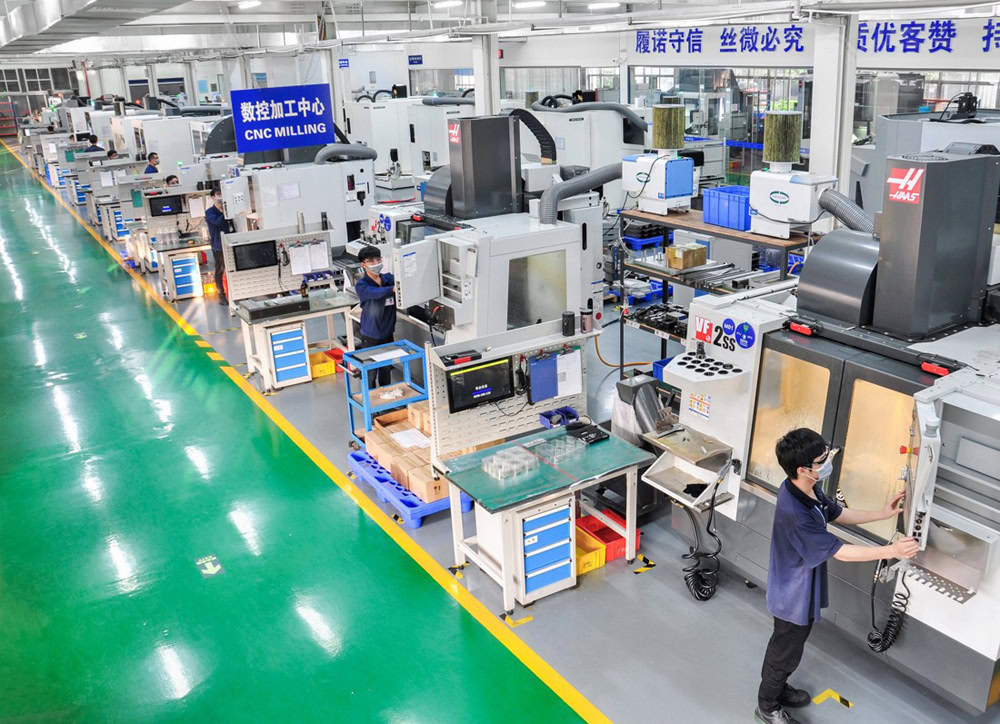
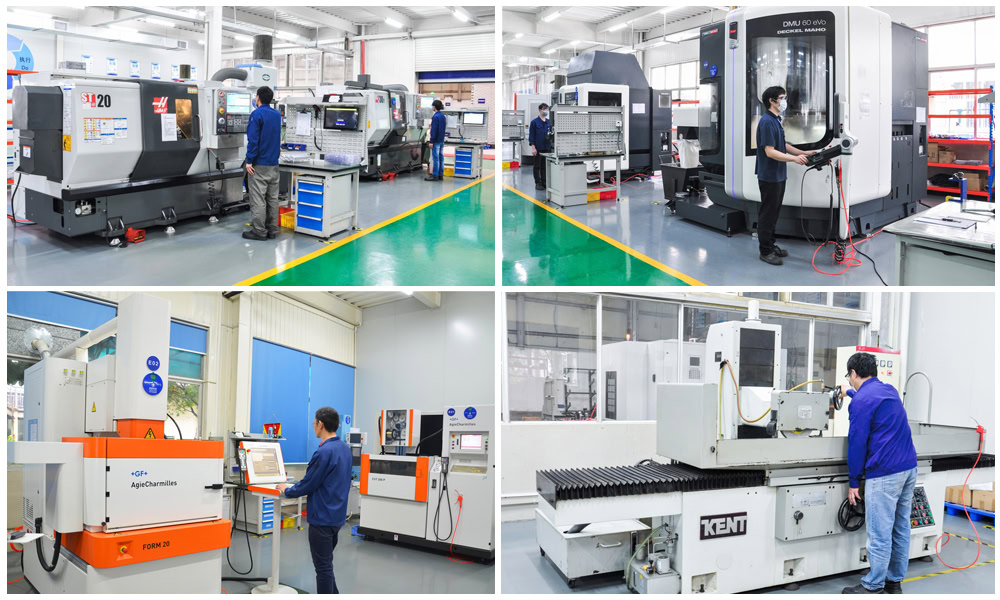
| Euipment | CNC Turning, CNC Milling, CNC 5-axis Turning-milling Compound, CNC Gear Hobbing Machine, CNC Gear Shaping Machine, Manual Milling Machine, Grinding Machine, and Laser Engraving Machine. |
| Quality | Two-dimensional Imager, CCD Image Detection Equipment, Rockwell Hardness Tester, Vickers Hardness Tester, Electron Microscope,Salt Spray Tester,etc. |
| Packing | PE bag,EPE, standardcardboard boxes or plastic trays, sponge trays,cardboard trays,etc |
| Precision | TIR ≤.002″ (0.02mm-5mm) |
| MOQ | In stock:50pcs Custom-made:100pcs |
| Color | Silver, black, red, yellow, green, blue, color, customized according to your requirements |
| Delivery time | In stock : Sample 3days,Bulk goods 7-15days. |
| Custom : Sample 7-10 working days, Bulk goods 15-20 working days. |


CNC Machining Aerospace Titanium Fasteners
Aerospace titanium fasteners require dimensional accuracy and geometric tolerances far exceeding those of ordinary industrial fasteners. For example, the pitch diameter tolerance of titanium alloy bolts in aircraft engine compartments must be controlled to GB/T 197 Grade 6g or higher. The coaxiality tolerance between the head and shank must not exceed 0.01mm. CNC machining uses digital program control to control tool movement, achieving positioning accuracy of ±0.001mm and repeatability of ±0.0005mm. This effectively eliminates errors caused by manual operation and ensures highly consistent dimensions of fasteners produced in batches, meeting the “zero defect” quality requirements of the aerospace industry.
1. CNC Turning: Precision Forming of Basic Shapes
CNC turning is the first core process in titanium fastener machining, primarily used for machining rotating structures such as shanks, head end faces, and external cylindrical surfaces. The tool rake angle is typically 5°-10°, and the clearance angle 8°-12° to reduce cutting resistance and tool sticking. Cutting parameters vary depending on the titanium alloy grade. For example, for TC11 titanium alloy (commonly used for fasteners in high-temperature environments), rough turning uses a cutting speed of 60-80 m/min, a feed of 0.15-0.2 mm/r, and a depth of cut of 1-2 mm. Finish turning uses a cutting speed of 80-100 m/min, a feed of 0.05-0.1 mm/r, and a depth of cut of 0.2-0.5 mm. Ensure a surface roughness Ra ≤ 1.6 μm.
2. CNC Milling: Precision Forming of Complex Structures
CNC milling is primarily used for machining titanium fasteners with special-shaped heads (such as hexagon sockets, dodecagonal sockets, and flange faces), grooved structures (such as locking grooves and undercuts), and flat surfaces. 5-axis CNC machining is particularly suitable for machining complex fasteners with angular features. The cutting depth per layer is controlled at 0.1-0.5mm to avoid excessive load in a single cut, which could lead to tool breakage. For example, when machining the flange end face of a titanium alloy flange bolt, a milling speed of 80-120m/min, a feed rate of 100-300mm/min, and a cutting depth of 0.3mm per layer can achieve a flange end face flatness tolerance within 0.01mm/m.
3. CNC Tapping: Precision Thread Machining
Threads are the core structure that enables the connection function of titanium fasteners. CNC tapping must ensure thread accuracy (typically 6H/6g), surface quality (Ra ≤ 1.6μm), and thread profile integrity. Common thread types include coarse threads, fine threads, and trapezoidal threads. Cutting speeds are typically 5-15m/min, with a feed rate equal to the thread pitch (e.g., for an M8×1.25 thread, the feed rate is 1.25mm/r).
For high-precision threads, a three-step method of pre-drilling, rough tapping, and fine tapping can be used. The pre-drilled bottom hole diameter is calculated according to the formula (internal thread bottom hole diameter = nominal diameter – 1.0825 × pitch). For example, for an M10×1.5 internal thread, the bottom hole diameter is 8.37mm. A small-diameter tap is used for rough tapping, leaving a machining allowance of 0.1-0.2mm. A standard tap is used for fine tapping to ensure final thread accuracy. Furthermore, after tapping, 100% inspection with a thread plug gauge (for internal threads) or a ring gauge (for external threads) is required to ensure thread conformity.
4. CNC Drilling: Precision Hole Machining
Aerospace titanium fasteners often require the machining of locating holes, through holes, and blind holes, such as pin holes in bolt shanks and retaining holes for nuts. CNC drilling requires guaranteed hole diameter tolerances (typically H7-H8), hole position accuracy (positioning tolerance ≤ 0.02mm), and hole surface finish. The drill bit’s top angle is designed to be 130°-140°, and the chisel edge should be ground to 0.5-1mm to reduce axial cutting forces. For deep holes (hole depth > 5 times the hole diameter), an internal coolant drill is required, with cutting fluid delivered directly to the cutting zone through internal channels.
Cutting parameters: drilling speeds of 30-80m/min and feeds of 0.05-0.15mm/r. Higher speeds are acceptable for smaller hole depths, while deeper holes require lower speeds and more retractions (one retraction every 2-3 times the hole diameter) to facilitate chip evacuation. For example, when drilling a φ4mm through-hole for an M6 bolt in TC4 titanium alloy, a φ4mm carbide drill is used, with a cutting speed of 50m/min and a feed of 0.1mm/r. Drilling to the desired depth in three passes is achieved, achieving hole position accuracy within 0.015mm and a hole wall roughness of Ra ≤ 1.6μm.
5. CNC Grinding: High-Precision Surface
CNC grinding is primarily used for the final precision machining of titanium fasteners, including external cylindrical grinding (for shank diameter refinement), face grinding (for head or end face flatness trimming), and thread grinding (for high-precision thread processing). It can maintain dimensional tolerances within ±0.002mm and improve surface roughness to Ra ≤ 0.4μm.
Cubic boron nitride (CBN) grinding wheels are used, with a grit size of 80#-120# and a medium-soft hardness. Grinding parameters include a grinding wheel linear speed of 30-50m/s, a workpiece rotational speed of 100-300r/min, and a feed rate of 0.001-0.005mm/stroke. Taking the grinding of TC6 titanium alloy bolt shank as an example, rough grinding removes 0.1-0.2mm of allowance, and fine grinding removes 0.02-0.05mm of allowance. The final shank roundness tolerance is ≤0.003mm, and the diameter tolerance is ±0.002mm.
Related products
-
Titanium Fasteners
Custom Manufacturing Titanium Screws
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Fasteners For Automotive
-
Titanium Products
Titanium Fasteners For Motorcycles
-
Titanium Fasteners
Custom Gr5 Titanium Fasteners
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Screws and Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Titanium Washers
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Wheel Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Gr5 Manifold Titanium Bolts