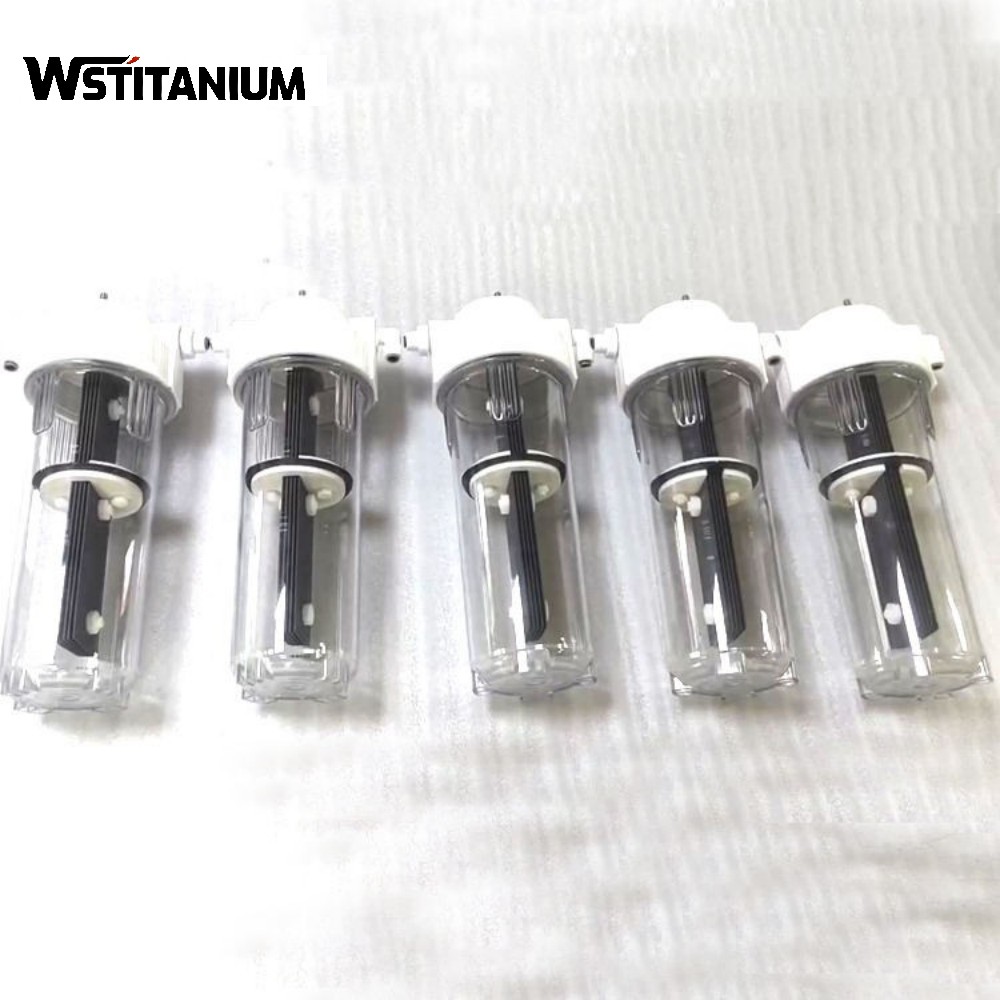
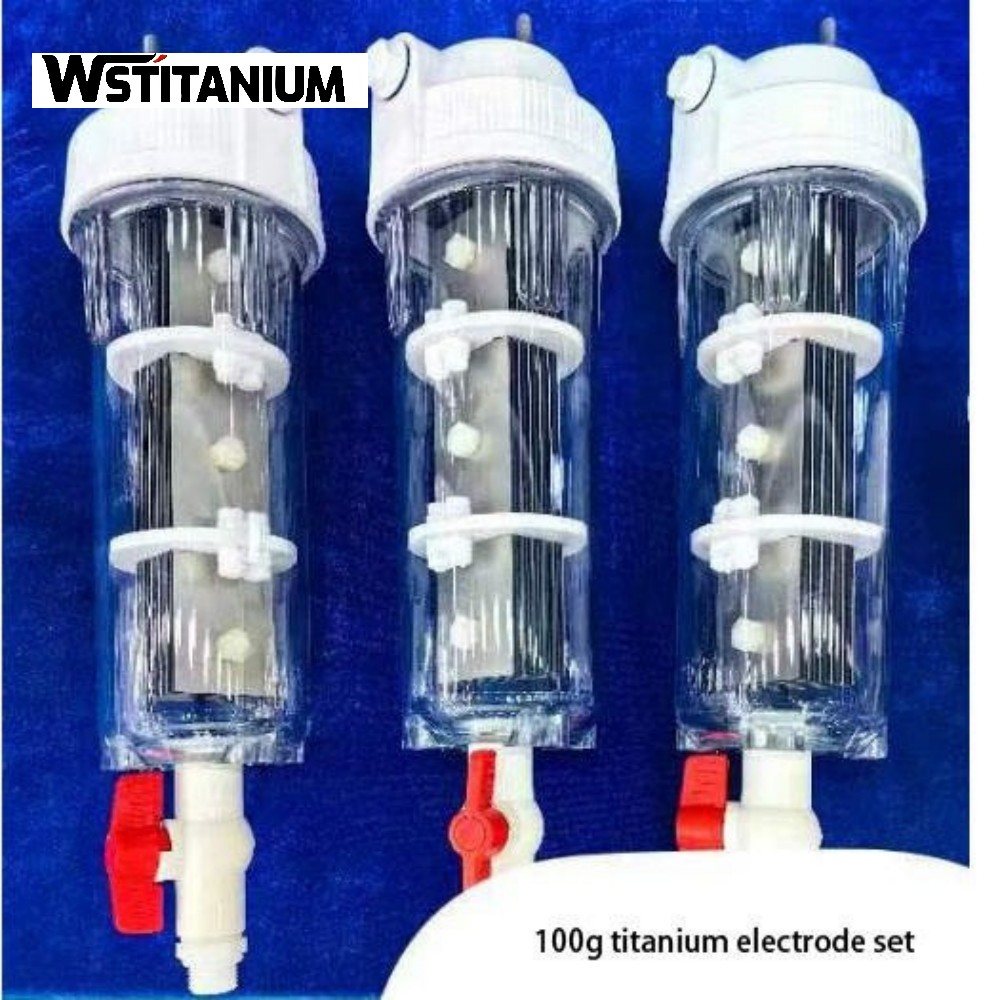
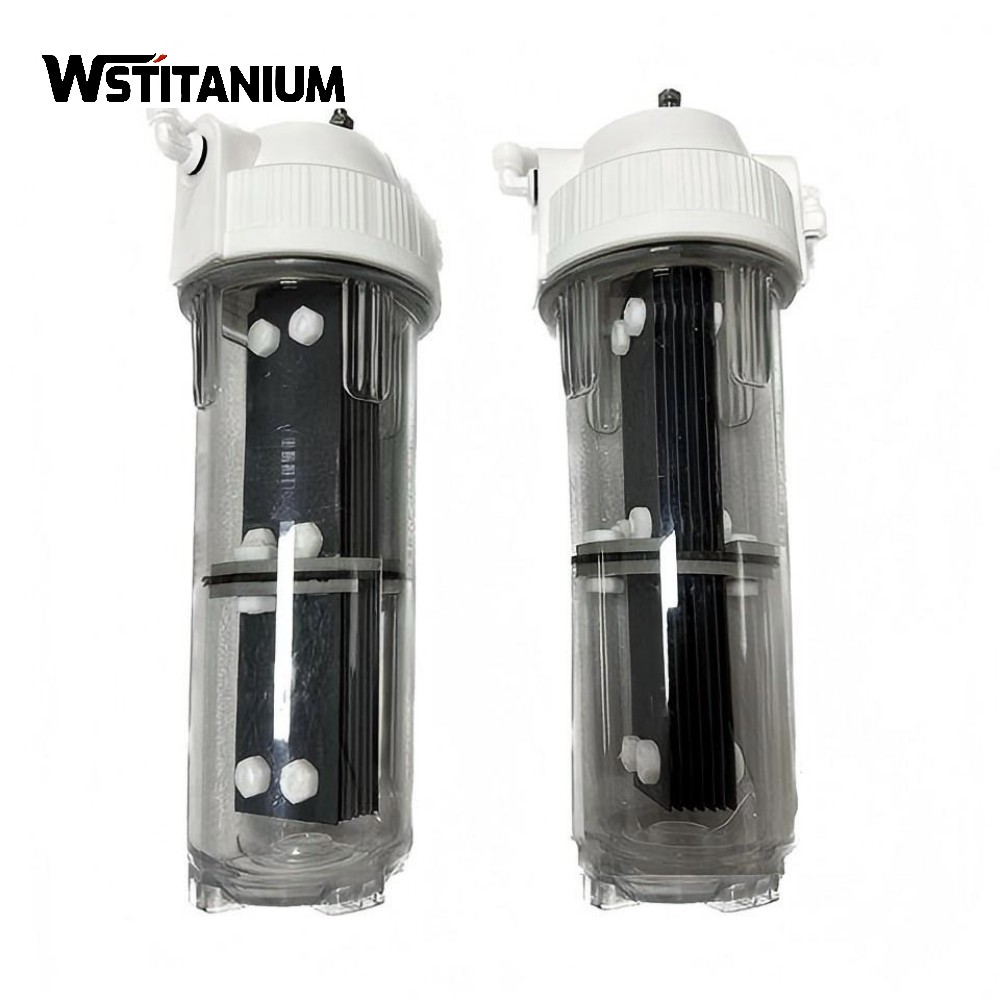
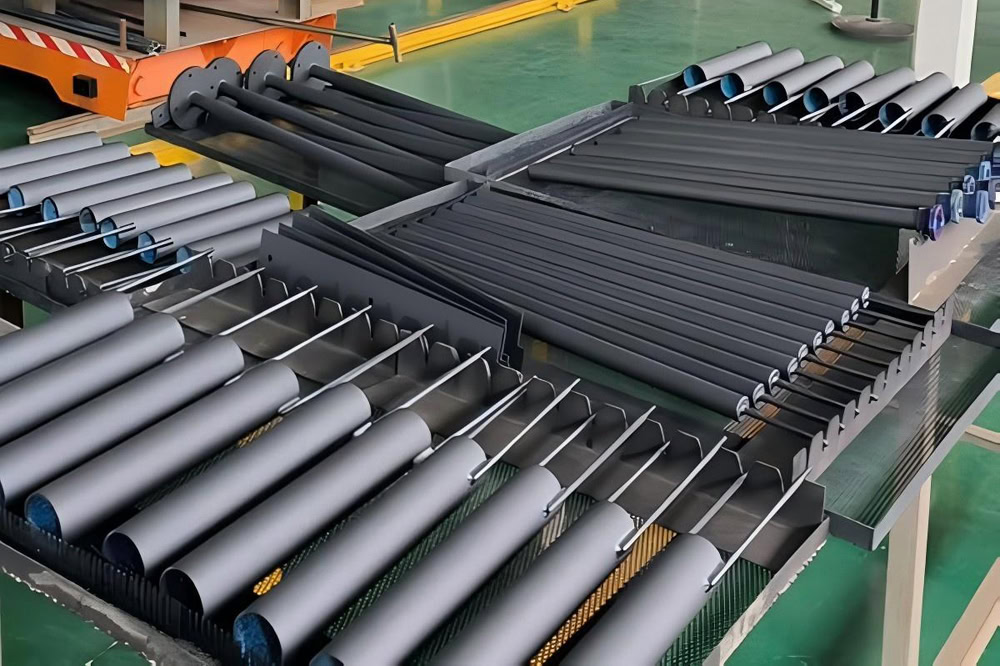
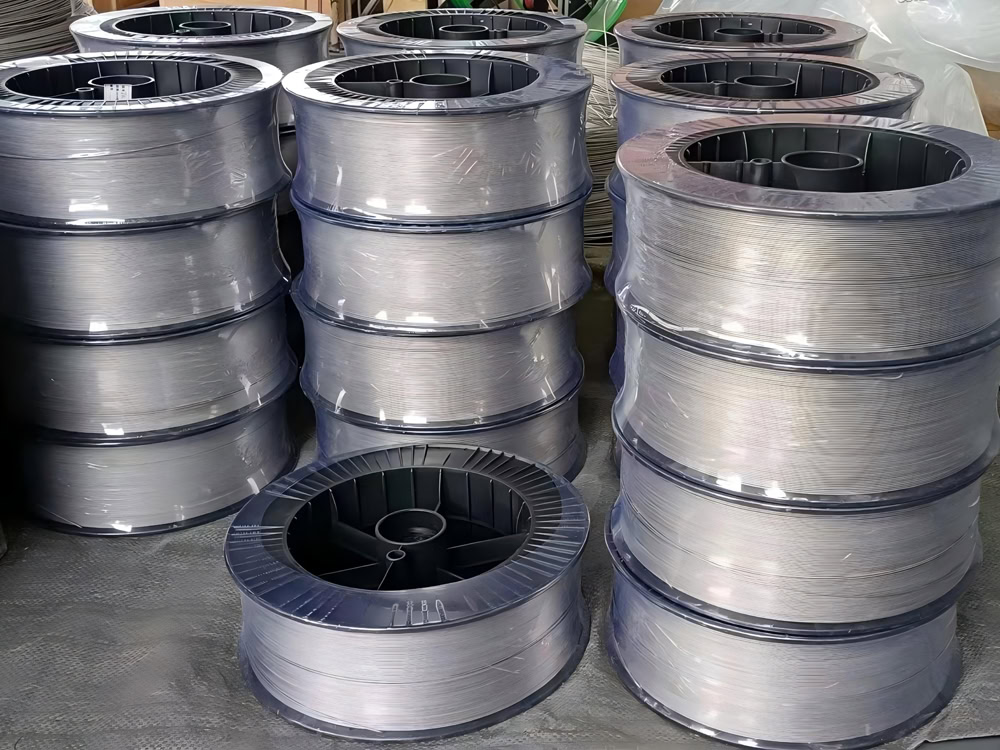
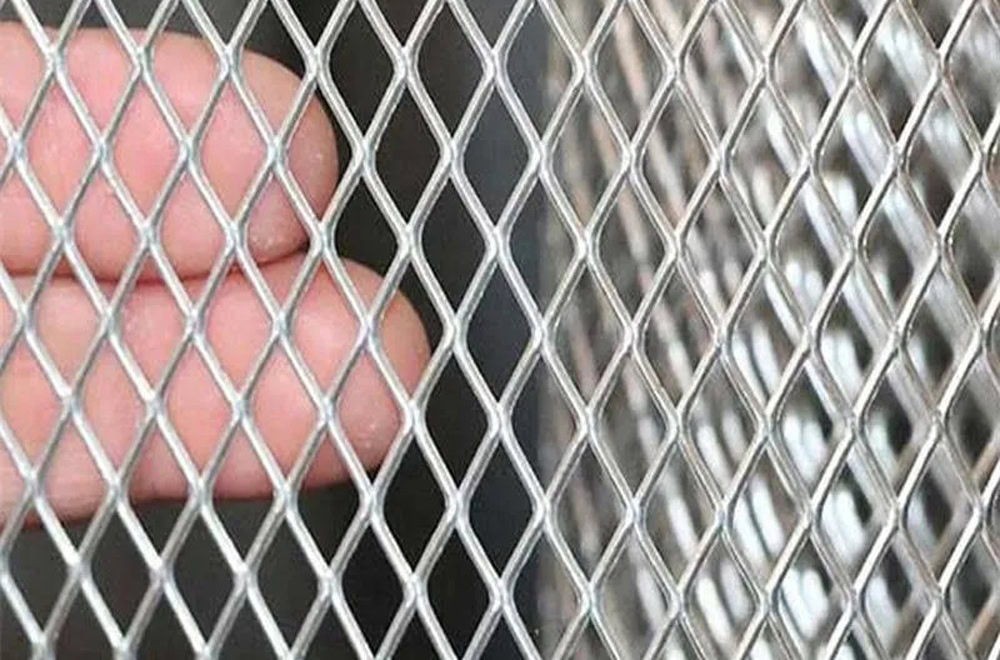
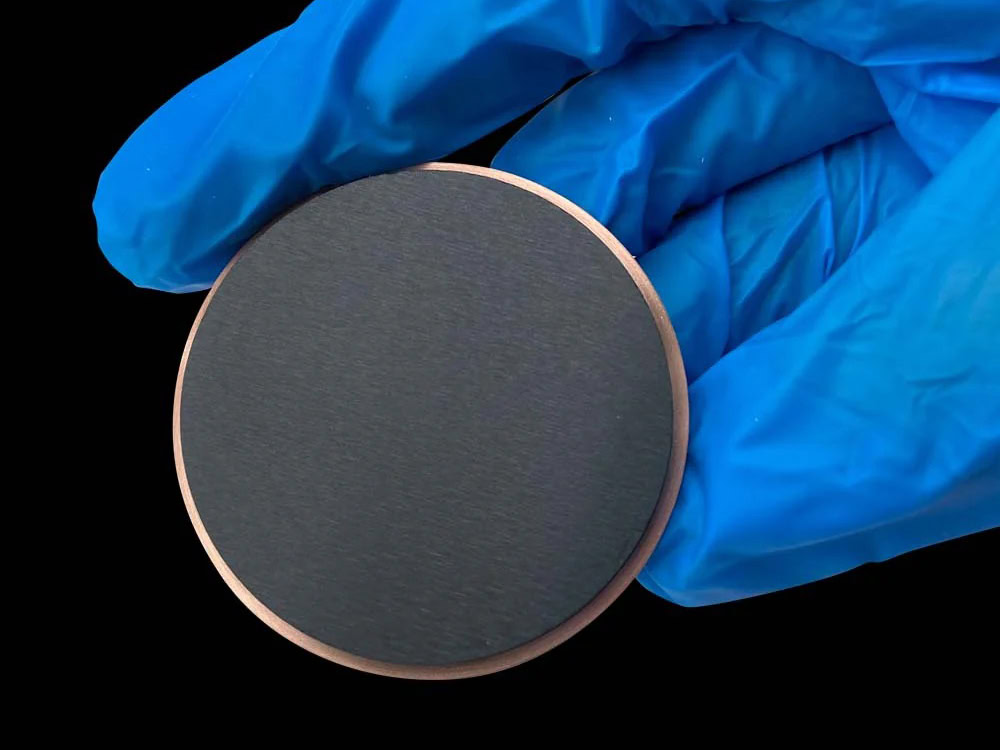
MMO Titanium Anode For Sewage Treatment
Certified: CE & SGS & ROHS
Shape: Requested
Diameter: Customized
Drawings: STEP, IGS , X_T, PDF
Shipping: DHL, Fedex, or UPS & Ocean Freight

20+ YEARS EXPERIENCE SENIOR BUSINESS MANAGER
Ask Michin For What You Want?
Wastewater treatment has become a core issue in ensuring ecological security and sustainable development. Industrial wastewater (such as that from printing and dyeing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and electroplating) contains persistent organic matter, heavy metal ions, and high concentrations of salt. Electrochemical treatment technology, with its advantages of high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and strong controllability, has become a key technology for addressing the challenges of complex wastewater treatment. The performance of the electrode material directly determines the efficiency and economic viability of this technology.
Titanium-based metal oxide-coated anodes (MMO titanium anodes, also known as DSA dimensionally stable anodes) use a pure titanium substrate coated with a composite coating of precious metal oxides such as ruthenium, iridium, and tantalum. This achieves a perfect combination of corrosion resistance and catalytic activity. They are widely used in industrial wastewater treatment, drinking water disinfection, and desalination of high-salinity wastewater, driving the transition to greener and more efficient wastewater treatment.
| Technical Measurement | Performance |
| Coating Element | Iridium Oxide (IrO₂), Ruthenium Oxide (RuO₂),Platinum |
| Substrate Material | Titanium Gr1 or Gr2 |
| Titanium Anode Shape | Customized Plate/Mesh/Tube/Rod/Wire/Disc |
| Coating Thickness | 8~20 μm |
| Coating Uniformity | 90% min. |
| Current Density | ≤ 20000 A/m² |
| Operating Voltage | ≤ 24V |
| PH Range | 1~14 |
| Temperature | < 80 °C |
| Fluoride Ion Content | < 50 mg/L |
| Warranty | More than 5 years |
Working Principle of MMO Titanium Anodes
MMO titanium anodes utilize the dual effects of current conduction and catalytic reactions to drive the oxidative degradation, flocculation, and electrochemical deposition of pollutants in wastewater, achieving efficient pollutant removal. Electrocatalytic oxidation is the core mechanism of MMO titanium anodes in treating difficult-to-degrade organic matter.
Direct Oxidation
Pollut molecules are directly adsorbed onto the active sites of the MMO coating and oxidized and decomposed through electron transfer. Precious metal oxides (such as IrO₂ and RuO₂) in the coating lower the activation energy of the reaction, breaking down the molecular chains of difficult-to-degrade organic matter such as benzene and phenols, ultimately converting them into CO₂ and H₂O.
Indirect Oxidation
The electrode catalyzes the generation of strong oxidants such as hydroxyl radicals (・OH) and hypochlorous acid (HClO) from water molecules or chloride ions. These active species have oxidation potentials as high as 2.8V and can indiscriminately attack pollutants. In the treatment of chlorine-containing wastewater, ruthenium-based coatings can efficiently convert chloride ions into hypochlorous acid, achieving both degradation and disinfection capabilities. In a chlorine-free system, the iridium coating preferentially generates hydroxyl radicals, specifically targeting recalcitrant organic matter.
Electroflocculation
When an MMO titanium anode is used with a soluble cathode such as iron or aluminum, it can separate pollutants through electrolysis to generate a flocculant. The current conducted by the anode dissolves the cathode, generating metal ions such as Fe⁺ and Al⁺. These ions hydrolyze in water to form flocs such as iron hydroxide and aluminum hydroxide, which effectively adsorb suspended matter, colloidal particles, and some heavy metal ions in wastewater, resulting in precipitation and removal. This mechanism eliminates the need for additional chemical flocculants and reduces sludge production by over 40% compared to traditional flocculation methods.
Electrochemical Deposition
For heavy metal wastewater and high-salinity wastewater, the MMO titanium anode achieves purification through two proprietary mechanisms. In heavy metal wastewater treatment, the electric field provided by the anode causes heavy metal ions such as Cu²⁺, Ni²⁺, and Cr⁶⁺ to be reduced and deposited at the cathode, achieving a recovery rate exceeding 95%. In high-salinity wastewater treatment, the electric field formed by the anode and cathode drives anions such as chloride and sulfate to migrate toward the anode, while cations such as sodium and calcium migrate toward the cathode, achieving synergistic desalination and organic matter degradation.
Types of MMO Titanium Anodes
The performance differences of MMO titanium anodes are primarily determined by the coating composition and product form. Different types of electrodes are suitable for different water quality characteristics and requirements. Considering the diversity of wastewater treatment scenarios, the industry primarily uses the following classification method to categorize MMO titanium anodes:
(I) Classification by Coating
The coating composition directly determines the electrode’s catalytic properties and applicable media, and is the core basis for the classification of MMO titanium anodes. MMO titanium anodes are primarily divided into three categories:
Ruthenium MMO Titanium Anodes (Chlorine Evolution Type)
Ruthenium-Based MMO Titanium Anodes (Chlorine Evolution Type) use RuO₂ as the core active ingredient, typically combined with IrO₂, TiO₂, or SnO₂ to form a composite coating system. These electrodes are the preferred electrode for treating high-chloride wastewater. Their key advantage lies in their low chlorine evolution potential (≤1.36V vs. SHE), enabling them to efficiently catalyze chloride ions into oxidizing species such as hypochlorous acid. They also possess excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to chlorine corrosion. These electrodes are suitable for applications with high chloride ion concentrations (typically >1000mg/L), such as electroplating wastewater and desalination brine. The operating current range is <7500A/m², and performance is stable within the temperature range of 25-80°C. The total ruthenium and iridium content in the coating is typically controlled between 8-35g/m². The surface is black, and a high-temperature oxidation process forms a uniform coating that is firmly bonded to the substrate.
Iridium MMO Titanium Anode (Oxygen Evolution Type)
Using IrO₂ as the primary active ingredient, and doped with oxides such as Ta₂O₅ and TiO₂ to enhance stability, this electrode is a core electrode for oxygen-evolution-dominated wastewater treatment. Its outstanding features include a moderate oxygen overpotential, efficient catalysis of water molecules to generate strong oxidants such as hydroxyl radicals (・OH), and excellent corrosion resistance in acidic and sulfate systems. This type of electrode is suitable for treating difficult-to-degrade organic matter such as printing and dyeing wastewater and pharmaceutical wastewater, as well as industrial wastewater with high sulfate content. The coating loss rate can be as low as 1-6mg/A·a.
Composite Coated MMO Titanium Anode
Specialized coating systems tailored to complex wastewater characteristics are typically composed of a titanium oxide composite coating and a platinum group metal modified coating. The titanium oxide coating offers excellent acid and alkali resistance, making it suitable for treating high-sulfate wastewater. The platinum group metal modified coating exhibits exceptionally high catalytic activity, making it suitable for high-precision pollutant degradation. This type of electrode offers excellent adaptability, allowing the coating ratio to be adjusted based on wastewater composition (e.g., fluorine, phosphorus, and heavy metal content). It performs exceptionally well in the treatment of specialty wastewater, such as electronic wastewater and fine chemical wastewater.
(II) Classification by Product Form
Depending on the structure and mass transfer requirements of the wastewater treatment equipment, MMO titanium anodes can be processed into a variety of shapes to achieve uniform current distribution and efficient reaction.
Mesh MMO Titanium Anode
Made of a grid-like structure cross-welded with titanium conductive strips, the mesh size can be customized (e.g., 12.7×4.5mm or 6×3mm). It offers the advantages of large surface area and high mass transfer efficiency. Suitable for use in open electrolytic cells, large oxidation tanks, and other applications requiring large-area current distribution, mesh electrodes can effectively reduce the “bubble shielding effect” and improve reaction uniformity. In dyeing wastewater treatment, mesh electrodes can improve dye degradation efficiency by over 30% compared to plate electrodes.
Tubular/Rod MMO Titanium Anodes
Adopting hollow or solid cylindrical structures, the length can be customized to meet treatment requirements. The tubular structure creates turbulent flow, ensuring more complete contact between the electrolyte and the electrode surface, improving reaction efficiency by 40% compared to plate electrodes. They are suitable for deep well treatment systems, pipeline corrosion protection, wastewater treatment, and cyclic electrolytic desalination processes for high-salinity wastewater. An electrolysis system using titanium tube anodes in an industrial park has maintained stable performance after five years of continuous operation, with a coating loss rate of less than 0.2μm per year.
Strip/Flexible MMO Titanium Anodes
Standard strip anodes are 6.35mm wide and 0.635mm thick, available in rolls up to 76.2 meters or 152.4 meters. Flexible anodes utilize a conductive polymer combined with an MMO coating, adapting to complex treatment equipment shapes. They are primarily used for tank floor corrosion protection and wastewater treatment in irregularly shaped reaction vessels. Laying them in concentric rings ensures uniform current distribution within ±0.1V of potential fluctuation, with a potential uniformity of 98%.
Related products
-
Titanium Fasteners
Custom Manufacturing Titanium Screws
-
Titanium Fasteners
Titanium Bolts For Motorcycle
-
Titanium Fasteners
Custom Gr5 Titanium Fasteners
-
Titanium Fasteners
Anodized Titanium Screws
-
Titanium Fasteners
Anodized Titanium Nut
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Automotive Titanium Bolts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Titanium Nuts
-
Titanium Fasteners
Colored Gr5 Manifold Titanium Bolts